Vitamins starting with the letter P. Medicines starting with the letter 'P'. With increased acidity
Hypertension is a lifelong diagnosis, so hypertensive patients have to take pills for the rest of their lives to prevent and reduce the consequences of hypertensive crises. Tablets for high blood pressure are presented on the pharmacological market in a huge assortment, which often confuses hypertensive patients - how to choose a drug with maximum effect and minimal side effects?
It is worth considering that the data given below is for informational purposes only and the final decision on the choice of drug should be made exclusively by the doctor after a full examination of the patient.
High blood pressure pills: which ones to choose?
Medicines for high blood pressure are a last resort in the treatment of hypertension, i.e. they are used if other means have failed to return the pressure to normal. Even the best and most effective pills for high blood pressure are practically never without side effects, which means that the medications will have a negative effect on other human organs and systems.
Therefore, doctors prescribe pills only as a last resort, and the patient must understand that it is easier and more beneficial to take care of one’s own health, adhere to a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, etc., than to constantly take medications. And only if such measures do not help return the pressure to normal, you should seek help from medications.
High blood pressure medications are prescribed if blood pressure exceeds 160/90 or more for a long time. If patients have high blood pressure due to diabetes mellitus, heart or kidney failure, then drugs are prescribed already at levels of 130/85 mm Hg.
Considering the fact that there are quite a lot of blood pressure pills, the choice of medications is made taking into account the patient’s condition.
Taking one drug (monotherapy) is indicated for the initial, mild stages of hypertension. Treatment achieves greater effect when taking combined drugs or when combining several drugs from different groups. It should be borne in mind that over time the body gets used to taking the same antihypertensive drugs, which significantly weakens the effect of taking them. Therefore, when treating high blood pressure, periodic replacement of medications is necessary, which is carried out only by a doctor.

Medicines that lower blood pressure can be fast-acting or long-acting (long-acting). Different pharmacological groups of drugs have different effects on processes in the body, therefore an individual treatment regimen must be selected for each patient.
Important! Only a doctor (GP or cardiologist) can prescribe medications for high blood pressure. Independently choosing and taking a hypertensive drug, about which you have heard good reviews from a neighbor, friends, etc., can lead to a worsening of the condition.
Let's look at the main groups of drugs used for high blood pressure.
All of these drugs are prescribed for persistent high blood pressure to treat arterial hypertension. When choosing a drug, the patient’s age, concomitant diseases, stage of hypertension, individual characteristics of the patient, etc. are taken into account.
Effective drugs for high blood pressure
Each medicine for high blood pressure has its own effective effect on the patient’s body - what suits one patient will not necessarily help another. Therefore, it is impossible to say unequivocally which blood pressure pills should be taken; the choice of medications is made on an individual basis.
Sartans
The most promising and effective for high blood pressure are new drugs from the sartan group. They have a quick effect, cause virtually no side effects and are used in cases where it is necessary to relieve vascular spasm quickly. A lasting effect is observed 4-6 weeks after starting to take the medicine.
Preparations of the sartan group are divided depending on the active substance included in their composition. For example, drugs containing losartan ( Lorista, Losarel, Presartan) - inexpensive (from 160 rubles), tablets with eprosartan and candesartan ( Teveten, Atakand) - more expensive (from 1200 rubles), etc.
Alpha blockers
Previously, this series of drugs was considered a priority in the treatment of high blood pressure. The tablets block alpha-adrenergic receptors located on the walls of blood vessels, as a result of which the vessels begin to dilate and the pressure decreases.
However, such drugs have serious side effects - they increase the risk of stroke or myocardial infarction.
Alpha blockers ( Clonidine, Doxazosin, Dopegyt) can be purchased in pharmacies at a price of 150 rubles.
Width="650" height="437">
ACE inhibitors
If it is necessary to provide emergency assistance to a patient, ACE inhibitors are prescribed, which act directly on the blood vessels - they counteract the narrowing of the arteries and reduce blood flow to the heart.
Most often, such drugs are prescribed to patients whose blood pressure increases due to coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus and other concomitant diseases.
ACE inhibitors should not be used during pregnancy, with liver and kidney failure, or with autoimmune diseases.
Medicines containing enalapril ( Renipril, Enalapril, Renitec) cost from 90 rubles, with the active ingredient perindopril ( Prestarium) – from 400 rubles, with ramipril ( Amprilan, Tritace) – from 1000 rub.
Beta blockers
The tablets regulate the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle - as a result, the blood flow into the bloodstream decreases and the pressure normalizes.
Beta-blockers are prescribed to patients with a history of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, in addition to high blood pressure.
The dosage and use of beta blockers is determined by your doctor. The best drugs: Anaprilin, Nebivalol, Levatol, Labetalol, Bisoporol.
Diuretics
Medicines that have a diuretic effect (diuretics) help reduce blood pressure by quickly removing excess fluid from the body, which reduces swelling of blood vessels.
Hypertensive patients should avoid salty foods and take diuretics to regulate blood pressure - Indapamide, Furosemide, Indapafone, Hypothiazide.
All drugs for high blood pressure can be divided into two groups: delayed-release and long-acting tablets, in which the active substances gradually accumulate in the body and begin to act after long-term use.
Fast acting tablets
The first group of drugs has an immediate effect and is used for sudden increases in blood pressure. But many of them contain narcotic substances that can negatively affect the central nervous system and other human organs and systems.

Fast-acting blood pressure medications:
- Anaprilin;
- Adelfan;
- Furosemide;
- Captopril;
- Enalapril.
If there is a sharp increase in blood pressure, it is enough to take an Adelfan or Captopril tablet under the tongue to lower blood pressure within 10-30 minutes. But this effect is usually short-lived, and the drugs will need to be taken 2-3 times a day.
Diuretic Furosemide also quickly lowers blood pressure, but has a strong diuretic effect - for several hours the patient will urinate frequently.
Long-acting tablets
The drugs have a long-lasting therapeutic effect, which is convenient in the treatment of hypertension. It is enough to take only 1-2 tablets per day to increase blood pressure at home and achieve stable remission.
List of new generation long-acting drugs:
- Diroton;
- Cordaflex;
- Bisoprolol;
- Metoprolol;
- Losartan;
- Prestarium;
- Propranolol.
Medicines are used for long courses of therapy for grade 2-3 hypertension. To achieve lasting results, you need to take the drugs for three or more weeks, without stopping even if your blood pressure does not increase.
Rating of the best drugs for high blood pressure
When choosing tablets for high blood pressure, you should understand that the best remedy is not the one that quickly normalizes your blood pressure. The medicine should also prevent the occurrence of new attacks and not cause side effects or complications. It is not possible to select such a drug right away; most often you have to go through several treatment regimens.
