Elevated hormone progesterone in women. Lack of progesterone in women: symptoms

Progesterone is a steroid hormone that is produced by the corpus luteum of the ovaries, adrenal glands and placenta during pregnancy. Its level varies depending on the phase menstrual cycle. Insufficient or excessive production of the hormone leads to infertility, miscarriage, and the development of diseases reproductive system.
In addition, prolactin enlarges the mammary glands of the expectant mother, and the production of postpartum milk begins. When there are too many of them: they begin to hurt the breasts - they are swollen and sensitive to the touch. Fun becomes irregular, very scarce, and over time it may disappear completely. Excess prolactin can also cause infertility. High concentration This hormone is usually the result of high stress or.
- It appears when a woman is not pregnant at all.
- In addition, excess prolactin leads to various cycle disorders.
- It appears that relationships become painful.
If progesterone in the blood is significantly increased, a woman’s health worsens, she becomes irritable, gets tired quickly, and suffers from headaches.
The sex hormone is responsible for preparing the inner layer of the uterus for consolidation ovum and gestation. Progesterone levels increase during formation corpus luteum in the ovary and reaches peak values at the time of ovulation. If pregnancy does not occur, its concentration decreases, after which menstruation begins.
If you have noticed any signs of excess or deficiency in your hormones or have been trying to get pregnant for a long time without success, you should consult an endocrinologist. The concentration of hormones is determined by a blood test. But for correct result the study does not matter at what point in the cycle you are at the time of blood collection. This is even a good time to get tested because hormone levels change throughout the day. Your doctor should tell you at what point you should investigate.
Thyroid hormones make you beautiful
Triododotronin speeds up metabolism, allowing you to quickly burn excess calories, which leads to a thin figure. Thyroxine is an excellent skin ally. Saves it in good condition, affects its nutrition and proper hydration. Thanks to this hormone, the skin is dense and firm. In addition, women with normal thyroxine levels can boast shiny hair and a smooth face without breakouts.

When conception occurs, the corpus luteum functions for another 16 weeks, after which the hormone is produced by the placenta. Progesterone suppresses a woman’s immune system so that the body does not reject the embryo. Under the influence of the steroid, the mammary glands enlarge and lactation is ensured.
Progesterone levels and norms during pregnancy
Calcitonin takes care of bones - it maintains calcium at the correct level, protecting against osteoporosis. This most often manifests itself as rapid weight loss, hyperactivity and excessive sweating. Blood pressure the heart rate rises and palpitations occur. Sometimes menstruation may disappear.
- The disease manifests itself in weight gain and a feeling of chronic fatigue.
- To do this, the signs give you mood swings.
- There is also a swollen, continuous cold sensation.
Another task of the sex hormone is normal functioning mammary glands. With an imbalance of estrogens, gestagens and testosterone, mastopathy develops, the menstrual cycle and reproductive ability are disrupted.
In addition to participating in the conception and bearing of a child, progesterone performs the following work:
Moreover, many times its proper concentration depends on its correct course. It is worth noting that this hormone is important throughout pregnancy. It is not surprising that women expecting to care for their children regularly check their levels. Among the most important functions This hormone includes, among other things, inhibition of labor by reducing uterine contractions. In addition, it effectively stimulates the mucous membranes reproductive organs highlight the necessary nutrients. When it comes to negative effects progesterone, it is worth mentioning here the greater tendency to edema and varicose veins veins
- reduces blood viscosity;
- normalizes blood glucose levels;
- prevents the formation of fibrous cysts in the glands;
- stabilizes blood pressure;
- regulates lipid metabolism.
A decrease and increase in progesterone affects a woman’s well-being in menopause, on the intensity of the manifestation of premenstrual symptoms.
This hormone also affects the lactation process by stimulating mammary glands. Sometimes the amount of progesterone drops sharply after childbirth. In such a situation, a woman often has to deal with the so-called postpartum depression. Women who have recently given birth often complain of mood swings. This is usually due to insufficient concentration of this hormone. As you can see, progesterone affects not only the functioning of our internal organs, but also on our psyche, contributing to mood disorders.
In our era, accurate hormone testing is possible. It is worth checking your health at regular intervals, especially if you are expecting a baby. In this case, progesterone is important for our body, which directly affects the normal course of pregnancy. It is important to note that during the weeks of pregnancy, appropriate standards for progesterone levels are established.

Progesterone norm
The level of the hormone depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle and the woman’s age. For a healthy, non-pregnant girl, the following values are considered normal:
Normal values steroid hormone in pregnant women:
With progesterone deficiency, a shortened luteal phase or an abnormal increase in temperature is noticeable. Progesterone levels should be monitored several days in a row, as the concentration of this hormone fluctuates significantly throughout the day. Norms and normal level progesterone.
Water retention in the body, decreased libido, decreased white blood cell activity, which leads to excessive bloating and gas, depression. Publications related to the progesterone slogan. Vitamins and minerals that support disease prevention and treatment.
In girls, before the onset of menstruation, the concentration of gestagen in the blood is low, and in puberty begins to rapidly increase and become cyclical. In women during pregnancy, girls taking oral contraceptives(Utrozhestan, Iprozhin), antitumor drugs, the level of progesterone in the blood will be significantly increased. Minimum levels are observed with the onset of menopause and the decline of reproductive function.
Hormones are microscopic particles that literally control our body. The correct course of the process of puberty, fertilization and, finally, reporting of pregnancy depend on them. How can disturbances in their secretion affect? Women who have hormonal disorders, are more likely to experience problems with conception and have a higher risk of miscarriage after conception. The problem of hormonal balance is complex and the cause may be related to dysfunction of various organs.
The luteal phase is the second half of the menstrual cycle, the period between ovulation and menstruation. This contributes improper preparation uterus to receive a fertilized egg. It is believed that most luteal phase problems are actually caused by disturbances in the follicular phase, that is, the period before ovulation.

