How to identify urethritis. Urethritis: features of the structure of the urinary tract, a description of the pathology. Pathogens that cause infectious urethritis
Urethritis is an inflammatory disease in which the urethra (or urethra) is affected. Urethritis, the symptoms of which appear against the background of exposure to the viruses or bacteria that provoked this inflammation, in its own course may correspond to the nature of the infectious process or the non-infectious process.
general description
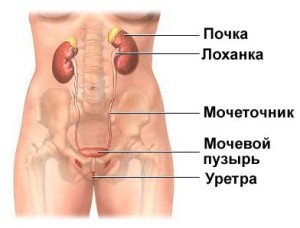
The urethra itself is the channel through which urine is carried outside, away from the bladder. Predominantly, urethritis is diagnosed in sexually active young patients, and it is the sexual route of transmission that determines the largest number of patients seeking appropriate medical care.
Symptoms of urethritis in women, by the way, are sometimes extremely difficult to distinguish from the symptoms that occur with cystitis. Actually, cystitis in women, which, as the reader probably knows, is a disease accompanied by inflammation of the bladder, is often a companion of urethritis, due to which, to some extent, it is more difficult to isolate both actual variants of the disease. The reason for this is the similar nature and symptoms. The difference is the actual localization of the inflammatory process and the symptoms that appear in both cases - the main symptoms of cystitis are based on an increase in urination, while with urethritis, urination is only combined with certain unpleasant sensations. Nevertheless, one cannot deny the possible relationship of both of these diseases, because urethritis can develop against the background of cystitis, or, conversely, serve as the basis for its future development. These options are due to the ascending or descending pathway of infection.
The disease is not life-threatening, but its appearance, as can be assumed, causes a certain kind of adjustment in life for the period of manifestation.
It should be immediately noted that due to the peculiarities of the location of the urethra, which in women is somewhat shorter, urethritis in men develops almost unhindered. The urethra in men has several physiological constrictions and bends, which determines for them a greater predisposition to urethritis. Returning to the peculiarities of the urethra in women, it remains to be noted that, as is already clear from the comparison, it is straight and short enough, which ensures practical flushing of the actual infection during urination.
So to speak, in a "pure" form, urethritis is detected in patients extremely rarely. Under the "pure" form, in particular, is meant such a course of this disease, in which the typical inflammation does not occur in the genitals. The first symptoms of urethritis without fail require a visit to the doctor. The reason for this is the possible aggravation of the course of this disease in the future, which, in turn, may manifest itself in a slightly different form. So, exposure to viruses or pathogenic bacteria against the background of urethritis with such an aggravation can provoke infection of the prostate gland or the epididymis in men.
Basically, urethritis develops as a result of infection with one or another sexually transmitted disease, which, as already noted, is facilitated by the main method of infection - sexual contact. Also, as a factor provoking urethritis, there is a violation of the rules provided for in terms of personal hygiene. In addition to these reasons, which, however, occurs somewhat less frequently, it is also possible to introduce microbes into the urethra, which occurs as a result of several other reasons. In particular, in this case, it means inflammation of the organs located above, or the introduction of microbes through the lymphatic and blood vessels from the foci of inflammation that are relevant to the body. Examples of such foci of inflammation include inflammatory processes in diseases of the teeth, inflammation of the tonsils (which occurs with tonsillitis), etc.
Urethritis can be gonococcal (specific urethritis) or, respectively, non-gonococcal (nonspecific urethritis), there is a more extended version of its classification.