However, there are a number of drugs that have received good reviews from patients and have proven themselves to be the most effective remedies for high blood pressure.
| Drug name | Action | pros | Minuses | Analogs |
| Arifon-retard | Belongs to the group of indapamide diuretics. It is used in minimal doses, therefore it stabilizes blood pressure without having a strong diuretic effect. | Ease of use (1 tablet per day); Affordable price; Minimum side effects. |
It is not suitable for use by people with lactose intolerance or impaired renal or liver function. | Acripamide, Indap, Indopamide, Perinide. |
| Veroshpiron | Potassium-sparing diuretic with a strong diuretic effect. Most often used in combination therapy. | If the dosage is observed, it practically does not cause side effects. | A long course of therapy can cause hormonal imbalances in women and lead to impotence in men. | |
| Captopril | ACE inhibitor, the most common drug for treating high blood pressure. May be prescribed in combination with other hypertensive drugs. | It quickly normalizes blood pressure, has a low cost, improves blood supply to the heart, and reduces the likelihood of blood clots. | Frequent use (up to 4 times a day), the presence of side effects and contraindications. | Kaptopres, Katopil, Blockordil, Copoten, Alkadil, Kapofarm. |
| Lisinopril | ACE inhibitor with a long-term cumulative effect. Helps reduce blood pressure within an hour after administration. | Stabilization of blood pressure levels for a long period. Suitable for the treatment of hypertension in people with diabetes, heart failure, and a tendency to heart attacks. | Side effects: dry mouth, sweating, dry cough, dizziness. | Renipril, Lisinovel, Lizacard, Sinopril, Diroton, Lipril, Dapril, Lysigamma. |
| Losartan | A group of sartans. The pressure decreases 6 hours after taking the medicine and the effect lasts throughout the day. | A pronounced and lasting effect of reducing pressure. Ease of administration, good tolerability (with a minimum of side effects). |
Quite a high cost. | Xartan, Lozap, Vasotens, Bloktran, Renicard, Presartan. |
Note. The drugs offered in the table are arranged alphabetically, and not by effectiveness. The choice of drug should be made exclusively by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Elderly people often use drugs such as Clonidine or Moxonidine. But these tablets are considered outdated and are not recommended for use by doctors, because... addictive. For high blood pressure, older people are more often prescribed drugs from the sartan series, drugs based on lisinopril, or combination drugs.

Combined treatment
When treating high blood pressure, combination treatment is more often used, which includes the prescription of two drugs from different drug groups.
Popular combination products
If the usual regimen for taking medications for high blood pressure does not help, then the combination may consist of three drugs in various versions, which is selected exclusively by the doctor.
Additionally, taking into account the patient’s condition, tablets for headaches with high blood pressure, sedatives, acetylsalicylic acid preparations, and antispasmodics may be prescribed.
When treating hypertension, you should not choose pills on your own, relying only on reviews from friends and data from various medical forums. Only a doctor can prescribe and indicate which pills to take, taking into account all the patient’s characteristics. Each patient is prescribed an individual treatment regimen, if it is insufficiently effective, the doctor can adjust the dosage or change the prescribed drugs.
symptom-treatment.ru
Who should take blood pressure pills?
Often among patients who need long-acting blood pressure pills, the majority are people of retirement age whose medical history is associated with age-related processes.
Taking into account the destructive effect on the body of the side effects of antihypertensive drugs, they are prescribed by a doctor only in cases where blood pressure is stable at 160/100.
In other cases, doctors recommend a healthy diet for hypertensive patients, excluding salty, fatty and fried foods. Also among the specialist’s recommendations will be giving up smoking and alcohol, moderate exercise to lose excess weight and avoiding stressful situations.
The principle of choosing blood pressure tablets
If all the doctor’s recommendations are followed and the blood pressure does not return to normal, specialized medications are prescribed. Since antihypertensive drugs have a purely individual effect, those pills that are effective in the case of one patient may not bring relief to another.
The principle of their purpose lies in a complex list of points:

Classification of blood pressure tablets
Diuretics
Diuretics or diuretics are divided into loop, thiazide and potassium-sparing agents:
- Loop agents, for example furosemide– tablets that quickly lower blood pressure during attacks and crises, due to their powerful action, but their long-term use can lead to a deficiency of potassium and sodium, which is fraught with arrhythmia and other cardiac disorders;
- Thiazide diuretics, such as arifon or indapamide - long-acting blood pressure tablets prescribed for the initial stages of arterial hypertension have a positive effect on the body, on the contrary, with prolonged use, without removing beneficial microelements from the body;
- The third subgroup of diuretics– potassium-sparing drugs: spironolactone, veroshpiron. These drugs are not used as independent diuretic tablets due to their weak hypotensive effect and are prescribed only in combination with antihypertensive drugs of other classes.
Contraindications: Diuretics, with the exception of furosemide, should be avoided in cases of concomitant acute renal failure.
Furosemide, along with uregitis, in turn, is contraindicated in case of anemia and hypovolemia. Veroshpiron is contraindicated in case of elevated potassium in the blood and atrioventricular block, and hypothiazide is prohibited from being prescribed for diabetes mellitus.
Antiadrenergic drugs
This group of drugs is dangerous to use without a doctor’s prescription and is not suitable for all patients.
Antiadrenergic drugs or sympatholytics are divided into 5 main groups, differing in their action:
- Central acting agents, manifesting itself inside neurons. They provide a central sedative effect and prevent the deposition of catecholamines in the hypothalamus. A striking example of sympatholytics is reserpine. In the form of tablets, the hypotensive effect begins on the 5-6th day, intravenously - after 2-3 hours.
Side effect: Nasal congestion, diarrhea, bradycardia, possible redness of the eyes, weakness, dizziness and shortness of breath are often observed. There are known cases of negative effects on the psyche of patients, manifesting themselves in the form of neuroses or depression.
Before prescribing reserpine The medical history of both the patient and close relatives is studied in detail for mental disorders. Reserpine is not available without a prescription.
Drugs of this group milder action are raunatin And rauvazan. In addition to their hypotensive effect, they calm the nervous system, restore heart rhythm and increase renal circulation.
Guanedine, ismelin, isobarine, belonging to the same group of central action, exhibit a slow effect in lowering blood pressure, manifesting it no earlier than 7 days after the start of the course of treatment, but after the end of their administration it persists for up to 14 days.
Side effects of these drugs: diarrhea, orthostatic hypotension - impaired coordination of movements when getting up from a sitting or lying position and in the heat, weakness, decreased performance. Drugs in this group are contraindicated in myocardial infarction, renal failure and pheochromocytoma. Also, they are unacceptable for atherosclerosis of the cerebral and coronary arteries.

They are not available without a prescription and are dangerous not only for health, but also for human life, if the dosage is not observed or some of them are combined with alcohol. They also have criminal notoriety.
Methyldopa– rapid action when administered intravenously, the effect lasts up to 2 days. The action is based on a decrease in peripheral resistance without changing cardiac output.
Side effect: drowsiness, dry mouth, poor coordination, may have a negative effect on the immune system and cause complications such as hepatitis or myocarditis.
Contraindicated during pregnancy and liver diseases. Drugs belonging to the clonidine subgroup have a similar effect, with the difference that the hypotensive effect does not manifest itself immediately: after administration of the drug, a sharp jump in pressure is observed, then a gradual decrease and the effect persists for up to 3 days.
These drugs used for immediate response in case of possible stroke or other complications associated with hypertension. When taking tablets, an improvement in the condition appears after 30 minutes, intravenously - up to 5 minutes. Side effects are the same as from methyldopa.
Caution needs to be shown with clonidine, because when it is discontinued, withdrawal syndrome is often observed, manifesting itself in tachycardia, agitation and anxiety. Cancellation is carried out gradually over several days. Clonidine leads to death in combination with alcohol.
Contraindications: depression, acute heart failure, alcoholism and atherosclerosis of the coronary and cerebral vessels.
- Peripheral alpha blockers reduce total peripheral resistance, increase the venous bed, relax the walls of blood vessels, reducing hypertension. Therapy is prescribed for at least 2 weeks, since their hypotensive effect begins to appear no earlier than 7-8 days.
The advantage over other drugs that lower blood pressure is the meager list of side effects: dizziness, headaches.
- Beta blockers– drugs that specialize not only in lowering blood pressure, but also cardiovascular pathologies: angina pectoris, arrhythmia, etc.
