Seismic monitoring or map of earthquakes online in the world. Earth - chronicles of life - feedback
There are special zones of increased seismic activity on Earth, where earthquakes constantly occur. Why is this happening? Why do earthquakes occur more often in mountainous areas and very rarely in deserts? Why do earthquakes occur constantly in the Pacific Ocean, generating tsunamis of varying degrees of danger, but we have heard almost nothing about earthquakes in the Arctic Ocean. It's all about the seismic belts of the earth.
Introduction
The earth's seismic belts are places where the planet's lithospheric plates come into contact with each other. In these zones, where the Earth's seismic belts are formed, there is increased mobility of the earth's crust and volcanic activity caused by the process of mountain building, which lasts for millennia.
The length of these belts is incredibly large - the belts stretch for thousands of kilometers.
There are two large seismic belts on the planet: the Mediterranean-Trans-Asian and the Pacific.

Rice. 1. Seismic belts of the Earth.
Mediterranean-Trans-Asian The belt originates off the coast of the Persian Gulf and ends in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean. This belt is also called the latitudinal belt, since it runs parallel to the equator.
TOP 1 articlewho are reading along with this
Pacific belt– meridional, it stretches perpendicular to the Mediterranean-Trans-Asian belt. It is along the line of this belt that a huge number of active volcanoes are located, most of whose eruptions occur under the water column of the Pacific Ocean itself.
If you draw the Earth's seismic belts on a contour map, you will get an interesting and mysterious picture. The belts seem to border the ancient platforms of the Earth, and sometimes penetrate into them. They are associated with giant faults in the earth's crust, both ancient and younger.
Mediterranean-Trans-Asian seismic belt
The Earth's latitudinal seismic belt passes through the Mediterranean Sea and all the adjacent European mountain ranges located in the south of the continent. It stretches through the mountains of Asia Minor and North Africa, reaches the mountain ranges of the Caucasus and Iran, and runs through all of Central Asia and the Hindu Kush straight to Koel Lun and the Himalayas.
In this belt, the most active seismic zones are the Carpathian Mountains, located in Romania, all of Iran and Baluchistan. From Balochistan, the earthquake zone stretches to Burma.

Fig.2. Mediterranean-Trans-Asian seismic belt
This belt has active seismic zones, which are located not only on land, but also in the waters of two oceans: the Atlantic and Indian. This belt also partially covers the Arctic Ocean. The seismic zone of the entire Atlantic passes through the Greenland Sea and Spain.
The most active seismic zone of the latitudinal belt occurs at the bottom of the Indian Ocean, passes through the Arabian Peninsula and stretches to the very south and southwest of Antarctica.
Pacific belt
But, no matter how dangerous the latitudinal seismic belt is, the majority of all earthquakes (about 80%) that occur on our planet occur in the Pacific belt of seismic activity. This belt runs along the bottom of the Pacific Ocean, along all the mountain ranges encircling this largest ocean on Earth, and captures the islands located in it, including Indonesia.

Fig.3. Pacific seismic belt.
The largest part of this belt is the Eastern one. It originates in Kamchatka, stretches through the Aleutian Islands and the western coastal zones of North and South America straight to the South Antilles loop.
The eastern branch is unpredictable and little studied. It is full of sharp and twisting turns.
The northern part of the belt is the most seismically active, which is constantly felt by residents of California, as well as Central and South America.
The western part of the meridional belt originates in Kamchatka, stretches to Japan and beyond.
Secondary seismic belts
It is no secret that during earthquakes, waves from vibrations of the earth's crust can reach remote areas that are generally considered safe with regard to seismic activity. In some places, the echoes of earthquakes are not felt at all, and in others they reach several points on the Richter scale.