The structure of the female organs: the urethra (urethra)
Causes of urethritis
The causes of urethritis, we generally identified a little higher. Upon closer examination, the causes are determined based on the conformity of the classification.
First of all, urethritis can be specific or non-specific.
Specific urethritis It is diagnosed in those cases if it is provoked by infections, the transmission of which is carried out through sexual contact. As such infections, one can distinguish the herpes virus, gonococcus, ureaplasma, Trichomonas. Somewhat less often, it is mycoplasma, chlamydia, gardnerella, etc. Specific urethritis is similarly defined as gonococcal urethritis (on the basis of the nature of one's own arising, as can be understood from the definition of this form).
As for the next form, which is nonspecific urethritis, then opportunistic microflora is considered here as an influencing factor. Examples include staphylococci and streptococci, Escherichia coli, various varieties of fungi.
Specific urethritis also defines a separate group in them, this nongonococcal urethritis. This group is characterized by the fact that urethritis in it is provoked by various types of viruses and infections, but with the exception of gonococci. In turn, this group defines two other forms of urethritis, and this infectious urethritis or noninfectious urethritis. And if, in principle, there are no questions with infectious urethritis regarding the specifics of its occurrence, and it is determined on the basis of the name itself, then non-infectious urethritis, of course, can provoke the corresponding interest of the reader.
The basis for the development of non-infectious urethritis can be a physical lesion of the urethra. For example, it can be a blow or a diagnostic procedure that led to such a lesion, thermal or chemical exposure. In accordance with the traumatic nature of non-infectious urethritis, it is also defined as traumatic urethritis. Non-infectious urethritis, among other things, can also be allergic. allergic urethritis, according to the specifics of allergies, it can act as an organism reaction that occurs in response to food, drug or other allergens. In some cases, urethritis is diagnosed in patients with diabetes mellitus and other types of metabolic disorders.
But these options do not complete our classification. In addition to the options already listed, urethritis can be primary or secondary. Primary urethritis is an independent disease that develops directly in the urethra, while secondary urethritis is the result of a complication of a disease. Infection with secondary urethritis occurs mainly from the bladder, from the vagina or from the prostate gland, etc.
Based on the classification options considered, urethritis, in accordance with the reasons that provoked it, can also be divided into two groups, and this venereal urethritis And non-venereal urethritis. As already noted, urethritis can be gonorrheal or non-gonorrheal, and both of these options can be attributed to venereal urethritis, provided that the route of infection was sexual.
Urolithiasis can provoke urethritis, which is caused by the movement of sand or stone through the urethra, as a result of which its walls are affected. Significant physical activity, features of sexual life (excessively active sex life, or, conversely, intermittent sex life) can also be noted as causes that provoke urethritis. Certain foods also contribute to the development of urethritis, and these are salty foods, foods that are sour, spicy or pickled. In reality, there can be many factors, and those that we have listed are only the basis.
The duration of the incubation period of the disease (and this is the time interval between infection and the appearance of the first symptoms) is determined on the basis of the specific pathogen that provoked urethritis. On average, the incubation period for gonococcal urethritis is about 3-10 days after the infection has occurred (actual contact), although its shortened version is not excluded. So, certain strains provoke the development of urethritis already 12 hours after contact. Nevertheless, the manifestation of this disease also 3 months after that is not excluded - here, of course, we are talking about a different type of strain that determines such a scenario.
Urethritis: symptoms
The main manifestation characterizing the course of urethritis is purulent discharge that appears from the urethra. Such secretions may be either yellow-green or pale yellow.
Symptoms of acute urethritis are characterized by the occurrence of itching, burning and soreness, all these manifestations are noted at the very beginning of the act of urination, again, the appearance of purulent discharge. The edges from the side of the external opening of the urethra begin to become inflamed and, as the process progresses, stick together. At the same time, it is possible to develop urethritis without the concomitant appearance of purulent discharge, but with the listed symptoms accompanying the act of urination itself.
Urethritis, the symptoms in men in which they manifest themselves in a rather sharp form, in women it manifests itself differently. So, the symptoms of urethritis in women are less pronounced, in some cases they may not be determined at all.
Types of urethritis are characterized by their own characteristics of the course, despite the already indicated features, depending on the stage of the course, several typical forms are determined, we will dwell on them in more detail.
Acute urethritis: symptoms
This variant of the manifestation of urethritis is accompanied by a characteristic soreness of urination and burning. These symptoms are also associated with profuse discharge, which, as already noted, comes from the urethra. The lips of the external opening of the urethra turn red, swelling is noted, the inflammatory process is concentrated in the area of the wall of the urethra. Slight pressure leads to the expiration of purulent discharge. After a night's sleep, purulent spots can be found on the linen. Feeling the urethra allows you to highlight some of its density.
In general, the sensations that the patient experiences with urethritis are characterized by the scale of the inflammatory process within the urethra (this is posterior urethritis, anterior urethritis, or complete urethritis), and the relevance of complications is also taken into account. So, some patients may experience burning or itching in the urethra, while others especially experience pain during urination.
If an acute variant of the course of torpid urethritis (an asymptomatic form of this disease) is considered, then here the urge to urinate is frequent, soreness is noted in the urethra, body temperature rises. The completion of the act of urination in this case is the appearance of a minimum amount of spotting, they are defined as terminal hematuria. There is also swelling of the urethra. In general, the course of torpid urethritis, if we are not talking about its acute form, is characterized by its own monotony, such a course does not have sharp boundaries, as a result, it passes into the chronic form of the course of gonorrhea.
Subacute urethritis: symptoms
This form is characterized by a gradual reduction in swelling and pain in the urethra. Purulent discharge or have a meager character, or disappear altogether. In some cases, the presence of discharge in the morning is allowed (they look like a crust, due to which the external opening in the urethra sticks together). Urine also changes: it becomes more transparent, slight purulent filaments are noted in its composition.
Chronic urethritis: symptoms
The transition to a chronic form occurs with ineffective therapy for the disease or in the absence of proper treatment as such. The appearance of complaints (exacerbation of urethritis) in this case is preceded by the impact of provoking factors, against which the appearance of a certain amount of purulent discharge is noted. These factors include hypothermia, alcohol consumption by the patient, etc. Basically, the symptoms of chronic urethritis coincide with the manifestations characteristic of the torpid form of urethritis, which we previously identified. The course of the disease can be long-term, which means not only months, but also years, which, ultimately, may cause a visit to the doctor (if this was done earlier, before the transition of the disease to this form). The prolonged course of this form of urethritis can provoke urethral stricture, in which the urethra in the lumen begins to narrow, due to which urination is accompanied by a change in the urine stream (it becomes weak) and pain.
Total urethritis: symptoms
The peculiarity of this form of urethritis is that the urethra is completely exposed to the inflammatory lesion in this case. Symptoms of total urethritis are characterized by similarities with the symptoms of prostatitis. In acute total urethritis, the urge to urinate has an irresistible manifestation, the completion of urination is accompanied by pain. Bloody and purulent components are noted in the urine.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is based on a physical examination of the patient if he has symptoms that indicate a possible urethritis. Inspection is carried out after 1-3 hours from the moment of the last act of urination. The diagnosis of acute urethritis or chronic urethritis is established on the basis of swelling and redness of the urethra, as well as on the basis of purulent discharge.
In the future, a Gram smear is done if there is a suspicion of the relevance of gonorrheal urethritis. The diagnosis of the disease is also supported by the results of a urinalysis when leukocytes are detected in the sediment, an analysis of scrapings of the urethra and vagina (the presence of chlamydia is determined). If necessary, a scraping from the rectal area can be done.
Treatment of urethritis
The determination of drug therapy measures is based on the nature of the disease. As the main treatment measures, washings using antiseptic preparations, focused directly on the area of the urethra, are used, antibiotics can also be used. Efficacy in the treatment of urethritis determines the use of erythromycin and tetracyclines. An additional effect is achieved through physiotherapy procedures (warming applications, electrophoresis, etc.), local treatment (for example, sitz baths based on herbal decoction), taking immunostimulants and immunomodulators.
Diet is mandatory during treatment. In particular, it excludes salty, smoked and spicy foods, alcohol. In the acute stage of the manifestation of the disease, the diet is based on products of lactic acid origin, and plenty of drinking is also indicated. The influence of negative provoking factors (physical overload, hypothermia) is excluded, restrictions also apply to sexual life within this period.
If you do not treat urethritis, there is a risk of developing already noted prostatitis (in a chronic form), and in some cases, epididymitis, and already this disease subsequently becomes the cause of infertility (obstructive form). Vesiculitis may also develop.
The main way to prevent urethritis is the implementation of the barrier method, which consists in contraception using condoms, which is especially important during sexual intercourse with non-permanent partners. Also an important point in the prevention of gonorrhea is the proper observance of hygiene measures.
If you suspect the relevance of urethritis, you should visit a venereologist, with nonspecific urethritis, the patient is referred to a urologist.
Urethritis is an acute or chronic inflammation in the urethra (urethra) in both men and women. Urethritis is one of the common urological diseases resulting from both infectious and non-infectious causes.
Causes
Urethritis is:
- infectious origin (microbial, viral, fungal),
- non-infectious (allergic, traumatic, cicatricial, as a result of foreign bodies, as a result of irritation from sand or salts in the urine, congestive, due to circulatory disorders in the pelvic area).
Usually, as a result of exposure to the primary factor, a secondary infection quickly attaches and forms a secondary infectious urethritis.
Infectious urethritis is divided into two large groups:
- specific, caused by infections that are sexually transmitted (gonorrhea, gardnerellosis, trichomoniasis),
- non-specific, caused by intestinal or skin microflora (E. coli, staphylococci, streptococci).
Specific urethritis most often occurs in young people, from 18 to 30-40 years old, as a result of sexual contact with the patient, nonspecific urethritis can develop at any age.
Urethritis can occur overtly and covertly, depending on the strength of the immune system and the characteristics of the pathogen. Predisposing factors are
- hypothermia,
- violation of intimate hygiene,
- alcohol intake and the presence of foci of infection.
For nonspecific urethritis, an important factor may be an exacerbation of urolithiasis with the detection of sand in the urine, a metabolic disorder with urine crystallization, etc.
Symptoms of urethritis
Symptoms of urethritis in men and women can vary significantly due to the anatomical features in the structure of the urethra.
In men, the urethra is long, thinner and tortuous, in women it is short and wide, funnel-shaped. Pain receptors in men in the urethra are much larger than in women, and men perceive pain differently. Urethritis in men usually occurs in isolation, as a separate disease, while in women, urethritis is often combined with cystitis.
Due to these features in men, the process usually begins acutely, with pronounced and acute manifestations, burning and unbearable pain and itching, while in women the manifestations can vary from gradual and not pronounced, to quite strong, but increasing gradually. In some women, subjective symptoms of urethritis are generally absent in the presence of inflammation in the urethra.
The main symptoms of urethritis include:
- burning along the urethra,
- pain when urinating,
- pain inside the urethra, especially in its initial part at the head of the penis or labia,
- discharge from the urethral canal in the morning is copious, mucous or purulent,
- foul-smelling discharge.
In men, in the morning, there may be difficulty urinating due to sticking of the sponges in the area of the head of the penis, there is a pronounced redness of the area where the urethra exits. As a variant of the course of urethritis in men, there can only be discomfort during urination, with a feeling of sand or broken glass along the urethra.
Usually urethritis is limited to local manifestations, there is no fever, malaise and weakness, which is why patients often practice self-medication without resorting to specialists.
Diagnostics