Their similarity to endogenous catecholamines allows them to neutralize their negative effects on the cardiovascular system. Hypotensive effect, prevention of tachycardia, prevention of hypertension due to stress or excessive physical activity. Also used for the prevention of myocardial infarction and heart rhythm disturbances due to hypertension.
Beta blockers are divided into into non-selective (propranolol, obzidan) and selective (kordanum, talinolol). Applicable for long-term use, subject to the correct dosage, which is prescribed after careful examination.
Side effects: sleep disorders, weakness and decreased performance, the appearance of atrioventricular block, withdrawal syndrome accompanied by tachycardia, cardialgia, stress and headaches when the drug is abruptly stopped.
Contraindications: sinus bradycardia, cardiogenic shock, gastric ulcer, diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure.
- α- and β-adrenergic receptor blockers.
Reduce peripheral resistance, reduce renin resistance in the blood, normalize cardiac output.
Characteristic drugs The following subgroups are considered: labetolol, trandate, albetol.
Fast action: when administered intravenously, the effect appears after 2 minutes. Contraindications: pregnancy, atrioventricular block and lung diseases.
Peripheral vasodilators
Such drugs are divided into 3 types:
- Arteriolar peripheral vasodilators (PV): hydralazine, apressin, diazoxide, hyperstat. They help reduce overall peripheral resistance, but cause a homeostasis reaction, which partially neutralizes the effect of the drug. The sympathoadrenal system begins to activate renin.
- Mixed vasodilators: isosorbide dinitrate, sodium nitroprusside. They act by dilating arterial vessels. The negative effect is the additional dilation of the veins, reducing the volume of blood returning to the heart, leading to blood stagnation.
- Soft action PV: papazole, dibazole, papaverine, andipal. Until recently, it was used in emergency care in cases of hypertensive crises and was included in the list of necessary drugs in ambulances. The drugs treat isolated cases of hypertension, but do not cure it.
Let's take a closer look at the drugs, their side effects and contraindications:
- Hydralazine has side effects in the form of headaches, tachycardia, and possible development of angina. Contraindications: SLE, hepatitis, stomach ulcer.
- Diazoxide has the ability to reduce pressure within 2 minutes, but is released only in ampoules.
- Nitroprusside sodium increases stroke volume, reduces pre- and afterload. Rapid action is used to eliminate hypertensive crises or acute left ventricular failure.
Calcium antagonists
The hypotensive effect of these drugs is based on their ability to block the flow of calcium ions into the muscles of the heart and arteries, due to which they relax. They also serve as preventatives for blood circulation disorders.
Side effects: dizziness, weakness, headache, swelling of the limbs.
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
Drugs that specialize in suppressing the kidneys' production of renin, which increases blood pressure.
Their ability to improve peripheral circulation and dilate coronary vessels makes them effective in the treatment of concomitant cardiac disorders.
Prescribed for heart failure and previous heart attacks. Contraindicated in renal failure, hyperkalemia.
Angiotensin-2 receptor blockers (ARBs)
Due to the similarity in their effect on blood vessels with the effect exerted by ACE inhibitors, these drugs are often prescribed instead of the latter, if the patient is individually intolerant of their components.
Possible combinations of different classes of blood pressure tablets
Antihypertensive drugs have different effects on the body and have different side effects.
For greater effectiveness, and sometimes in order to reduce the negative impact on the patient’s health, such drugs are prescribed in the following acceptable complexes:

Blood pressure pills during pregnancy
Despite the fact that high blood pressure- a phenomenon common in women during pregnancy, and complications are dangerous not only for the expectant mother, but also for the gestating fetus.
The prescription of drugs with antihypertensive properties is approached with extreme caution and only after attempts to lower blood counts using all sorts of other methods: diet and adherence to the regimen, folk remedies.
If all means have been exhausted, and they have not given a hypotensive effect, drugs from the following list are carefully administered, but mainly intravenously, and not in tablet form:
- Nifedipine is used to quickly reduce blood pressure in emergency situations.
It is used only intravenously, since resorption of the tablet can sharply lower arterial parameters, which will inevitably lead to disturbances in placental blood flow. The hypotensive effect occurs within 30-40 minutes. - Clonidine preparations are prescribed in dosages not exceeding 0.6 mg per day.
- Diazoxide is dangerous possible side effects: increased blood sugar, fluid retention in the body and inhibition of labor.
Therefore, the drug is administered intravenously only in cases of hypertensive crises in a small dosage - 15-45 mg. The effect occurs within 5 minutes. - Sodium nitroprusside It is dangerous due to possible intoxication of the fetus with cyanide products, therefore it is used extremely rarely as an emergency drug, only in cases of ineffectiveness of all other means. Prescribed intravenously through a drip. The effect occurs within 2-3 minutes. Dosage: per 250 ml of glucose 0.25 mcg.
- Labetalol intravenously. Cases of distress in the fetus, as well as bradycardia in the newborn, have been recorded. Contraindications: bronchial asthma, cardiac dysfunction. 25-50 grams are administered as a bolus.
- Hydralazine is more harmful than labetalol and nifedipine. It is dangerous due to possible heartbeat disturbances in the fetus and an excessive drop in blood pressure in the mother. There is also a risk of developing eclampsia.
Prices for drugs
- Clonidine (active ingredient - clonidine) - 26.2-32.4 rubles.
- Moxonidine – 136–161.08 rubles.
- Moxonitex – 290–391.8 rub.
- Physiotens – 245.6–304.9 rub.
- Albarel (active ingredient - rilmenidine) - 161.35–271 rub.
A short list of antihypertensive drugs in alphabetical order
- Acridilol;
- Bisoprolol;
- Valsartan;
- Hydrochlorothiazide;
- Quadropril;
- Lotensin;
- Metoprolol;
- Niperten;
- Prestarium;
- Trandolapril;
- Furosemide;
- Hortil;
- Eprosartan.
Folk remedies for blood pressure
Along with the drugs listed above, there are a number of folk remedies that help keep blood pressure normal. Their effect extends only to the early stages of the disease or its mild forms.
But, given the fact that antihypertensive pills without side effects have not yet been discovered, you can use the following recipes:

cardiohelp.com
Pressure norm
On average, in adulthood the norm is 120/80 mmHg. Art. This type of blood pressure is observed in healthy patients. Despite the fact that the indicator may fluctuate depending on individual characteristics, if there is a persistent decrease or increase, most likely the person is sick. If such a symptom or frequent surges in pressure occur, he must consult a doctor and undergo the necessary examinations.
Return to contents
Characteristics of hypertension
 High blood pressure causes headaches.
High blood pressure causes headaches. Hypertension is a prolonged increase in blood pressure. Manifestations of pathology may appear from time to time or be present constantly, depending on the severity of the disease. The prolonged course of hypertension, constant high blood pressure leads to disturbances in the functioning of the heart muscle, brain and blood vessels. Therefore, rapid normalization of the patient’s condition is required. With a latent course of the disease, the patient experiences:
- frequent headaches;
- aching pain in the sternum;
- hot flashes;
- noise and ringing in the ears;
- shortness of breath;
- swelling of the face and eyelids;
- weakness in the body.
Return to contents
How to choose a medicine?
The doctor selects medications for high blood pressure. When choosing a drug to stabilize blood pressure, it is necessary to take into account the patient’s symptoms, his general well-being and test results. Most medications for hypertension are addictive, so during therapy it will be necessary to replace one group of drugs with another. It is also recommended to drink medications to normalize well-being and eliminate unpleasant accompanying symptoms.