Fig.4. Map of Earth's seismic activity.
Basically, these zones, sensitive to vibrations of the earth's crust, are located under the water column of the World Ocean. The planet's secondary seismic belts are located in the waters of the Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean and the Arctic. Most of the secondary belts are located in the eastern part of the planet, so these belts stretch from the Philippines, gradually descending to Antarctica. The echoes of tremors can still be felt in the Pacific Ocean, but in the Atlantic there is almost always a seismically calm zone.
What have we learned?
So, on Earth, earthquakes do not occur in random places. It is possible to predict the seismic activity of the earth's crust, since the bulk of earthquakes occur in special zones called seismic belts of the earth. There are only two of them on our planet: the Latitudinal Mediterranean-Trans-Asian seismic belt, which stretches parallel to the Equator, and the meridional Pacific seismic belt, located perpendicular to the latitudinal one.
Test to check
Evaluation of the report
Average rating: 4.1. Total ratings received: 494.
The strongest earthquakes throughout human history have caused colossal material damage and caused a huge number of casualties among the population. The first mention of tremors dates back to 2000 BC.
And despite the achievements of modern science and the development of technology, no one can still predict the exact time when the elements will strike, so quick and timely evacuation of people often becomes impossible.
Earthquakes are natural disasters that kill the most people, much more than, for example, hurricanes or typhoons.
In this rating we will talk about the 12 most powerful and destructive earthquakes in human history.
12. Lisbon
On November 1, 1755, a powerful earthquake occurred in the capital of Portugal, the city of Lisbon, later called the Great Lisbon Earthquake. A terrible coincidence was that November 1 - All Saints Day and thousands of residents gathered for mass in the churches of Lisbon. These churches, like other buildings throughout the city, could not withstand the powerful shocks and collapsed, burying thousands of unfortunates under their rubble.
Then a 6-meter tsunami wave rushed into the city, covering the surviving people rushing in panic through the streets of destroyed Lisbon. The destruction and loss of life were colossal! As a result of the earthquake, which lasted no more than 6 minutes, the tsunami it caused and numerous fires that engulfed the city, at least 80,000 residents of the Portuguese capital died.
Many famous figures and philosophers touched on this deadly earthquake in their works, for example, Immanuel Kant, who tried to find a scientific explanation for such a large-scale tragedy.
11. San Francisco

On April 18, 1906, at 5:12 am, powerful tremors shook sleeping San Francisco. The force of the tremors was 7.9 points and as a result of the strongest earthquake in the city, 80% of the buildings were destroyed.
After the first count of the dead, authorities reported 400 victims, but later their number increased to 3,000 people. However, the main damage to the city was caused not by the earthquake itself, but by the monstrous fire it caused. As a result, more than 28,000 buildings throughout San Francisco were destroyed, with property damage amounting to more than $400 million at the exchange rate of that time.
Many residents themselves set fire to their dilapidated houses, which were insured against fire, but not against earthquakes.
10. Messina

The largest earthquake in Europe was the earthquake in Sicily and Southern Italy, when on December 28, 1908, as a result of powerful tremors measuring 7.5 on the Richter scale, according to various experts, from 120 to 200,000 people died.
The epicenter of the disaster was the Strait of Messina, located between the Apennine Peninsula and Sicily; the city of Messina suffered the most, where practically not a single surviving building remained. A huge tsunami wave, caused by tremors and amplified by an underwater landslide, also caused a lot of destruction.
Documented fact: rescuers were able to pull two exhausted, dehydrated, but alive children from the rubble, 18 days after the disaster struck! The numerous and extensive destructions were caused primarily by the poor quality of buildings in Messina and other parts of Sicily.
Russian sailors of the Imperial Navy provided invaluable assistance to the residents of Messina. The ships as part of the training group sailed in the Mediterranean Sea and on the day of the tragedy ended up in the port of Augusta in Sicily. Immediately after the tremors, sailors organized a rescue operation and thanks to their brave actions, thousands of residents were saved.
9. Haiyuan

One of the deadliest earthquakes in human history was the devastating earthquake that struck Haiyuan County, part of Gansu Province, on December 16, 1920.
Historians estimate that at least 230,000 people died that day. The force of the tremors was such that entire villages disappeared into the faults of the earth’s crust, and large cities such as Xi’an, Taiyuan and Lanzhou were greatly damaged. Incredibly, strong waves formed after the disaster were recorded even in Norway.
Modern researchers believe that the death toll was much higher and totaled at least 270,000 people. At that time, this was 59% of the population of Haiyuan County. Several tens of thousands of people died from the cold after their homes were destroyed by the elements.
8. Chile