Urologists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of urethritis. It is necessary to conduct an examination and take smears from the urethra, conduct a general analysis of urine and culture of urine for flora, with the determination of their sensitivity to antibiotics.
Additionally, an ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys is prescribed, and in men, the prostate is also prescribed to exclude the transfer of infection to these organs.
Treatment of urethritis
The basis of treatment for urethritis in both men and women is antimicrobial therapy.
The antibiotic is selected based on the suspected nature of the infection, with adjustment based on culture results - usually
- sulfonamides,
- norfloxacin,
- tetracyclines,
- erythromycin.
Often the antibiotic is prescribed with as little dose as possible, usually once or twice a day. The course of treatment is on average 5-10 days, depending on the severity of the disease. Treatment is carried out at home, under the supervision of a doctor.
In addition to the main treatment, urological preparations and uroantiseptics, substances of chemical and plant origin that have antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects can be prescribed. Cranberry juice, bearberry leaf, kidney tea, uloresan and parsley infusion are useful.
It is necessary to drink enough fluids to maintain adequate diuresis and to flush out tissue breakdown products and germs or viruses.
It is also important to follow a fairly restrictive diet, categorically exclude alcohol, reduce the consumption of salty, spicy and irritating foods to a minimum, take more vegetable and dairy foods that alkalize urine - microbes survive worse in an alkaline environment.
At the time of treatment, it is necessary to refrain from sexual activity, and if a sexual infection is detected, it is necessary to conduct an examination and treatment of the sexual partner. After the course of treatment, it is necessary to take control tests to make sure that the infection is completely eliminated.
Complications
If you do not treat urethritis, its manifestations gradually subside or become chronic. The infection spreads deep into the genitourinary system and affects the prostate and seminal vesicles, in women it passes to the bladder and glands of the vestibule of the vagina. When exposed to provoking factors, relapses of inflammation occur, the infection can spread to the bladder, ureters and kidneys.
There is an opinion that people are most susceptible to diseases of the genitourinary system, so the question arises, what is urethritis in men? It is believed that this is an exclusively female deviation, although this is not so. Pathology is equally observed in both sexes. When the disease occurs, inflammation of the urethra. The causes of inflammation of the urethra in men are different, but most often they become infected after sexual intercourse. Depending on the foci of exposure, infectious and non-infectious urethritis are distinguished. The problem is manifested by pain during the excretion of urine, discharge, redness of the urethra and other unpleasant symptoms are observed. Urethritis needs prompt diagnosis and treatment to avoid possible complications. If the pathology is not treated, then in the future it will affect the reproductive function and there will be a violation in the genitourinary system.
As a rule, urethritis in men occurs from questionable sexual intercourse.
Features of the structure of the male urethra
Paying attention to the fact that the male urethra is different from the female, the stronger sex more clearly feels the symptoms and more difficult to tolerate inflammation of the urethra. This organ in men consists of a narrow hollow tube, which is 16–24 centimeters in length, while the female urethra is no more than 4 centimeters long. Therefore, the weaker sex often suffers pathology without symptoms.
Due to the special structure of the urethra, men often experience signs of pathology from the first days of infection.
The urethra in men consists of three sections: prostatic, membranous and spongy. The first section (posterior) is located in the prostate and is about 4 centimeters long. The length of the membranous or membranous section is 2 cm and is located between the prostate and the base of the penis. This part of the urinary canal in men is the narrowest. The longest is the spongy or spongy section, which is located in the trunk of the male genital organ. The disease in this part is called anterior urethritis and needs special treatment.
Classification of urethritis
Depending on the pathogen that caused urethritis, various factors and other diseases occurring in the body, special symptoms appear. In frequent cases, it is observed, the development of which was served by various harmful bacteria. In medicine, there are many classifications of urethritis.
Given the type of pathogen, they distinguish specific and. The sources of specific urethritis lie in bacteria that are transmitted through sexual contact: trichomonas, chlamydia and others. Symptoms of acute nonspecific urethritis are detected when the pathogens are fungi, Staphylococcus aureus and other microorganisms.
 Urethritis is classified depending on the pathogen and the course of the disease.
Urethritis is classified depending on the pathogen and the course of the disease. Pathology of a non-infectious nature is classified into congestive, traumatic and allergic urethritis. In turn, an infectious lesion has its own varieties, which depend on the specific pathogen. So, doctors talk about gonorrheal, viral, trichomonas, bacterial, chlamydial and tuberculous lesions. There is also a species such as ureaplasma urethritis. Mixed urethritis occurs when infections of different types attack the body.
Depending on the course of the disease, acute and chronic urethritis in men are distinguished. Pathology can enter the body directly through the genitourinary system, externally, then it is called primary. Secondary urethritis occurs due to infection of other organs. Urethritis is also distinguished, depending on the degree to which it is expressed: a weakly active disease, a pathology of moderate activity and a disease with a high degree of activity.
Main reasons
The causes of inflammation in the urethra are varied. Most often, infection occurs in the case of sexually transmitted diseases that are transmitted through sexual contact. But it also happens that a fungal pathogen enters the body due to non-compliance with intimate hygiene.
Often, E. coli enters the genitals, and then into the urethra after the act of defecation and actively spreads.
Staphylococcal urethritis is often diagnosed, and microorganisms such as streptococcus, E. coli and others cause pathology. Urolithiasis can affect urethritis, since stones located in the kidneys injure the urethra at the exit. Pathology in men occurs for the following reasons:
- physical fatigue;
- stressful situations;
- alcohol abuse;
- disturbed nutrition;
- lack of vitamins;
- various inflammations.
 The cause of the disease h is an infection
The cause of the disease h is an infection In some cases, urethritis in males is observed after surgery. In this case, the urethra is injured, which leads to inflammation. In the resulting abrasions, an infection is formed that spreads rapidly.
Symptoms of urethritis
After the penetration of the infection, the pathology begins to appear after a few days, and sometimes even after a few weeks. Viral urethritis may not make itself felt for several months, and tuberculosis is not detected for many years. The patient in most cases complains of pain with urethritis, and the following symptoms are also present:
- irritation around the urethra;
- burning sensation when going to the toilet;
- the presence of unpleasant discharge;
- congestion of the urethra.
Blood impurities in urine, pus and mucus are also observed. Symptoms vary and are expressed with different intensity depending on the pathogen and the degree of the course. Infectious urethritis has more pronounced symptoms than non-infectious. And in some men, signs of pathology may be completely absent.
 Non-infectious urethritis is characterized by itching, redness of the penis.
Non-infectious urethritis is characterized by itching, redness of the penis. Non-infectious pathology
Pathology of a non-infectious type has a special symptomatology and other manifestations join the main signs. With a non-infectious lesion, there is a violation in sexual function, and the main symptoms are mild. With allergic pathology, itching is present and a red urethra is observed due to the inflammatory process. It is important to seek help in a timely manner so that the symptoms of urethritis in men do not provoke a dangerous complication.
Infectious lesion
Infectious type urethritis is the most common and more pronounced. Chronic desquamative urethritis is characterized by common symptoms, but changes in the epithelial cover occur. Along with viral pathology, conjunctivitis occurs and the joints become inflamed. The most dangerous is, because it tends to quickly turn into a chronic one and proceed in a latent form. Such a deviation is difficult to treat and leads to the occurrence.
Pathology poses a danger to internal organs and health in general. Acute urethritis in men leads to a decrease in sexual function and libido. In this case, the prostate and gonads are most injured. Pathology entails a decrease in the quantity and quality of spermatozoa. It is worth getting rid of urethritis with the help of medicines that will be prescribed by a qualified specialist after diagnosis.
Diagnosis of urethritis in men
 Diagnostics includes laboratory and instrumental methods
Diagnostics includes laboratory and instrumental methods In case of discomfort, pain and suspicion of inflammation in the urethra, a set of examinations is prescribed, which is aimed at a complete examination of the disease. First of all, it is worth contacting a urologist who will conduct an examination. If an infectious pathology is detected, then the patient is referred for a consultation with a venereologist. The patient is assigned the following studies:
- a urine and blood test;
- take a smear of discharge from the urethra;
- collect urine samples for bacterial culture and nutrient medium;
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys and organs of the genitourinary system;
- ureteroscopy.
In the presence of pathology, the results of the tests will indicate a significant excess of the norm of leukocytes and bacteria. If fungi are found, then a candidal urethritis is diagnosed. During the diagnosis, studies are carried out that determine which antibiotics will affect the pathology. A complete study allows doctors to understand how to treat urethritis and what drugs to use so that the therapy brings the maximum effect.
Urethritis is an inflammatory process that is located in the urethra. This disease is very common, while the pathology develops regardless of the age and gender of the patient. In order to clearly understand what urethritis is in a man, what are the symptoms and methods of treating this pathology, it is necessary to clearly understand the anatomy of the male urethra.
Anatomical features and structure of the male urethra
The outlet in the bladder is the beginning of the urinary canal, which in medical and scientific circles is commonly called the urethra. This is a genital tube of small diameter, which has a length of 16 to 24 centimeters. It is worth noting that the urethra in women has a length of only 4 centimeters. It is these comparative characteristics that are the main reason for the differences in the manifestations of urethritis in representatives of different sexes, respectively, if in women urethritis can pass without visible pathological symptoms, then in males the disease has very intense symptoms and can manifest itself soon after direct infection and the development of the inflammatory process .
The male urinary canal consists of the following sections:
prostatic section. This is a part of the urethra, which is located in the prostate gland and is about 4 centimeters long. The prostatic department is also called the prostate;
membranous section. Also called webbed. Its length is 2 centimeters. The beginning of the department is located behind the prostate gland, and ends at the base of the penis. This gap of the male urethra is the narrowest;
spongy department, or spongy. It is the longest section of the urinary canal and is located inside the shaft of the penis. Compared with the membranous and prostatic, the spongy section is characterized by mobility. This section of the urethra ends with an outlet, which is called the meatus.
Classification of urethritis
The clinical picture and methods of therapy depend on the type of infectious agent that caused inflammation, the stage of neglect and intensity of the disease, the presence of concomitant diseases and provoking factors. That is why the appointment of effective and adequate treatment depends on the nature of the pathology.
|
Classification of urethritis by etiological indicators |
|
|
Non-infectious urethritis |
Infectious urethritis |
|
Non-infectious diseases include: congestive urethritis - may appear due to venous stasis in the pelvis; traumatic urethritis - appears against the background of ruptures and tears of the urethra, as well as after surgical interventions (catheterization, cystoscopy); allergic urethritis - develops due to exposure to allergens. |
Each of the types of infectious urethritis has its own specific type of pathogen, and only with mixed urethritis can inflammation occur against the background of the action of two or more pathogenic organisms: tuberculosis; mixed; gardnerella; chlamydial; ureaplasmic; mycotic; bacterial; trichomonas; viral; mycoplasma; trichomonas. |
|
Classification according to severity of symptoms |
Classification according to the characteristics of the course of the disease |
|
Chronic urethritis is divided into periods without exacerbations and an acute stage: urethritis is weakly active; moderate degree of disease activity (urethritis); a high degree of activity of inflammation of the urinary canal. |
Fresh urethritis is divided into: torpid; subacute; |
|
Classification according to the specificity of the disease |
Classification according to the features of the onset of the disease |
|
specific - these are sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea) and tuberculosis; non-specific - the causative agent of infection are microorganisms that are constantly present in the body, but are suppressed by a healthy immune system. |
primary - the disease occurs as an isolated pathology; secondary - develops due to the presence of other diseases in the body. |