Return to contents
List of tablets for normalizing blood pressure
| Group of drugs | Effect on the body | Name in alphabetical order |
| Diuretics | Removes water and flushes sodium from the body. Because of this, there is a decrease in blood volume and normalization of the load on the vessels. |
|
| Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors | They have a vasodilating effect by blocking the transformation of angiotensin I into angiotensin II. These are medications that effectively level blood pressure and do not increase heart rate. |
|
| Dilating vessels | A drug that equalizes blood pressure by reducing vascular tone. Allows blood to circulate more easily throughout the cardiovascular system. |
|
| Calcium antagonists | They help regulate the flow of calcium into cellular structures by blocking calcium channels. This provokes a decrease in vascular tone. |
|
| Alpha blockers | Used to quickly lower blood pressure. The active substance acts on alpha-adrenergic receptors in blood vessels. Has a lot of negative effects. |
|
| Beta blockers | They have a restraining effect on beta-adrenergic receptors, causing vasodilation. Drugs that restore normal blood pressure, but lower the patient’s pulse. |
|
| Sartans | They block angiotensin II receptors, helping to gently stabilize blood pressure. |
|
Pagluferal - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medications for the treatment of epilepsy.
Pazopanib - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of cancer of the kidney, peritoneum, neck, soft tissue sarcoma.
Paclitaxel - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of breast, ovarian, and lung cancer.
Paxeladine - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medicine for the treatment of cough with influenza, pneumonia, bronchitis.
Paxil - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of depression and phobias.
Palin - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medications for the treatment of cystitis, pyelonephritis and urethritis.
Palora - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medications for the treatment of increased nervousness, irritability, sleep disorders, insomnia.
Panavir - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of various viruses.
Panadol - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medications for the treatment of various pains and fever.
Panangin - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of potassium and magnesium deficiency, heart failure and myocardial infarction.
Panatus - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of cough with whooping cough and other diseases.
Pangrol - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, enzyme deficiency.
Panzinorm - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medications for the treatment of chronic pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis.
Panimune Bioral - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of psoriasis, eczema, rheumatoid arthritis, neurodermatitis.
Panitumumab - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of rectal and colon cancer.
Pancreatin - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of a medicinal product for the treatment of pancreatitis and other diseases of the pancreas and gastrointestinal tract.
Panoxen - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medications to relieve pain from arthritis, osteochondrosis, neuralgia, gout, dislocations and sprains.
Pantovigar - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug to improve hair growth and prevent hair loss and baldness.
Pantogam - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medications for the treatment of cerebral palsy and encephalopathies.
Pantocalcin - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of epilepsy, enuresis and stuttering.
Pantocrine - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of asthenia, neurasthenia and hypotension (increased blood pressure).
Pantocrine Panthea - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medications for the treatment of asthenia, hypotension, neurasthenia, mental and physical stress.
Pantoprazole - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medications for the treatment of ulcers, gastritis, esophagitis of the stomach and duodenum.
Pancef - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of sore throat, sinusitis, otitis and other infectious diseases.
Pancitrate - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of chronic pancreatitis, bloating, and other digestive disorders.
Papaverine - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medications for antispasmodic therapy.
Papazol - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of a drug for the treatment of spasms and blood pressure reduction.
Paracetamol - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for fever relief and analgesic effect.
Pariet - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of gastritis and ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, including Helicobacter.
Parlazin - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of allergic rhinitis, urticaria, itchy dermatoses.
Paroxetine - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of an antidepressant drug for the treatment of depression.
Partusisten - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of threatened miscarriage and threat of premature birth.
PASK - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medicines for the treatment of various forms of tuberculosis.
Patentex Oval N - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of a contraceptive drug for local contraception in women.
Pegasis - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medications for the treatment of hepatitis C and B.
Pectusin - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of cough.
Penzital - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of pancreatitis, absorption disorders and improvement of food digestion.
Pentaxim - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the DPT vaccine for the prevention of whooping cough, tetanus and diphtheria.
Pentalgin - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medications for the treatment of headache, toothache and other pain and fever.
Pentaflucin - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of colds and ARVI, magnesium and zinc deficiency.
Pentovit - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medications for the treatment of asthenia and hypovitaminosis.
Pentoxifylline - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of circulatory disorders and tissue trophism.
Peponen - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of a medicinal product for the treatment of prostate adenoma, hepatitis, stomach ulcers and hemorrhoids.
Pepsan R - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of heartburn, flatulence, GERD, increased acidity of gastric contents.
Perindopril - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of arterial hypertension and blood pressure reduction.
Perineva and Co-Perineva - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medicinal products for the treatment of arterial hypertension and blood pressure reduction.
Perinorm - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of nausea, vomiting, hiccups.
Permixon - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medications for the treatment of prostate adenoma.
Persen - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of excitability, irritability and insomnia.
Pertussin - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of cough with bronchitis and tracheitis.
Perfectil - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a complex of vitamins for the treatment of hypovitaminosis, psoriasis and hair loss.
Piaskledin 300 - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of arthrosis of joints of various localizations.
Pidotimod - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of a medicinal product for the treatment of infections and immunodeficiency.
Picamilon - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of a drug for the treatment of stroke, encephalopathy and alcohol intoxication.
Pikovit - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medications for the treatment of vitamin deficiency (vitaminosis and hypovitaminosis).
Pikogam - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medications for the treatment of ischemic strokes, neurasthenia, depression, migraines, encephalopathy, alcoholism.
Picoprep - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a laxative drug for preparation for diagnostics and intestinal operations.
Pilobact - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medication for the treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers.
Pilocarpine - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of primary and secondary glaucoma.
Pimafukort - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of dermatoses complicated by candidiasis or thrush.
Pimafucin - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of candidiasis (thrush), vaginitis, as well as fungal diseases of the skin and mucous membranes.
Pinosol - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of the common cold.
Pyobacteriophage - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of infections caused by bacteria sensitive to it.
Pyolysin - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medications for the treatment of burns, pimples or acne, eczema.
Pipem - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis and prostatitis.
Piperazine - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of ascariasis, enterobiasis and other worms.
Pipofezin - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of a drug for the treatment of anxiety, depression and neurasthenia.
Pyrantel - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of worms (ascariasis, enterobiasis and other pathogens).
Piracetam - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of vascular disorders, Alzheimer's disease, epilepsy and blood pressure.
Pyridoxine - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of a medicinal product for the treatment of hypovitaminosis (vitamin B6 deficiency).
Pyrogenal - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of adhesions, uveitis and chronic prostatitis.
Piroxicam - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of gout, arthritis and before planning pregnancy and IVF.
Pitavastatin - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia or reducing high blood cholesterol and hyperglyceridemia.
Plavix - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment and prevention of thrombosis and thromboembolism in patients with heart attack and angina.
Plagril - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the prevention of myocardial infarction, stroke, thrombosis and thromboembolism.
Plaquenil - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, systemic and discoid lupus erythematosus.
Plantex - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of a medicinal product for the treatment of constipation and intestinal spasms in children.
Platiphylline - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of spasms and colic.
Pneumo 23 - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the vaccine medicinal product for the treatment and prevention of pneumococcal infection.
Polydexa - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of otitis, rhinitis and sinusitis.
Polygynax - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medicines for the treatment of vaginitis, thrush.
Polyoxidonium - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of immunodeficiencies and related infectious diseases.
Polysorb - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medicines for treating intoxications, cleansing the body and losing weight.
Polyphepan - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medicines for the treatment of poisoning, allergies, weight loss.
Poludan - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of antiviral medicines for the treatment of influenza, colds and conjunctivitis.
Posterizan - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medications for the treatment of hemorrhoids, fissures and anal itching.
Postinor - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for emergency contraception.
Pofol - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of a drug for intravenous anesthesia and pain relief.
Pravastatin - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medications for lowering high cholesterol levels and treating hypercholesterolemia and hyperlipidemia.