The earthquake in Chile on May 22, 1960, considered the strongest earthquake in the history of seismology, measured 9.5 on the Richter scale. The earthquake was so powerful that it caused tsunami waves more than 10 meters high, which covered not only the coast of Chile, but also caused enormous damage to the city of Hilo in Hawaii, and some of the waves reached the coasts of Japan and the Philippines.
More than 6,000 people died, most of whom were hit by the tsunami, and the destruction was unimaginable. 2 million people were left homeless and the damage amounted to more than $500 million. In some areas of Chile, the impact of the tsunami wave was so strong that many houses were carried away 3 km inland.
7. Alaska

On March 27, 1964, the most powerful earthquake in American history occurred in Alaska. The magnitude of the earthquake was 9.2 on the Richter scale and this earthquake was the strongest since the disaster struck Chile in 1960.
129 people died, of which 6 were victims of tremors, the rest were washed away by a huge tsunami wave. The disaster caused the greatest destruction in Anchorage, and tremors were recorded in 47 US states.
6. Kobe

The Kobe earthquake in Japan on January 16, 1995 was one of the most destructive in history. Tremors with a magnitude of 7.3 began at 05:46 am local time and continued for several days. As a result, more than 6,000 people died and 26,000 were injured.
The damage caused to the city's infrastructure was simply enormous. More than 200,000 buildings were destroyed, 120 of the 150 berths in the port of Kobe were destroyed, and there was no power supply for several days. The total damage from the disaster was about $200 billion, which at that time was 2.5% of Japan's total GDP.
Not only government services rushed to help the affected residents, but also the Japanese mafia - the Yakuza, whose members delivered water and food to those affected by the disaster.
5. Sumatra

On December 26, 2004, a powerful tsunami that hit the shores of Thailand, Indonesia, Sri Lanka and other countries was caused by a devastating earthquake measuring 9.1 on the Richter scale. The epicenter of the tremors was in the Indian Ocean, near the island of Simeulue, off the northwestern coast of Sumatra. The earthquake was unusually large; the earth's crust shifted at a distance of 1200 km.
The height of the tsunami waves reached 15-30 meters and, according to various estimates, from 230 to 300,000 people became victims of the disaster, although the exact number of deaths is impossible to calculate. Many people were simply washed into the ocean.
One of the reasons for such a number of victims was the lack of an early warning system in the Indian Ocean, with which it was possible to inform the local population of the approaching tsunami.
4. Kashmir

On October 8, 2005, the worst earthquake to hit South Asia in a century occurred in the Pakistani-controlled region of Kashmir. The strength of the tremors was 7.6 on the Richter scale, which is comparable to the San Francisco earthquake in 1906.
As a result of the disaster, according to official data, 84,000 people died, according to unofficial data, more than 200,000. Rescue efforts have been hampered by military conflict between Pakistan and India in the region. Many villages were completely wiped off the face of the earth, and the city of Balakot in Pakistan was completely destroyed. In India, 1,300 people became victims of the earthquake.
3. Haiti

On January 12, 2010, an earthquake measuring 7.0 on the Richter scale occurred in Haiti. The main blow fell on the capital of the state - the city of Port-au-Prince. The consequences were terrible: almost 3 million people were left homeless, all hospitals and thousands of residential buildings were destroyed. The number of victims was simply enormous, according to various estimates from 160 to 230,000 people.
Criminals who had escaped from a prison destroyed by the elements poured into the city; cases of looting, robberies and robberies became frequent on the streets. Material damage from the earthquake is estimated at 5.6 billion dollars.
Despite the fact that many countries - Russia, France, Spain, Ukraine, the USA, Canada and dozens of others - provided all possible assistance in eliminating the consequences of the disaster in Haiti, more than five years after the earthquake, more than 80,000 people still live in improvised camps for refugees.
Haiti is the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere and this natural disaster has dealt an irreparable blow to the economy and living standards of its citizens.
2. Earthquake in Japan

On March 11, 2011, the strongest earthquake in Japanese history occurred in the Tohoku region. The epicenter was located east of the island of Honshu and the strength of the tremors was 9.1 on the Richter scale.
As a result of the disaster, the nuclear power plant in the city of Fukushima was severely damaged and power units at reactors 1, 2, and 3 were destroyed. Many areas became uninhabitable as a result of radioactive radiation.
After underwater tremors, a huge tsunami wave covered the coast and destroyed thousands of administrative and residential buildings. More than 16,000 people died, 2,500 are still considered missing.
The material damage was also colossal - more than $100 billion. And given that the complete restoration of the destroyed infrastructure may take years, the amount of damage may increase several times.
1. Spitak and Leninakan