In most cases, chlamydia and gonococci are the causative agent of urethritis, while in about 50% of cases it is not possible to detect these infectious agents when examining the material.
Symptoms of urethritis
After direct infection of the body, the symptoms of urethritis appear after some time, while the time interval from the moment of infection to the first signs of pathology directly depends on the incubation period of the pathogen. With allergic urethritis - it is several hours, with tuberculosis - several years, with viral - several months, with candidiasis and trichomoniasis - two to three weeks, with chlamydia - 7-14 days, with gonorrhea - 3-7 days.
The most typical symptoms of male urethritis are:
the presence of characteristic secretions that appear from the urethra;
burning, itching and pain when urinating.

Other symptoms characteristic of STDs, such as general weakness and hyperemia, are not observed with urethritis. However, the nature of the discharge may be different and depends on the type of pathogen that caused the urethritis. In most cases, a green or white discharge with an unpleasant odor appears, against which yellow crusts can form on the penis. Allocations are most noticeable in the morning.
In addition, along with the discharge, redness and sticking of the external opening of the urethra may be present. Pain in the lower abdomen can occur regardless of the type of urethritis, but even they are not a constant symptom of the pathology.
The process of urination is also disturbed, which in the initial stage is quite often accompanied by cloudy urine, pain, along with this, the number of daily urges to urinate increases. The end of this process may be accompanied by sharp pains and sometimes blood impurities.
If the disease has become chronic, then the symptoms of the disease may disappear altogether, there is no discharge, and the patient may be disturbed only by mild itching and discomfort in the urethra. More pronounced symptoms are observed only during periods of exacerbation of the disease.
With bacterial urethritis, purulent discharge is observed, with trichomoniasis - whitish, with gonorrheal urethritis - gray-yellow or greenish. Also, the discharge may be insignificant or completely absent, but the man will be disturbed by blood in the semen or urine, burning and itching at the time of urination, swelling of the penis, pain at the time of sexual intercourse.