Pradaxa - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medications for the treatment of thrombosis, embolism and the prevention of strokes.
Prajisan - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of a drug for the treatment of infertility, when planning pregnancy in women.
Pram - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of depression, anxiety, neuroses, fears, panic disorders.
Prevenar 13 - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the prevention of pneumococcal infection and vaccination.
Pregabalin - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of epilepsy, seizures, convulsions, neuropathic pain.
Pregnil - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of infertility, stimulation during IVF, maintaining the corpus luteum phase.
Pregnoton - instructions for the use of vitamins, analogues and reviews of the drug to prepare for pregnancy and when planning in women.
Predizin - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of coronary artery disease and the prevention of angina attacks in cardiology, tinnitus.
Prednisolone - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment of shock and urgent conditions, allergic reactions, inflammatory manifestations.
Preductal - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a medicinal product for the treatment of coronary heart disease and the prevention of angina attacks.
Prezista - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of the drug for the treatment of HIV infection.
Prelax - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of laxative medicines for the treatment of constipation.
Prestance - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of medications for the treatment of arterial hypertension and blood pressure reduction.
Prestarium - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medications for the treatment of arterial hypertension and heart failure.
Primadophilus - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of medicines for the treatment of dysbacteriosis, constipation and diarrhea.
Primafungin - instructions for use, reviews and analogues of the drug for the treatment and prevention of thrush or genital candidiasis, vulvitis and vaginitis.
Priorix - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of vaccinations for the prevention of measles, mumps and rubella.
Probifor - instructions for use, analogues and reviews of a probiotic for the treatment of diarrhea, dysbacteriosis, allergies.
Coughing is a protective physiological reflex aimed at cleansing the respiratory system. It occurs when there is irritation, inflammation or accumulation of mucus in the nasopharynx and bronchi. May be the result of a foreign body entering the nose, mouth or ear. The intensity and duration of cough depends on the degree of impact of the disease on the respiratory system.
Cough itself is not a disease, but one of its symptoms. As soon as the patient begins to recover, the severity of the symptoms weakens. Some manifestations may bother you for some time after the infection ends, then the respiratory organs return to normal.
Cough treatment is prescribed to alleviate the general course of the disease and speed up recovery. In some cases, taking cough medications can help avoid possible complications. Timely prescribed effective cough tablets will clear the upper respiratory tract and prevent bacteria from entering the lower respiratory tract.
Features of choosing tablets
First of all, it is necessary to fight the disease itself that caused the cough. To decide on the choice of cough tablets, first identify the cause of its occurrence. Not only colds cause this symptom, but also some disorders of the brain and heart, chronic diseases of the respiratory system.
The list of diseases for which cough may be a symptom is quite large:
- Viral infections (ARVI):
Upper respiratory tract (laryngitis, pharyngitis, tracheitis, tonsillitis)
Lower respiratory tract (bronchitis, tracheobronchitis, pneumonia, pleurisy)
- Allergic reaction.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Foreign body in the respiratory tract.
- Cancerous tumors of the respiratory system.
- Exposure to aggressive chemicals (carbon monoxide, paint, gasoline, acetone, etc.)
- Angina pectoris, congenital heart disease, heart failure.
- Interstitial lung diseases.
- Gastroesophageal reflux.
- Smoking.
- Brain disorders (Parkinson's disease, dementia).
- Taking medications to lower blood pressure.
Most often, you encounter a cough during colds. In case of a viral respiratory infection, the patient is prescribed bed rest, rest, and plenty of warm fluids. The amount of liquid should reach 2-2.5 liters per day, not counting liquid food. You can drink tea by adding herbs and honey, mineral and regular water, juices, compotes, and berry fruit drinks. A sufficient amount of fluid prevents the mucus in the respiratory tract from thickening, making it easier to cough up. It is especially important to maintain a drinking regime at high temperatures, since water losses in this case increase.
 In case of severe viral infection, it is recommended to take antiviral drugs containing interferon and other auxiliary components. In the case of a bacterial infection, broad-spectrum antibiotics are most often added to treatment. To improve the general condition, use anti-cough, runny nose, sore throat and antipyretic medications. Comprehensive treatment increases the chances of a quick recovery without complications.
In case of severe viral infection, it is recommended to take antiviral drugs containing interferon and other auxiliary components. In the case of a bacterial infection, broad-spectrum antibiotics are most often added to treatment. To improve the general condition, use anti-cough, runny nose, sore throat and antipyretic medications. Comprehensive treatment increases the chances of a quick recovery without complications.
To understand how to properly deal with a cough, determine its type - dry or wet. Suppression of the cough reflex is justified only in cases where the cough is dry and causes spasms, difficulty breathing, and pain in the chest area. Severe attacks can provoke vomiting, a feeling of suffocation, and make it difficult to fall asleep.
If sputum is released during expectoration, then the absence of a cough will lead to its excessive accumulation and worsening of the condition. In such cases, the main task of the prescribed tablets is to facilitate the discharge of discharge. Medicines thin out thick mucus and increase its quantity, stimulating the body to actively cleanse.
Anti-cough medications are available in various forms: tablets, syrups, drops, tinctures, ointments, solutions for inhalation. Adult patients are often prescribed tablets in doses according to the instructions, and children are prescribed liquid forms. For each case, the medicine is selected individually.
Important! Only a doctor can accurately diagnose and select the most effective active ingredients in the right dosage.
Depending on the type of cough, the doctor must promptly change the treatment regimen for the disease in order to maintain patency of the airways to ensure normal free breathing.
Classification of cough tablets
Pharmacy windows display an incredible number of cough medications. Not all of the existing tablets are available on the counter; the pharmacist will find the less popular ones upon request. In addition to medicines, in any store you can find mint, eucalyptus, and honey lozenges that ease breathing and cough.
When choosing tablets, it is better to rely on the prescription prescribed by your doctor. If a visit to a specialist is postponed or the prescribed drug is not available, then it is worth understanding a little about the main types of tablets and syrups. Knowing the mechanisms of action of different groups of cough medicines will help you avoid getting confused by the names and choose the best and safest drugs.
All drugs prescribed for cough can be classified into one of three main groups:
- Antitussives,
- Mucolytics,
- Expectorants.
Antitussives
This group of drugs acts on the area of the brain that is responsible for the cough reflex. The action of the reflex is reduced or blocked for a certain time until the drug is removed from the blood.
Cough suppressants are divided according to the mechanism of action on subgroups:
1. Centrally acting drugs.
They act directly on the central nervous system, that is, on the medulla oblongata. The part of the brain responsible for coughing stops sending a signal. The cause of the cough is not eliminated, but the patient stops debilitating attacks and has the opportunity to rest.
Among these drugs there are a number of substances classified as narcotic. They may have different commercial names and contain as active substance:
- codeine,
- morphine,
- demorphan,
- codipront,
- hydrocodone.
Use is limited as they can be addictive. A side effect of taking it is also depression of respiratory activity, which is usually indicated in the instructions. They are mainly used for particularly strong, barking and severe coughs due to whooping cough or pleurisy.
Important! It is prohibited to take narcotic drugs without a doctor’s prescription!
More modern centrally acting drugs are non-narcotic and do not cause addiction:
- glaucine (Bronholitin),
- oxeladine citrate (Tusuprex),
- ethylmorphine,
- dextromethorphan,
- butamirate (Sinekod, Intussin).
They can be prescribed for a long period of time for advanced influenza and other complicated forms of respiratory diseases.
2. Peripheral drugs.
They affect signal transmission from the cough center to nerve endings and smooth muscles. They have virtually no effect on the area of the brain itself, but the impulse from it does not reach the organs of the respiratory system.