There are many tragic dates in the history of the USSR, and one of the most famous is the earthquake that shook the Armenian SSR on December 7, 1988. Powerful tremors in just half a minute almost completely destroyed the northern part of the republic, capturing the territory where more than 1 million inhabitants lived.
The consequences of the disaster were monstrous: the city of Spitak was almost completely wiped off the face of the Earth, Leninakan was severely damaged, more than 300 villages were destroyed and 40% of the republic’s industrial capacity was destroyed. More than 500 thousand Armenians were left homeless, according to various estimates, from 25,000 to 170,000 residents died, 17,000 citizens remained disabled.
111 states and all republics of the USSR provided assistance in the restoration of destroyed Armenia.
Images reminiscent of a disaster movie have emerged in the final hours from the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia. After a powerful earthquake, a tsunami hit him: the wave swept away everything in its path - houses and roads were destroyed, ships were overturned. At the epicenter is a city inhabited by more than 300 thousand people. At the moment, the death toll is approaching fifty, and this figure is unlikely to be final.
People gathered on the balcony of this building to film the destruction and at the same time look at the raging ocean. Moreover, before this, the threat of a tsunami after the earthquake was lifted. Within a few seconds the wave becomes higher and more powerful. Panic, screams are heard, then the phone falls from the owner’s hands.
The fate of these people is unknown. Rescue services cannot yet say even approximately how many people became victims of the tsunami. But we are definitely talking about dozens.
Hospitals in the city and its surroundings are overcrowded. Help for victims is provided right on the streets. The number of wounded, according to preliminary data, is close to five hundred.
“We are sending medical teams from around the area, the Marine Corps and the Army, as well as members of the national search and rescue agency,” said Indonesian National Armed Forces commander Hadi Tzhanjanto.
The cause of the tsunami, which was so underestimated, was a series of earthquakes. After the first one, with a magnitude of 6, a more powerful, repeated one, with a magnitude of 7.7, occurred. And even a whole series of aftershocks. The strength of the tremors can be assessed from CCTV footage. During prayer, people did not immediately understand what was happening. They began to sway sharply from side to side. Hundreds of homes have been destroyed throughout the region. The ships washed ashore. Huge cracks in the asphalt. A horrific photo spread across the world's media: a man holding his dead child in his arms. In the background is all that remains of their home.
“I and all our people express our condolences for the earthquake and tsunami that hit Palu and its surrounding areas. We will use all resources to resolve the consequences of the disaster as quickly as possible,” Indonesian President Joko Widodo.
Such natural disasters are not uncommon for residents of Indonesia. The islands are located at the junction of tectonic plates, in an area of increased seismic and volcanic activity. Not long ago, the popular tourist island of Lombok was hit by two powerful earthquakes. Then a total of more than five hundred people died, and about one and a half thousand were injured.
Earthquakes are a terrible natural phenomenon that can bring numerous disasters. They are associated not only with destruction, which may result in human casualties. The catastrophic tsunami waves they cause can lead to even more disastrous consequences.
Which areas of the world are most affected by earthquakes? To answer this question, you need to look at where the active seismic areas are. These are zones of the earth's crust that are more mobile than the surrounding regions. They are located at the boundaries of lithospheric plates, where large blocks collide or move apart. It is the movements of powerful rock layers that cause earthquakes.
Dangerous areas of the world
There are several belts on the globe that are characterized by a high frequency of underground impacts. These are seismically dangerous areas.
The first of them is usually called the Pacific Ring, since it occupies almost the entire ocean coast. Not only earthquakes, but also volcanic eruptions are frequent here, which is why the name “volcanic” or “ring of fire” is often used. The activity of the earth's crust here is determined by modern mountain-building processes.
The second major seismic belt stretches along the high young from the Alps and other mountains of Southern Europe and to the Sunda Islands through Asia Minor, the Caucasus, the mountains of Central and Central Asia and the Himalayas. The collision of lithospheric plates also occurs here, which causes frequent earthquakes.
The third belt stretches across the entire Atlantic Ocean. This is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is the result of the spreading of the earth's crust. Iceland, known primarily for its volcanoes, also belongs to this belt. But earthquakes here are by no means a rare phenomenon.
Seismically active regions of Russia
Earthquakes also occur in our country. Seismically active regions of Russia are the Caucasus, Altai, the mountains of Eastern Siberia and the Far East, the Commander and Kuril Islands, Fr. Sakhalin. Tremors of great force can occur here.
One can recall the Sakhalin earthquake of 1995, when two-thirds of the population of the village of Neftegorsk died under the rubble of destroyed buildings. After the rescue work, it was decided not to restore the village, but to relocate the residents to other settlements.