The table shows the most characteristic symptoms of urethritis for its different types.
|
Non-infectious urethritis |
|
|
Traumatic urethritis |
Symptoms depend on the nature of the injury - it is a burning sensation and pain when urinating. |
|
Allergic urethritis |
Also pain and burning, however, a feature is the presence of allergic edema. |
|
Congestive urethritis |
The classic symptoms are often completely absent. Manifested by various types of sexual dysfunction. |
|
Infectious urethritis |
|
|
Tuberculous urethritis |
In most cases, it occurs against the background of tuberculosis of the kidneys or genital tuberculosis. There is a penetration of mycotic tuberculosis bacteria into the urethra with urine flow. It proceeds with few symptoms (sweating, increased fatigue, subfebrile condition). |
|
Gardnerella urethritis |
The incubation period is from one week to several months. In most cases, it is present as a component of mixed urethritis. |
|
Chlamydial urethritis |
There are no cuts and burning, slight discharge. In most cases, it proceeds according to the chronic type. |
|
Ureaplasmic urethritis |
Most often accompanies trichomoniasis or gonorrheal urethritis. The incubation period is about 1 month. There is a green or white discharge, there is a burning sensation and itching when urinating. Exacerbation of symptoms occurs against the background of sexual intercourse or alcohol intake. |
|
Mycotic urethritis |
The incubation period is about 20 days, there is burning and itching. The discharge is watery or mucus, sometimes a pale pink color. |
|
Bacterial urethritis |
Purulent discharge. Symptoms are gone. The incubation period can last several months. |
|
Trichomonas urethritis |
It is characterized by constant itching in the area of the head of the penis, the presence of grayish-white discharge and difficulty urinating are also characteristic. |
|
Viral urethritis |
The course of the pathology is sluggish, the symptoms are mild. May be complemented by conjunctivitis or inflammation of the joints |
|
Mycoplasma urethritis |
Rarely occurs on its own. In most cases, it is combined with gonorrheal or trichomonas urethritis. |
|
gonorrheal urethritis |
Gray-yellow discharge from the urethra, sharp pain at the time of urination. The pus contained in the urine gives it a cloudy color. Blood impurities appear in semen and urine. |

Treatment of urethritis in men
The choice of treatment for urethritis, like any other disease, is made on the basis of diagnostic data. First of all, laboratory test results are used. A general analysis of blood and urine, ureteroscopy data, examination of urethral smears, and bacteriological culture of urine are taken into account.
Medical procedures can be carried out on an outpatient basis, during treatment it is important to observe the systematic and accurate implementation of medical prescriptions, hospitalization is not required. If the intake of antimicrobials is interrupted, carried out irregularly, or during the period of therapy the patient consumes alcohol, the disease threatens to become chronic.
It is quite obvious that the selection of drugs for the medical treatment of male urethritis is carried out by a doctor, and the patient must follow the necessary rules throughout the entire period of treatment: drink plenty of fluids, do not use pickled, smoked foods, spices, spices, give up alcohol, observe personal hygiene rules, exclude sex life.

The selection of drugs is carried out purely individually. Any infectious urethritis is treated with antibiotics. The most pronounced effect is achieved with the use of an antibacterial drug selected on the basis of a sensitivity analysis. It is thanks to this study that you can choose the most effective remedy for treatment.
Treatment of bacterial, gonorrheal urethritis
Excellent results in the treatment of gonorrheal urethritis are demonstrated by antibiotics of the cephalosporin group. In addition to them, kanamycins, oletetrins, erythromycins, tetracyclines can be prescribed. In this case, kanamycins must be used with extreme caution, since these drugs are highly toxic. Long-acting drugs - bicillin-5 and bicillin-3 should be prescribed in short courses. In some cases, if gonorrheal urethritis is complicated by other infections, the simultaneous use of several antibacterial drugs is practiced. In such cases, it is best to use the complex "Gentamicin" and "Azithromycin" ("Ecomed", "Hemomycin", "Azitrox", "Azitsid", "Zi-factor", "Sumamed").

In order to prevent the occurrence of candidiasis, due to prolonged antibiotic therapy, Levorin, Fluconazole, Nystatin, Pimafucin and other antimycotic drugs are prescribed. The most important aspect of treatment is the individual selection of drugs. Quite often, men who suffer from gonorrheal urethritis ask acquaintances to “prick injections” and use antibiotics uncontrollably and without consulting a doctor. Such self-treatment is unacceptable, since long-term use of strong anti-inflammatory drugs without a clear treatment regimen and control of cure can lead to the transition of urethritis to a chronic form and the development of drug resistance of the pathogen.
In addition to antibiotics, the patient must take immunostimulating drugs and vitamins. To be completely convinced that the body has freed itself from gonococcus and is completely cured, it is necessary to pass control smears three times. Only after receiving negative test results can we assume that the patient is completely healthy.
Gardnerella, ureaplasma and mycoplasma urethritis
These types of urethritis are treated with the antibiotics lincosamines, fluoroquinolones, macrolides, and tetracyclines. The most effective is the tetracycline group, and specifically doxycycline. The macrolide group (clarithromycin) also gives excellent results. Immunostimulants are also prescribed.

With any specific urethritis, it is necessary to carry out simultaneous therapy of both sexual partners.
Trichomonas urethritis
If a man is diagnosed with trichomonas urethritis, when choosing drugs, they turn to metrogil, trichopolum and metronidazole. If urethritis is chronic, antibiotic therapy is added to the treatment. In case of inadequate treatment, infertility may develop.
Candida urethritis
Treatment of candidal urethritis in a man requires a completely different approach. The main drugs to combat this pathology are antimycotic agents, such as Pimafucin, Nystatin, Clotrimazole, Fluconazole. A well-chosen treatment of the underlying disease, which is the cause of candidal urethritis, is important.
Chlamydial urethritis
The only antibiotic that actively fights the causative agent of this infection is azithromycin. If you choose the wrong drug for chalmidia urethritis, serious complications can occur - inflammatory diseases, epididymitis, Reiter's syndrome, infertility. If the patient has an individual intolerance to azithromycin, alternatively use: doxycycline, levofloxacin, erythromycin, ofloxacin, clarithromycin. Also in the complex should be used immunostimulating drugs and vitamins.
Viral urethritis
Treatment is with antiviral drugs. The sooner treatment is started, the faster recovery will occur. Among antiviral drugs, preference is given to: Gerpevir, Famciclovir, Riboverin, Acyclovir. It is not advisable to use antibiotics for this form of pathology, since they are not able to fight viruses.
Nonspecific chronic urethritis
Treatment of nonspecific chronic male urethritis is not as fast as with infectious ones. The chronic course of the disease is quite often aggravated by concomitant pathologies, and the signs of the disease are mild or may be absent altogether. Therefore, the therapy of chronic urethritis should begin with the use of immunostimulants. Only this approach allows you to activate the body's defenses to fight infection. After receiving the result, antibiotic therapy is selected individually. The main feature of the treatment of nonspecific forms of urethritis is the absence of the need to treat the sexual partner.