Most often prescribed:
- Libexin,
- Levopront,
- Helicidin.
Less effective, but safer means than the central action group. For the treatment of uncomplicated forms of dry cough, it is better to choose tablets from this group.
There are antitussive drugs that combine several therapeutic actions. They inhibit the cough center and at the same time help the formation of sputum to make the cough moist and productive:
- Stoptussin,
- Tussin plus,
- Prothiazine.
Some combination drugs stop coughing and relieve inflammation in bronchopulmonary tissues:
- Bronholitin,
- Hexapneumin,
- Lorraine.
Mucolytic
These medications must be used to thin accumulated mucus. Mucus, which flows down the walls of the larynx and accumulates in the bronchi, tends to thicken, become dense and viscous. As a result, it sticks to the cilia of the bronchi, settles in the nasopharynx, and is difficult to expectorate. The respiratory organs, irritated by mucus, try to clear themselves and a cough begins with difficult to separate sputum. It can be painful and protracted.
Mucolytic drugs make sputum more liquid, it is easily coughed up and quickly comes off from the walls and tissues. The following groups are conventionally distinguished:
Direct acting drugs.
They destroy the binding molecules of sputum, disrupting its viscous structure and elasticity. Two subgroups of substances have the same effect, but break bonds in different chemical ways:
- Acetylcysteine (ACC, Mucomist, Mukobene, Fluimucil, Acestine),
- Trypsin, chymotrypsin, chymopsin, ribonuclease.
Indirect acting drugs (mucoregulators).
Relatively new drugs for the treatment of cough, the principle of which is to increase the amount of secretion, which provokes a more active cleansing of the respiratory tract. At the same time, the water content in sputum increases.
Mucoregulators include:
- Ambroxol (Ambrobene, Lazolvan, Ambrohexal, Halixol, Ambrolanlazolvan, Medovent, Flavamed),
- Bromhexine (Bronchostop, Bronchotil, Phlegamine, Flecoxin).
Expectorants
Reflex drugs.
They act on the walls of the stomach, causing specific irritation of the mucous membrane. A certain part of the brain is activated - the vomiting center. At the level of the reflex, the secretion of saliva and mucus in the bronchi increases, which leads to a gradual dilution of sputum. The liquid part of the mucus increases, its total amount increases, stimulating productive expectoration.
This group includes preparations based on plant extracts: licorice, marshmallow, thermopsis, ivy, plantain, primrose, thyme, thyme, anise and others.
Important! Herbal remedies should be prescribed to children with caution!
Natural bases are not always safe. In young children, the bronchi are small and have narrow openings, so an increase in the amount of mucus can lead to obstruction and other complications. In addition, plant squeezes and extracts can cause a severe attack of allergies, Quincke's edema.
Resorptive drugs.
They enter the blood from the gastrointestinal tract and are then excreted through the bronchial mucosa. The medicine comes with additional fluid, which thins the mucus. These include: sodium or potassium iodide, ammonium chloride, sodium bicarbonate (baking soda). Recently, tablets of this group are rarely prescribed.
Principles of treatment of dry cough
A dry cough is much more difficult to tolerate than a wet cough. It is a consequence of irritation and inflammation of the ENT organs when exposed to a viral or bacterial infection, aggressive and toxic chemicals, and allergens.
There are different types of dry cough:
- Periodic. It occurs against the background of a cold and does not cause much discomfort. Quickly turns into wet.
- Paroxysmal. Lasts for several minutes and has pronounced strength. There is severe tension in the pectoral muscles, pain or cramps. It is debilitating.
- "Barking". Accompanied by suffocation and difficulty breathing. In the respiratory tract you can hear wheezing, wheezing, and wheezing.
- Chronic. Occurs periodically throughout the year. Can be caused by allergies, asthma, nervous exhaustion, smoking.
With a dry cough, there is no separation of sputum, which means that dead cells and dead microorganisms are not removed. In addition, a dry cough can be painful, paroxysmal, and prolonged. It is very tiring, depriving you of strength and the opportunity to sleep and relax. In children, a hysterical cough leads to bronchospasm, causing significant difficulty breathing. Adult patients report chest pain and a feeling of heaviness when inhaling.
If you experience a debilitating dry cough, you must definitely visit a doctor to understand its causes and promptly take effective measures to treat the disease. The therapist will tell you which cough tablets are the best at the moment.
The cough itself is often blocked to relieve the patient's condition until mucus begins to be coughed up. As soon as a dry cough turns into a wet one, treatment tactics are changed and expectorants and mucolytic drugs are prescribed.
It is important to understand that substances prescribed for a wet cough will not only not be effective for a dry cough, but may worsen the situation.
Important! Use cough tablets according to the instructions inside the package!
The main drugs prescribed for dry cough are antitussives. They inhibit the functioning of the cough center or block its signals at the nervous level. This method of treatment does not act on the cause of the cough and does not cure the disease, but it significantly improves well-being.
Potent drugs for dry cough include drugs of the narcotic group of central action. Since they form a dependence and can depress breathing, non-narcotic drugs are more often prescribed, which also inhibit the cough center. They are not addictive and do not affect respiratory function.
Peripheral-acting drugs that prevent the cough signal from reaching the smooth bronchial muscles are also widespread. They are somewhat less effective, but much safer and acceptable for use in children.
Codeine.
 Codeine is a narcotic antitussive. Contraindications include childhood, pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is prohibited for patients with bronchial asthma and respiratory failure to take codeine, in these cases it will cause exacerbations. Drinking alcohol is strictly prohibited; driving a car is not recommended during therapy.
Codeine is a narcotic antitussive. Contraindications include childhood, pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is prohibited for patients with bronchial asthma and respiratory failure to take codeine, in these cases it will cause exacerbations. Drinking alcohol is strictly prohibited; driving a car is not recommended during therapy.
Important! Only a doctor can prescribe codeine!
The most popular codeine-based drug is Codelac cough tablets. Their composition additionally includes thermopsis and licorice herbs, sodium bicarbonate. These drugs provoke the production of sputum, helping to transform a dry cough into a productive one.
Butamirat.
 It is not a narcotic drug and is not addictive. Refers to centrally acting drugs. Reduces the excitability of the area of the brain responsible for coughing. It has moderate bronchodilator properties and reduces inflammation. Improves blood circulation in the respiratory organs.
It is not a narcotic drug and is not addictive. Refers to centrally acting drugs. Reduces the excitability of the area of the brain responsible for coughing. It has moderate bronchodilator properties and reduces inflammation. Improves blood circulation in the respiratory organs.
The most prescribed and effective butamirate drugs are:
- Sinekod
- Codelac Neo
- Omnitus.
Treatment is continued until a wet cough appears, but not longer than the time determined by the attending physician. Prescribed to children with whooping cough, it is safest for young children compared to other centrally acting drugs. For adults it is available in tablets.
Oxeladine.
The drug is approved for use only in the treatment of adults. Does not affect the activity of the respiratory center and does not cause addiction.
Preparations based on oxeladin are available in tablets and capsules:
- Tusuprex
- Paxeladine
Like other antitussives, it has a long list of side effects. The instructions for use warn that the drug may cause drowsiness and lethargy.
Dextromethorphan.
Included in combination anti-cold medications. Most often combined with an antipyretic (paracetamol), a vasoconstrictor and an antihistamine. As a result of taking the powder or effervescent tablets, the patient feels better: the fever subsides, swelling, runny nose and cough decrease.
Included in anti-cold medications:
- Fervex for dry cough
- Tussin plus
- Flupex
- Kaffetin Cold
- Tylenol for colds.