In 2012-2014, several earthquakes occurred in the North Caucasus. Fortunately, their sources were located at great depths. There were no casualties or serious damage.
Seismic map of Russia

The map shows that the most seismically dangerous areas lie in the south and east of the country. At the same time, the eastern parts are relatively sparsely populated. But in the south, earthquakes pose a much greater danger to people, since the population density here is higher.
Irkutsk, Khabarovsk and some other large cities are in the danger zone. These are active seismic areas.
Anthropogenic earthquakes
Seismically active areas occupy approximately 20% of the country's territory. But this does not mean that the rest is completely insured against earthquakes. Shocks with a force of 3-4 points are observed even far from the boundaries of lithospheric plates, in the center of platform areas.
At the same time, with the development of the economy, the possibility of anthropogenic earthquakes increases. They are most often caused by the collapse of the roof of underground voids. Because of this, the earth's crust seems to shake, almost like a real earthquake. And there are more and more voids and cavities underground, because people extract oil and natural gas from the subsoil for their needs, pump out water, build mines for the extraction of solid minerals... And underground nuclear explosions are generally comparable to natural earthquakes in their strength.
The collapse of rock layers in itself can pose a danger to people. Indeed, in many areas, voids form directly under populated areas. Recent events in Solikamsk have only confirmed this. But even a weak earthquake can lead to dire consequences, because as a result it can destroy structures that are in disrepair, dilapidated housing in which people continue to live... Also, violation of the integrity of rock layers threatens the mines themselves, where collapses can occur.
What to do?
People are not yet able to prevent such a terrible phenomenon as an earthquake. And they haven’t even learned to predict exactly when and where it will happen. This means you need to know how you can protect yourself and your loved ones during tremors.
People living in such dangerous areas should always have an earthquake plan in place. Since a disaster may find family members in different places, there should be an agreement on a meeting place after the tremors stop. The home should be as safe as possible from falling heavy objects; it is best to attach furniture to the walls and floor. All residents should know where they can urgently turn off gas, electricity, and water in order to avoid fires, explosions and electric shocks. Stairs and passages should not be cluttered with things. Documents and a certain set of products and essentials should always be at hand.
Starting from kindergartens and schools, the population needs to be taught the correct behavior in case of a natural disaster, which will increase the chances of salvation.