Non-infectious urethritis
With allergic urethritis, it is necessary to use antihistamines. If urethritis is caused by stagnation of blood in the pelvic area (congestive), it is necessary to eliminate the cause of this stagnation. In traumatic urethritis, in addition to antimicrobial therapy, surgical intervention may also be required.
Antibiotics may be prescribed for:
installation of the drug by catheter injection into the urethra;
intravenous infusions in 0.2% of cases of acute urethritis;
intramuscular injections in 18%;
oral administration in 81%;
the use of only one antibiotic - monotherapy 41%;
two - 41%;
three - 13%;
four antibiotics - 5% of cases.
The most popular antibiotics for acute male urethritis, which are prescribed by a doctor, depending on the type of pathogen
|
Trichomonas urethritis in combination with atypical agents |
Gonococal urethritis |
Mixed urethritis |
|||||
|
"Ornidazole" |
"Doxycycline" |
"Josamycin" |
|||||
|
"Josamycin" |
"Ciprofloxacin" |
"Ceftriaxone" |
|||||
|
"Azithromycin" |
"Metronidazole" |
"Ornidazole" |
|||||
|
"Doxycycline" |
"Azithromycin" |
"Seknidazol" |
|||||
|
"Metronidazole" |
"Ceftriaxone" |
"Fluconazole" |
|||||
|
"Doxycycline" |
|||||||
|
"Azithromycin" |
|||||||
|
Nongonococcal urethritis that is caused by atypical agents |
Urethritis of unknown etiology |
||||||
|
"Clarithromycin" |
"Clarithromycin" |
||||||
|
"Seknidazol" |
"Ciprofloxacin" |
||||||
|
"Josamycin" |
"Tinidazole" |
||||||
|
"Metronidazole" |
"Nimorazole" |
||||||
|
"Doxycycline" |
"Josamycin" |
||||||
|
Ofloxacin |
"Seknidazol" |
||||||
|
"Fluconazole" |
"Fluconazole" |
||||||
|
"Azithromycin" |
"Ceftriaxone" |
||||||
|
"Doxycycline" |
|||||||
|
"Metronidazole" |
|||||||
|
"Azithromycin" |
|||||||

Complementary Therapies
In addition to the basic course of treatment with antibacterial drugs that suppress the acute symptoms of the disease, other therapeutic methods are also widely used, which are related to local and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Local procedures involve the introduction of drugs directly into the opening of the urethra. Urethral installations are performed with the help of hydrocortisone, Dioxidin and Mirimistin. Local treatment gives a good result, subject to complex use with other drugs.
Physiotherapy treatment is used exclusively in cases of chronic urethritis, it is strictly contraindicated to use these methods in acute inflammatory processes. Magnetotherapy, laser therapy, UHF, electrophoresis can be prescribed. However, all these methods should be carried out only systematically and only under the supervision of specialists.
Causes of urethritis in men
genital infections - are the most common cause of urethritis in men who are sexually active. If sexual intercourse is performed without the use of barrier contraceptives, then the probability of penetration of the pathogen into the urethra is very high;
urolithiasis - much more often found in men than in women. Such a disease causes traumatic urethritis, for the reason that the stones, moving along the genitourinary tract, actively injure the mucosa and lead to the attachment of pathogenic microorganisms;
any trauma to the penis and heavy physical exertion can cause the development of urethritis;
hypothermia is one of the most important provocateurs of exacerbations of chronic diseases (including extrapulmonary tuberculosis, viruses, infections), since in this case the protective functions of the body are significantly reduced;
a general decrease in immunity - smoking, alcohol abuse, overwork, lack of sleep, malnutrition leads to a natural depletion of the body's defenses;
medical manipulations (bladder catheterization, smear) - carry the risk of injury to the urethral mucosa, and urethritis can also develop if the necessary disinfection measures are not followed;

nutrition - an abundance of acidic, spicy, salty foods leads to irritation of the mucous membranes, which contributes to the attachment of infection. The lack of fluid is the cause of rare urination, respectively, there is no natural washing of the genitourinary tract from harmful microorganisms that can accidentally enter the urethra.
Prevention of complications of urethritis
Statistics say that every second man on the planet after 50 years of age has prostatitis. Do not think that prostatitis can cause urethritis directly. However, quite often the occurrence of prostatitis occurs against the background of active infectious diseases of the genitourinary system. Urethritis can cause the development of Reiter's syndrome, infertility, sexual dysfunction, colliculitis, balanoposthitis, orchitis, vesiculitis. In order to minimize the risk of complications of urethritis, a man should:
avoid excessive and intense physical activity;
do not get involved in salty, spicy, fatty foods, alcohol;
empty the bladder at the first urge to urinate, try to “tolerate” less;
avoid hypothermia;
timely conduct therapy of any pathologies of a chronic nature;
conduct a decent sex life, observe the rules of intimate hygiene.
Urethritis in fact, an inflammatory process that develops in the tissues that form the urethra (urethra). Any inflammation is characterized by edema and local stagnation of blood, leading to pain and subsequently to disruption of the normal functioning of the affected organ. With urethritis, the wall of the urethra swells, preventing the passage of urine, and the integrity of the epithelium is violated, which manifests itself in pain or.