Libexin (Prenoxdiazine).
Refers to drugs of peripheral action. Reduces the sensitivity of the nerve fibers of the respiratory organs. Dilates the bronchi and relieves spasms, fights the inflammatory process. These effective dry cough tablets are comparable to codeine, but have significantly fewer side effects.
Stoptussin.
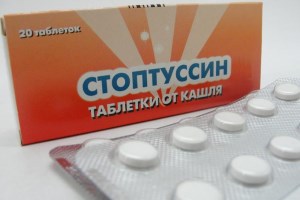 It is a successful combination of an antitussive and mucolytic. It blocks a debilitating cough due to the butamirate included in the composition, and guaifenesin provokes sputum production. After a few days of taking the tablets according to the instructions, the dry cough is replaced by a wet one.
It is a successful combination of an antitussive and mucolytic. It blocks a debilitating cough due to the butamirate included in the composition, and guaifenesin provokes sputum production. After a few days of taking the tablets according to the instructions, the dry cough is replaced by a wet one.
Wet cough therapy
A wet cough is accompanied by the release of bronchial secretions, which are called sputum. Different diseases and stages of their development may produce different amounts of sputum. The color of the discharge can range from light and transparent to dark green and purulent. The greater the viscosity and density of the sputum, the more difficult it is to expectorate, settling tightly in the bronchi and interfering with their normal functioning.
The human bronchi are lined with mobile epithelial “cilia” that trap invading bacteria and viruses. Normally, the bronchi contain a small amount of clear mucus, which binds foreign microorganisms retained by the cilia. The smooth muscles of healthy bronchi contract rhythmically, gradually removing fluid through the nasal and oral cavities. If a small amount of mucus has accumulated overnight, then in the morning you may experience a short cough, which is normal.
When a lot of sputum settles on the cilia of the bronchial tree, they stop retaining bacteria. The action of the mucociliary transport mechanism, that is, the normal removal of mucus, is disrupted. The more thick the mucus, the more tightly it covers most of the eyelashes.
The cough center reacts and a cough begins, aimed at removing phlegm. At the same time, the amount of secretion in the bronchial tree increases. Under unfavorable conditions, the mucus continues to thicken, making it more and more difficult to cough up. In children and some adults, the coughing process is further complicated by narrow airways. Under such conditions, pathogenic bacteria begin to multiply very actively and bacterial bronchitis occurs. Ultimately, a neglected wet cough can lead to the penetration of bacteria into the lungs and the development of pneumonia.
To help the body naturally remove phlegm, you need to change its properties and make it as liquid as possible. Good tablets for wet coughs will help you clear your respiratory tract more effectively and get better faster.
Antitussive drugs that inhibit the reactions of the cough center and suppress its signal are not used in the treatment of wet cough. This is due to the fact that the absence of a cough will lead to the accumulation of a large amount of sputum in the bronchi, which can cause obstruction and an increase in the number of bacteria.
Important! Taking antitussive medications for a wet cough can be dangerous!
In the treatment of wet cough, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Mucolytic
- Expectorants
- Combined.
Action of mucolytics.
Mucolytics act on the upper thick layer of sputum, which is called the “gel.” They destroy the bonds between molecules, which leads to liquefaction of the upper layer of secretion. The result is easy and effective coughing. The total amount of mucus practically does not increase.
Based on their chemical composition, mucolytics are divided into non-enzymatic and proteolytic enzymes. I often use non-enzyme drugs, as they have fewer side effects and are well tolerated by patients.
Acetylcysteine.
 Among the non-enzymatic mucolytics, the substance acetylcestin is distinguished, which has high proven effectiveness. Medicines have been created on its basis under the trade names:
Among the non-enzymatic mucolytics, the substance acetylcestin is distinguished, which has high proven effectiveness. Medicines have been created on its basis under the trade names:
- Mukobene
- Mucomist
- Fluimucil
- Mukonex
- VicksActive ExpectoMed.
The principle of its action is to destroy the bonds of certain components of sputum - mucopolysaccharides. At the same time, the mucus loses its density and viscosity. Effervescent cough tablets ACC act faster than coated tablets.
The use of acetylcysteine has several features:
- When bronchospasm intensifies, obstruction may develop, so taking a mucolytic is combined with drugs that expand the lumen of the bronchi. Important! In the treatment of cough in children, acetylcysteine is used with caution, since children are more prone to developing bronchial obstruction.
- Drugs in this group reduce the absorption of antibiotics. It is important to maintain a sufficient interval between doses or choose tablets from a different group.
- Long-term use (more than 10 days) provokes a decrease in local immunity.
Carbocysteine.
It acts similarly to acetylcysteine, but is considered a safer drug, since it does not provoke bronchospasm and does not affect one’s own immunity.
Produced under the names:
- Bronchobos
- Mukodil
- Mucopront
- Mucosol
- Libexin Muco
- Fluditek.
Ambroxol.
 It occupies a separate place in the group of mucolytics, as it is somewhat different in its principle of action.
It occupies a separate place in the group of mucolytics, as it is somewhat different in its principle of action.
It thins mucus by increasing the substance that coats the alveoli and prevents them from sticking together (surfactant). In this case, the amount of sputum does not change, but it becomes less thick. In addition, ambroxol stimulates the work of the bronchial epithelium, activating the movement of cilia. Coughing becomes active and productive.
Produced under the following brands:
- Lazolvan
- Ambrobene
- Ambrohexal
- Ambroxol
- Bronchoxol
- Flavamed
- Halixol
Preparations based on ambroxol have a number of advantages:
- These are the most effective remedies for wet coughs if antibiotics are taken at the same time.
- Combines well with other drugs for wet cough.
- They are produced and used in various forms: tablets, syrups, solutions for inhalation).
- They are safe, well tolerated and have minimal side effects.
Use of expectorants.
Expectorant drugs are conventionally divided into means of reflex action and resorptive action.
Plant-based expectorants are most widely represented on the pharmaceutical market and are very popular. They are mainly produced in liquid forms (drops, syrups).
Ivy leaf extract.
This universal herbal remedy is prescribed for any type of cough. Provide effective softening and removal of sputum thanks to natural saponins in the composition.
Included in drugs called:
- Gedelix
- overslept
- Gelisal.
Contraindicated in pregnant and lactating women with bronchial asthma. Not prescribed for children under two years of age, as it may cause laryngospasm.
Primrose and thyme extract.
It not only has an expectorant effect, but also relieves inflammation and fights the proliferation of pathogenic flora. Improves blood circulation.
Included in the preparations:
- Gerbion
- Bronchicum
- Bronchipret.
Not prescribed for bronchial asthma, after suffering from croup, or with a tendency to allergic reactions.
Marshmallow root extract.
Used for the complex treatment of unproductive wet cough for adults and children over one year of age. May cause increased dry cough and allergic reactions
Preparations based on marshmallow root:
- Marshmallow syrup
- Marshmallow syrup
- Marshmallow syrup
- Mukaltin.
Mucaltin is available in tablet form - a proven and inexpensive cough remedy. The tablets are convenient to take with you to work or on the road.
Eucalyptus.
In addition to the expectorant effect, it soothes sore throats and makes breathing easier.
Eucalyptus is used to prepare a variety of lollipops and cough lozenges, which can be found not only in pharmacies, but also in regular supermarkets. Inexpensive eucalyptus lozenges are called:
- Pectusin
- Evamenol.
Complex compositions.
One of the most popular and inexpensive cough tablets is Travisil. They contain a complex of more than 10 herbs and plant extracts. Lozenges are available in various flavors.
Combined drugs.
They combine drugs from different groups, providing several therapeutic effects in the fight against cough.