Seismically active regions of Russia place special demands on both industrial and civil construction. Earthquake-resistant buildings are more difficult and expensive to build, but the cost of their construction is nothing compared to the lives saved. After all, not only those who are in such a building will be safe, but also those nearby. There will be no destruction and rubble - there will be no casualties.
As earthquake statistics show, seismological disasters account for 13% of the total number of natural ones. Over the past hundred years, about 2,000 tremors with a magnitude of 7 or more have occurred in the world. Of these, 65 cases exceeded the 8 mark.
World situation
If you look at a world map on which seismological activity is displayed as dots, you will notice one pattern. These are some characteristic lines along which tremors are intensely recorded. The tectonic boundaries of the earth's crust are located in these zones. Statistics have established that strong catastrophic earthquakes, which entail the most destructive consequences, occur due to tension in the source of “rubbing in” of tectonic plates. 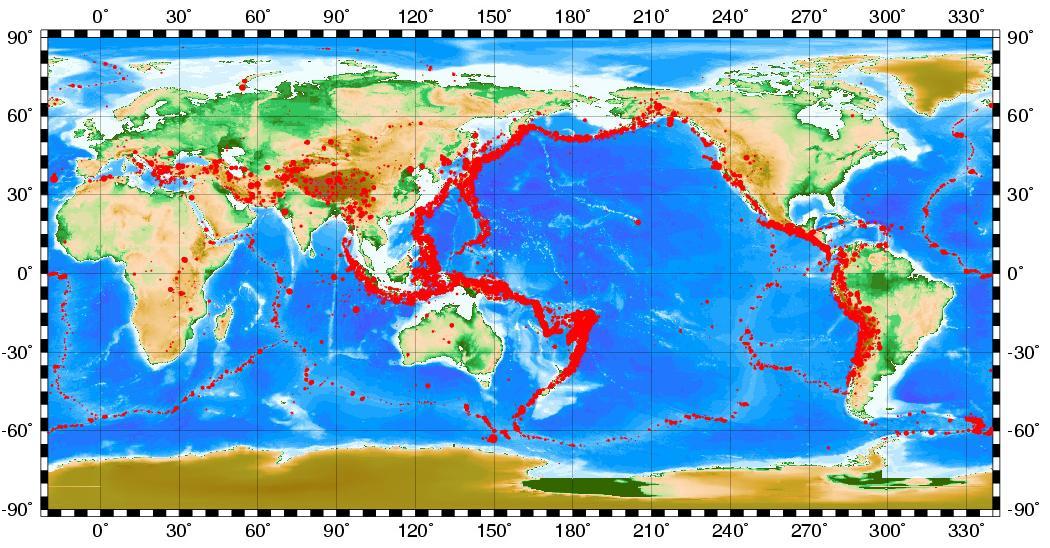
Earthquake statistics over 100 years show that about a hundred seismic disasters occurred on continental tectonic plates (not oceanic) alone, in which 1.4 million people died. A total of 130 strong earthquakes were recorded during this period.
The table shows the largest known seismic disasters since the 16th century:
| Year | Scene of the incident | Destruction and casualties |
| 1556 | China | The victims were 830 thousand people. According to current estimates, the earthquake can be assigned the highest value - 12 points. |
| 1755 | Lisbon (Portugal) | The city was completely destroyed, 100 thousand inhabitants died |
| 1906 | San Francisco (USA) | Most of the city was destroyed, 1,500 people became victims (7.8 points) |
| 1908 | Messina (Italy) | The destruction claimed 87 thousand lives (magnitude 7.5) |
| 1948 | Ashgabat (Turkmenistan) | 175 thousand people died |
| 1960 | Chile | The largest earthquake recorded in the last century. It was rated 9.5 points. Three cities were destroyed. About 10 thousand residents became victims |
| 1976 | Tien Shan (China) | Magnitude 8.2. 242 thousand people died |
| 1988 | Armenia | Several cities and towns were destroyed. More than 25 thousand victims were recorded (7.3 points) |
| 1990 | Iran | About 50 thousand inhabitants died (magnitude 7.4) |
| 2004 | Indian Ocean | The epicenter of the 9.3 magnitude earthquake was at the bottom of the ocean, which killed 250 thousand people |
| 2011 | Japan | An earthquake with a magnitude of 9.1 caused the death of more than 15 thousand people and had enormous economic and environmental consequences not only for Japan, but for the whole world. |
Over the 30 years of the end of the 20th century, about 1 million people died in seismic disasters. This is approximately 33 thousand per year. Over the past 10 years, earthquake statistics show an increase in the average annual figure to 45 thousand victims.  Every day, hundreds of imperceptible vibrations of the earth's surface occur on the planet. This is not always associated with the movement of the earth's crust. Human actions: construction, mining, blasting - all of them entail vibrations that are recorded by modern seismographs every second. However, since 2009, the USGS geological service, which collects data on earthquake statistics in the world, has stopped taking into account tremors below 4.5 points.
Every day, hundreds of imperceptible vibrations of the earth's surface occur on the planet. This is not always associated with the movement of the earth's crust. Human actions: construction, mining, blasting - all of them entail vibrations that are recorded by modern seismographs every second. However, since 2009, the USGS geological service, which collects data on earthquake statistics in the world, has stopped taking into account tremors below 4.5 points.
Crete
The island is located in a tectonic fault zone, so increased seismological activity there is a frequent occurrence. According to statistics, earthquakes in Crete do not exceed 5 points. With such force, there are no destructive consequences, and local residents do not pay any attention to this shaking. On the graph you can see the number of registered seismic shocks by month with a magnitude greater than 1 point. You can see that their intensity has increased somewhat in recent years. 
Earthquakes in Italy