Common signs of urethritis are pain of varying intensity during urination, mucous or purulent discharge from the urethral canal, and redness of the tissues that surround the urethral outlet. The severity of symptoms depends on the clinical form of the disease - acute, subacute or chronic. Symptoms of urethritis vary depending on the type of pathogen and the anatomical features in the structure of the male or female urethra.
Anatomical features of the urethra
In men, the length of the urethra is on average 20-23 cm. Conventionally, it is divided into the back part, which combines the membranous and prostatic parts of the canal, and the cavernous part, which is called anterior urethra. Topography is important for the choice of medical tactics: with inflammation of the anterior or posterior urethra, different approaches to the treatment of urethritis are used. Anterior urethritis in 90-95% of cases is complicated, back - inflammation of the bladder with ascending infection, frequent urge to urinate.
The male urethra is distinguished by physiological local expansions and narrowing of its lumen. The wide part (navicular fossa) has a length of up to several centimeters and ends with an external opening, a narrow section falls on the posterior urethra. Several depressions in the mucosa are formed by the outlets of the urethral glands. The walls of the urethra outside of urination are always closed, the external opening is covered with folds of the skin of the head of the penis.

the structure of the female (left) and male (right) urethra
In women, the urethra is short, only 1.5-3 cm, and about one and a half times wider than the male. The outer opening is covered by the labia minora, inflammation from the urethra easily passes to the vagina and then to the cervix. Urethritis is very often combined with inflammation of the bladder - cystitis, complicated by ascending infection of the ureters and renal pelvis. In the chronic form of urethritis, urinary incontinence may develop.
Video: urethritis and its consequences in medical animation
Clinical forms of urethritis
Acute urethritis is characterized by intense inflammation, during the day - multiple, which may not stop even after urination. For subacute urethritis, the main symptom is the appearance of discharge only after active pressure on the urethra.
Chronic urethritis is harder to spot: discharge occurs mainly after provocations, which can become in men - alcohol, spicy food, in women - the onset of menstruation, the abolition of contraceptives, menopause. The diagnosis of chronic urethritis is made in cases where the duration of the disease is more than two months, or the patient is not exactly sure about the time of the onset of the first symptoms.
Urethritis nonspecific and specific
According to the type of pathogen, urethritis can be bacterial, viral and fungal, that is, infectious. Non-infectious urethritis develops with inflammation of the urethra due to allergic reactions, after trauma to the urethra with catheters or bougies, with strictures.
Urethritis caused by an infection that is sexually transmitted is called specific, all the rest are nonspecific.
Nonspecific urethritis is caused by bacteria for which sexual transmission is not the main one. Bacterial non-specific urethritis can be obtained by household contact (through linen or a towel, toilet paper, “public” solid soap), if the usual hygiene rules are not followed, or when an infection spreads from an inflammation site inside the body. The main pathogens are strepto- and staphylococci, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Haemophilus influenzae.
Manifestations of gonorrheal (gonococcal) urethritis
Wu mu acute urethritis is the most common manifestation. After infection, an average of 2 to 7 days pass quietly, gonococci multiply in the urethra asymptomatically. When a certain critical number of pathogens is reached, symptoms of urethritis appear. The time elapsed from the moment of infection to the pronounced onset of the disease is called the incubation period. For gonorrheal urethritis, it varies from 2 days to 2 weeks.
The main symptoms are discharge from the urethra and acute pain when urinating. At first, the discharge of the urethra is rather meager and mucous, but quickly turns into profuse and purulent. It is these signs that distinguish gonococcal urethritis from non-gonococcal urethritis. Men with “erased” forms of gonorrheal urethritis, the development of which is possible when the disease passes into a chronic form or with improper treatment, are especially dangerous as spreaders of the infection. In addition, this group is more prone to complications that can lead to male infertility.

Among women diagnosed with gonococcal urethritis, more than 70% experience no urethral discomfort. Drawing pains in the lower abdomen, slight irritation and hyperemia (redness) of the labia minora are possible. Discharge from the urethral canal is scarce, often women do not notice them at all. Sometimes the disease is determined quite late, when the inflammation affects the internal genital organs - the vagina, uterus and fallopian tubes.
In this case, the pain intensifies, the discharge becomes larger, and during menstruation, heavy bleeding (menorrhagia) begins. Gonococci can also spread through the bloodstream, causing inflammation of the kidneys and liver, brain and heart, muscles and joints.
Chlamydial urethritis
The incubation period lasts on average from 4 days to 4 weeks, then there is a tingling and burning sensation in the urethra when urinating. Mucous discharge in men, can be completely transparent or slightly cloudy, turning into purulent . In women, the symptoms of urethritis are an increase in the urge to urinate, during intercourse - pain in the lower abdomen, yellowish mucous or purulent discharge from the urethra and
Without adequate treatment, non-gonococcal urethritis becomes chronic, with inflammation lasting for months and years. As a result, women develop scars in the fallopian tubes, leading to ectopic pregnancy or infertility. In men, chronic urethritis is complicated by inflammation of the epididymis (), which is manifested by unilateral or bilateral swelling of the scrotum and prostatitis.
Complications: inflammation can result in the formation of persistent narrowing or partial adhesions of the walls of the urethra, lead to female and male infertility, sexual dysfunction.
Candidal and viral urethritis
These types of urethritis are characterized by burning in the urethra, severe pain and frequent painful urination and periodic relapses.
Candida urethritis manifests itself with direct (sexual or domestic) infection with yeast fungi of the genus Candida, as well as a complication after antibiotic treatment or with a decrease in the body's immune defenses. Often combined with vaginal candidiasis, commonly known as. Characterized by abundant liquid discharge, grayish plaque in the area of the external opening of the urethra. 
Viral urethritis is caused by a simple human. The reproduction cycle of this virus is only 14 hours, it is transmitted mainly through sexual contact. So the patients' suspicions that urethritis appeared after sex are quite justified. Symptoms can develop quickly, during the day, especially against the background of stress or hypothermia. In men, the discharge from the urethra is mucous, mostly noticeable in the morning in the form of a drop. During urination, a tingling sensation is felt, then the pain intensifies. Inguinal lymph nodes may increase, body temperature may rise.
Distinctive visible signs of viral urethritis are the appearance of small vesicles, erosions and sores, grouped around the external opening of the urethra. The elements of the rash can merge, eventually forming yellowish-crusted lesions with jagged edges. The duration of viral urethritis is up to 2 weeks, relapses are possible at intervals from a month to several years.
Trichomonas urethritis
The asymptomatic presence of Trichomonas, called carriage, is found in 20-37% of infected people.
Inflammation is moderate, but the waste products of Trichomonas are toxic to the human body: they loosen the surrounding tissues, contributing to the spread of the process. A distinctive feature of Trichomonas urethritis is constant itching. In men, at the onset of the disease, a sensation of "goosebumps" may appear in the area of \u200b\u200bthe head of the penis, on the first day - small watery discharge of a grayish-white color, semen with an admixture of blood. Within a month, these manifestations subside, then torpid urethritis develops, which is aggravated by alcohol intake, after intercourse, with general and local hypothermia.
Local complications of trichomonas urethritis are erosions and ulcers on the genitals, resembling when. Ulcers often have a clean bottom of a bright red color, less often - with a purulent coating, and soft, tucked edges of irregular outlines.
Trichomonas urethritis is especially dangerous for the female body., as it proceeds in most cases without specific treatment and leads to complications during pregnancy or to infertility. In men, inflammation spreads from the anterior to the posterior urethra, causing prostatitis, epididymitis, and subsequently also infertility. Trichomonas have been nicknamed "silent killers" for the contrast between the insignificance of symptoms and the severity of common complications.
Urethritis in pregnant women
Urethritis during pregnancy often occurs against the background of pharyngitis(inflammation of the pharynx) caused by chlamydia, mycoplasma or ureaplasma infection, gonorrhea. Infection can occur before pregnancy or during it. An exacerbation of an asymptomatic chronic infection occurs due to an increase in internal pressure on the urethra and expansion of its external opening, infection in the early stages of pregnancy is due to increased libido.