For example, Codelac Broncho cough tablets contain ambroxol, sodium glycyrrhizinate and thermopsis. Ambroxol and thermopsis thin and remove phlegm, and sodium glycyrrhizinate has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. There is another version of the drug with thyme instead of thermopsis (Codelac Broncho thyme).
The previously popular tablets, which are called “Cough Tablets,” combine an expectorant of plant origin (thermopsis) and a resorptive (soda). These are inexpensive and effective cough tablets, but they often cause unpleasant reactions from the gastrointestinal tract, therefore they are contraindicated in children under 12 years of age, pregnant women and people with diseases of the digestive system.
 If the disease is accompanied by bronchospasm, then in addition to affecting the consistency of sputum, it is necessary to expand the bronchial lumen to ensure easy drainage of secretions. In such cases, combination drugs based on bromhexine are used, including the bronchodilator salbutamol:
If the disease is accompanied by bronchospasm, then in addition to affecting the consistency of sputum, it is necessary to expand the bronchial lumen to ensure easy drainage of secretions. In such cases, combination drugs based on bromhexine are used, including the bronchodilator salbutamol:
- Joset
- Ascoril.
Important! Bronchodilator drugs are used in specific cases according to the doctor’s instructions. Self-medication is unacceptable.
Cough is a common symptom that goes away along with the disease. Pharmacological companies offer a wide selection of products to relieve coughs, remove phlegm, get rid of attacks and prevent complications. In order not to harm yourself, you need to carefully choose cough tablets, follow the instructions and do not neglect visiting a doctor.
PANANGIN
PANGEXAVIT (Panhexavitum)
PANGROL 400 (Pangrolum 400)
PANZINORM FORTE (Panzinorm forte)
PANCREATIN (Pancreatinum)
Pankreoflat
Pancurmen
PANSTAlum
PANTHENOL
PANTOCRIN (Pantocrinum)
PANTOCID (Pantocidum)
PANTRYPIN (Pantrypinum)
PAPAVERINA HYDROCHLORIDE (Papaverini hidrochloriduin)
PAPAZOL (Papazohim)
PARA PLUS (Para plus)
PARATHYROIDIN (Parathyreoidinum)
PARACETAMOL (Paracetamolum)
PARMIDINA (Parmidinum)
PAROMOMYCIN (Paromomycin)
PARTUSISTEN
PASOMYCIN (Pasomyciniun)
GRAMICIDIN PASTE (Pasta gramicidini)
SHEPHERD'S BURSA GRASS (Herba Bursae pastoris)
Paphencylum (Paphencylum)
Pedilin
PELIOIDODISTILLATE (PeloidodistiUatum)
PENAMECILLIN (Penamecillin)
PENBUTOLOL (Penbutolol)
PENICILLINASE (PeniciHinasum)
PENTAGASTRI N (Pentagastrinum)
PENTAZOCINUM (Pentazocinum)
PENTAMIN (Pentaminum)
PENTACIN (Pen (acinum)
PENTOVIT (PenUvitnra)
PENTOXYL (Pentoxylum)
PENTOXYFYLLINE (Pentoxyphyllin)
PEPONEN (Reropep)
PEPSIDIL (Pepsidilum)
PEPSIN (Pepsinum)
PERGOGREEN (Pergogreen)
PERGONAL
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE SOLUTION (Solutio Hydrogen peroxydi diluta)
HYDROGEN PEROXIDE CONCENTRATED SOLUTION (Solutio Hydrogen peroxydi concentrate)
PERIACTIN
PERCASALAN (Percasaladum)
PERLINGANITE
PERMETHRIN
PERNEXIN ELIXIR (Pernexin elixir)
PERSALAN (Persalanum)
PERTUSSIN (Pertussinum)
PERFILLON (PerphyUon)
WATER PEPPER (Herba Polygon hydropiperis)
Capsicum tincture (Tincture capsici)
PEPPER FRUIT (Fructus Capsici)
PEFLOXACIN (Pefloxacinum)
Tansy FLOWERS (Flores Tanaceti)
Pilosuryl
Pinabinum
PINDOLOL (Pindololum)
PIPEMIDIC ACID
PIPERAZINE ADICINATE (Piperazini adipinas)
PIPERACILLIN
PYRAZINAMIDE (Pirazinamidum)
PYRANTEL
PYracetamum
Pyrvinii pamoas
PIRENZEPIN (Pirenzepine)
PIRETANIDE
PYRIDOXALPHOSPHATE (Pyridoxalphosphatum)
PYRIDOXINE HYDROCHLORIDE (Pyridoxini hydrochloridum)
PYRIMETHAMINE
PYROGENAL (Pyrogenalum)
Pyroxicam
Pyromecainum
PIRROXANE (Rugtohap)
PITUITRIN (Pituitrinum)
PLASMOL (Plasmolum)
Plaquenil
PLANTAGLUCID (Plantaglucidum)
PLANTEX
PEPPER PLASTIC (Emplastrum Capsici)
SIMPLE LEAD PLASTIC (Emplastrum Plumbi simplex)
LEAD PLASTIC COMPLEX (Emplastmm Plumbi compositum)
PLATINUM
PLACENTA SUSPENSION (Suspensio placentae)
PLACENTA EXTRACT (Extractum placentae)
Plenyl
COLLAGEN FILM (Membrana coDagenica)
FIBRIN ISOGENIC FILM (Membrana fibrinosa isogena)
EYE FILMS WITH SULFAPYRIDAZINE-SODIUM (Membranulae opKthalmice cum Sulfapyridazino-natrio)
FILMS WITH ANABAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE (Membranulae cum Anabasino hydrochloridi)
FILMS WITH CYTIZINE (Membranulae cum Cytisino)
Plivalgin
LARGE LEAF PLANTAIN (Folia Plantaginis majoris)
PLANTAIN JUICE (Succus Plantaginis majoris)
PODOPHYLLIN (Podophyllinum)
COVERED (Tabulettae "Propolinum" obductae)
POLYAMIN (Polyaminum)
POLYBIOLIN (Polybiollnum)
POLYBION N (PoUblon N)
POLYVIT BABY (Polyvit b"by)
POLYVIT GERIATRLC (Polyvit geriatrlk)
POLYGLUCIN (Polyglucnum)
POLYGYNAX
POLYMYXIN "B" SULPHATE (Polyjnyxini "B" sulfas)
POLYMYXIN-M SULPHATE (Potymyxini - M sulfas)
POLYMINEROL
POLYUNIN (Polysponinum)
POLYPHEPAN (Polyphepanum)
POLYPHER (Polyphemm)
POLYESTRADIOL PHOSPHATE
POLUDAN (Poludanum)
MORGUM BITTER HERB (Herba Absinthii)
WORMWORM CITVA FLOWER (Flores Cinae)
POLKORTOLON TS (Polcortolon TS)
PONDERAL
COMPOSITE MALT ROOT POWDER (Pulvis Glycyrrhizae compositus)
POSTERIZAN
POSTERIZAN FORTE
POSTINOR
POTESEPTIL (Poteseptil)
POTESETGA (Potesetta)
PRAVASTATIN (Pravastatinum)
PRAZIQUANTEL
PRAZOSIN (Prazosinum)
PRAMILET FA
PRAMOXIN
PRDVDNIZOLONE (Prednisolonum)
PREGNAVIT (Pregnavit)
PREGNIN (Praegninum)
PREGESTROL (Praegoestrolum)
PREDNISOLONE GEMISUCCINATE (Phednisolon gemisuccinas)
PREDNISOLONE OINTMENT 0.5% (Unguentum Prednisoloni 0.5%)