The country is located in a zone of seismic activity on the territory of the same tectonic fault as Greece. Earthquake statistics in Italy over the past 5 years show an increase in the number of monthly tremors from 700 to 2000. In August 2016, a strong earthquake with a magnitude of 6.2 occurred. That day claimed the lives of 295 people and injured more than 400.
In January 2017, another earthquake with a magnitude of less than 6 occurred in Italy; there were almost no casualties from the destruction. However, the shock was caused in the province of Pescara. The Rigopiano Hotel was buried under it, killing 30 people.
There are resources that display earthquake statistics online. For example, the IRIS organization (USA), which collects, systematizes, studies and distributes seismological data, presents a monitor of this type:  The website contains information showing the presence of earthquakes on the planet at the moment. Here their magnitude is shown, there is information for yesterday, as well as events from 2 weeks or 5 years ago. You can take a closer look at the areas of the planet you are interested in by selecting the appropriate map from the list.
The website contains information showing the presence of earthquakes on the planet at the moment. Here their magnitude is shown, there is information for yesterday, as well as events from 2 weeks or 5 years ago. You can take a closer look at the areas of the planet you are interested in by selecting the appropriate map from the list.
The situation in Russia
According to earthquake statistics in Russia and the OSR (General Seismic Zoning) map, more than 26% of the country's area is located in seismically hazardous zones. Tremors of magnitude 7 may occur here. This includes Kamchatka, the Baikal region, the Kuril Islands, Altai, the North Caucasus and the Sayan Mountains. There are about 3,000 villages, about 100 thermal power plants and hydroelectric power stations, 5 nuclear power plants and enterprises of increased environmental hazard.
Krasnodar region
The zone contains about 28 districts of the region, with a population of approximately 4 million people. Among them is the large resort city of Sochi - according to earthquake statistics, the last seismic activity above 4 points was registered in the fall of 2016. Kuban is mostly located in the zone of magnitude 8–10 earthquakes (MSK-64 scale). This is the highest seismic hazard index throughout the Russian Federation.
The reason is the resumption of tectonic processes in 1980. Earthquake statistics in the Krasnodar region annually record about 250 seismic shocks of more than 2 points. Since 1973, 130 of them have been force 4 or higher. Tremors with a magnitude greater than 6 are recorded once every 5 years, and above 7 - once every 11 years. 
Irkutsk
Due to its location near the Baikal Rift, earthquake statistics for Irkutsk record up to 40 minor tremors every month. In August 2008, seismic activity with a magnitude of 6.2 was recorded. The epicenter was in Lake Baikal, where the indicator reached 7 points. Some buildings were cracked, but no significant damage or casualties were recorded. In February 2016, another earthquake of magnitude 5.5 occurred.
Ekaterinburg
Despite the fact that the growth of the Ural Mountains has long ceased, the statistics of earthquakes in Yekaterinburg continues to be updated with new data. In 2015, an earthquake with a magnitude of 4.2 was recorded there, but there were no casualties.
Conclusion
Between the end of 2008 and 2011, there was a decrease in seismic activity on the planet, to a level of less than 2,500 events per month and a magnitude above 4.5. However, after the earthquake in Japan in 2011, between 2011 and 2016 there was a tendency for earthquake activity around the world to almost double. Earthquake statistics for recent years are as follows:
- tremors from 8 points and above – 1 time/year;
- from 7 to 7.9 points – 17 times/year;
- from 6 to 6.9 – 134 times/year;
- from 5 to 5.9 – 1319 times/year.
 Predicting earthquakes is very difficult. It is often possible to say with certainty where it will happen, but when exactly it will happen is impossible to determine. However, there are biological precursors. On the eve of a strong earthquake, other representatives of the fauna living in this territory begin to behave abnormally.
Predicting earthquakes is very difficult. It is often possible to say with certainty where it will happen, but when exactly it will happen is impossible to determine. However, there are biological precursors. On the eve of a strong earthquake, other representatives of the fauna living in this territory begin to behave abnormally.