Symptoms of urethritis are the same as in non-pregnant women. Concerned about frequent urge to urinate, burning and pain in the urethra, itching in the perineum, discharge from the vagina and urethra.
The main danger of urethritis during pregnancy is a negative impact on the child and the development of complications during gestation and childbirth. The risk for the newborn is sepsis, infection of the membranes, intrauterine death. The infection can be transmitted to the child during childbirth: a common form of gonorrhea is specific conjunctivitis or gonoblenorrhea, which doctors should suspect first of all by noticing discharge from the eyes of a newborn before 2-3 days of life.
Chlamydia can cause pneumonia, inflammation of the conjunctiva, nasopharyngitis in a child. Mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas easily penetrate into the amniotic fluid and into the body of the fetus, but appear only in premature babies.
The risk to the mother is preterm birth, spontaneous abortion and bleeding.
Pregnant women with chlamydial and mycoplasmal infections belong to the risk group and are treated before delivery and, if necessary, after. Chlamydial urethritis is treated in both sexual partners with antibiotics, prescribing them to pregnant women only after 12-16 weeks; use josamycin, amoxicillin. With gonorrheal urethritis, specinomycin, ceftriaxone, cefixime are prescribed. Ureaplasma and mycoplasma urethritis: treatment is carried out with josamycin, starting from the II trimester of pregnancy.
Diagnosis of urethritis
- Survey, analysis of the information received. The doctor is interested in what exactly worries the patient and when the first manifestations of urethritis appeared, finds out the temporal connection of the symptoms of the disease with sexual intercourse.
- Urological examination performed by a urologist or gynecologist. The external opening of the urethra is visually assessed, the presence and nature of the discharge is serous or purulent, they are liquid or viscous, abundant or scarce. Examination of the perineum and external genitalia: detection of hyperemia, plaque, rash, erosions and ulcers, external cicatricial changes.
- from the urethra for seeding on a nutrient medium and microscopic examination of the cellular composition of the material. With Trichomonas urethritis in fresh secretions under a microscope, you can see actively moving flagellates: the phenomenon is called the "dance of Trichomonas."
- ureteroscopy, an instrumental method of examination. A thin probe with fiber light guides is inserted into the urethra, thanks to which it is possible to examine the condition of the canal walls, to assess the degree of its narrowing. A contraindication for ureteroscopy is urethritis in the acute phase.
- urethrography, X-ray examination of the urethra with the introduction of an X-ray contrast agent into it.
- Traditional analyzes:
- a general blood test for urethritis will indicate signs of acute or chronic inflammation - leukocytosis, with purulent inflammation - an increase in the number of neutrophils;
- biochemical analysis - an increase in the marker of inflammation, c-reactive protein;
- urinalysis, the first portion - the presence of epithelial cells, leukocytes, traces of blood.
- (polymerase chain reaction), a fast and reliable option for diagnosing specific urethritis infections. As a material, epithelial scrapings, discharge from the urethra, blood and blood serum are suitable.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs: in women - control of the condition of the ovaries, uterus and bladder; in men - the bladder, seminal vesicles and prostate gland.
The diagnosis is made after evaluating the data obtained as a result of examinations. A correctly executed diagnosis should fit into the medical history (or outpatient card) in Latin and contain an indication of the location of the process - urethritis, the clinical form - acute, subacute or chronic, and the pathogen. In the Russian version, the diagnosis looks somewhat different, in the first place - the form, then - the pathogen, at the end - urethritis. For example, acute gonococcal urethritis.
Principles of treatment of urethritis
 Treatment of urethritis begins with antibiotics. The drug is selected depending on the pathogen and the severity of the inflammation. In an acute process, broad-spectrum antibiotics are immediately prescribed, then they switch to drugs to which microflora sensitivity has been identified in a particular case of urethritis.
Treatment of urethritis begins with antibiotics. The drug is selected depending on the pathogen and the severity of the inflammation. In an acute process, broad-spectrum antibiotics are immediately prescribed, then they switch to drugs to which microflora sensitivity has been identified in a particular case of urethritis.
- Nonspecific urethritis: cephalosporins (cefataxime, ceftriaxone), macrolides (clarithromycin), a group of fluoroquinolones (clinafloxacin).
- gonorrheal urethritis: cefacor, spectinomycin, ceftriaxone. Antibiotics are selected, to which both gonococci and chlamydia are sensitive.
- Trichomonas urethritis: imorazole, trichopolum (metronidazole), iodovidone suppositories.
- Candida urethritis: clotrimazole (vaginal tablets or cream, capsules), fluconazole.
- Mycoplasma and chlamydial urethritis: a group of tetracyclines (doxycycline), macrolides (clarithromycin).
- Viral urethritis: ganciclovir, ribavirin - antiviral drugs.
Used to reduce inflammatory and reactive edema non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs(aspirin), antihistamines (suprastin), antispasmodics (no-shpa, papaverine) and diuretics.
Immunostimulants and probiotics prescribed to activate the body's natural defenses: injections of cycloferon, ribomunil, vitamins (B-groups, PP, A, E, C), linex or yogurt.
Biostimulants- aloe, homeopathic preparations - used for targeted exacerbation of chronic urethritis. As a result, the susceptibility to treatment increases, the susceptibility of pathogens to antibiotics increases.
Enzyme Therapy: prescribe enzymes that break down proteins. Action - anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory.
Local treatment: instillation - the introduction of liquid medicines into the urethra. Silver preparations (collargol) are used, the procedure is performed only in honey. facility with a sterile catheter.
Bougienage- instrumental expansion of the urethra with the development of strictures of the urethra.
Physiotherapy: locally - medicinal baths, UHF exposure, electrophoresis with antibiotics.
Folk remedies only complement the main treatment. Chamomile tea, parsley roots and greens, carrots and celery, lingonberries and cranberries, beets - products are introduced into the daily diet. Herbal preparations are prepared separately and taken for at least a month (St. John's wort, sage, horsetail).
Diet: it is recommended to exclude spicy and salty foods, alcohol. Drink more clean water, focus on fresh vegetables and fruits. When using diuretics, potassium is excreted, therefore the diet is supplemented with dried apricots, prunes, raisins.
You can treat urethritis at home, only patients with an acute form of the disease are hospitalized. Home treatment allows you to take medications, use vaginal suppositories, use therapeutic baths, adhere to a regimen and a therapeutic diet. All manipulations (injections, instillations, bougienage) are carried out in a hospital.
Video: folk remedies useful for urethritis
Prevention of urethritis
- Use a condom.
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene. If sexual intercourse took place without a condom: urinate, wash the external genitalia with plenty of warm water and liquid soap. Use antiseptic solutions (miramistin, gibitan) for a maximum of 2 hours after intercourse.
- Prevent hypothermia, timely treat diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Periodically (1-2 times a year) undergo a medical examination.
- Refrain from casual sex.
Video: urethritis in the program “Live great!”