Changes in progesterone levels by day of the cycle
An increase in the steroid hormone in the blood is observed with the approach of ovulation, the maximum values are recorded in the second half of the menstrual cycle. On the last day, the level drops sharply and menstruation begins, if conception has not occurred. If the egg is fertilized, the concentration of the hormone continues to increase.
Watch the video: “Pregnancy vitamins”
The problem may also be present in the decreased sensitivity of the ovaries to this hormone. As a result, insufficient development of ovarian follicles can lead to too little progesterone production by the corpus luteum, which prepares the uterus to fertilize embryos.
Another type of luteal phase defect can be caused by excessive levels of luteinizing hormone at early stages menstrual cycle or due to a violation of the peak moment of secretion of this hormone, which is necessary for normal ovulation. It is a steroid hormone that is necessary for fertilization and correct flow pregnancy. The name progesterone comes from the Greek gestara, meaning “to carry,” and suggests a role for this compound in supporting proper embryonic development. This female hormone secreted by the corpus luteum after the ovulation process.
How do progesterone levels change during the menstrual cycle?
| Day | Progesterone norm, pmol/l |
| 1–5 | 0,3–2,2 |
| 6–8 | 0,35–4,4 |
| 9–13 | 0,4–4,8 |
| 14–16 | 0,49–9,4 |
| 16–18 | 0,5–9,6 |
| 19–21 | 7,0–56,9 |
| 22–23 | 7,0–56,9 |
| 24–28 | 7,0–56,9 |
Small amounts of progesterone are also produced by the adrenal glands. This hormone promotes the production of other steroid hormones such as estrogen, cortisol and testosterone. Progesterone plays important role in regulating the menstrual cycle and preparing the uterus for embryo implantation and pregnancy.
The main function of progesterone is as a preparation, that is, the membrane of the uterine mucosa, for the implantation of a fertilized egg. Progesterone enhances and stimulates the growth of the endometrium, which is the basis for the growing fetus. After ovulation and in the first trimester of pregnancy, progesterone is produced by the ovary, more specifically the corpus luteum, a remnant of the ovarian fissure. Once the embryo is implanted, the placenta develops over time and hormonal production begins to increase so as not to interfere with the developing embryo.
Reasons for increased progesterone
High levels of steroid hormone may indicate the following pathologies:
- oncological hormone-producing tumors of the adrenal glands, ovaries;
- amenorrhea;
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding;
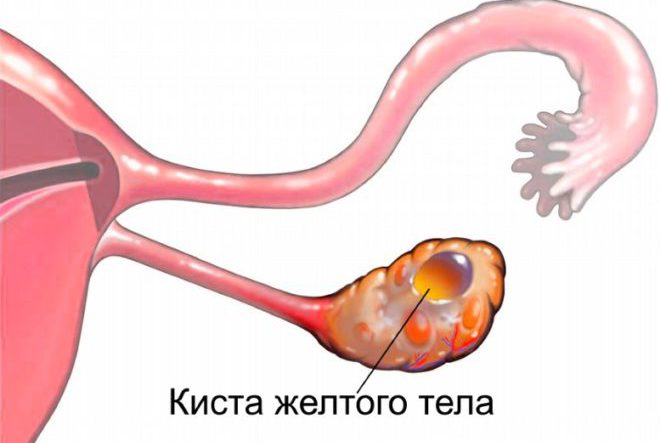
- luteal ovarian cyst;
- taking progesterone medications;
- hydatidiform mole;
- pathological processes during the formation of the placenta;
- renal failure;
- congenital anomalies of the ovaries, adrenal glands;
- pregnancy.
Elevated levels of progesterone can be observed when the hormone is insufficiently absorbed by tissues. Pathology occurs when there is a deficiency of certain enzymes in the body, dysfunction of steroid receptors. In such cases, hyperprogesteronemia has no effect negative influence on the functioning of the reproductive organs or they experience a lack of the hormone when it is sufficiently produced.
If progesterone production is insufficient, exfoliation of the uterine lining and menstrual bleeding may occur. Given the role of progesterone in maintaining normal uterine linings, it appears that it low level may be associated with miscarriage. However, whether progesterone use prevents pregnancy remains controversial. Currently none medical organization does not recommend the addition of progesterone in women with recurrent miscarriage and luteal phase disorders.
The exception is women using assisted reproduction methods such as progesterone readings. None Scientific research did not show that progesterone administration prevented miscarriage in women who did not use assisted reproduction methods. However, there are anecdotal reports that progesterone may be beneficial for women who have had recurrent miscarriages. However, the data are currently too small to determine whether these findings are significant, and further research in this area is needed.

Diseases of the urinary system can cause an increase in progesterone secretion. Toxins formed during biochemical reactions are not completely eliminated from the body and affect the functioning of other organs and hormonal balance.
Low progesterone levels are undoubtedly associated with miscarriage, but the reasons for this phenomenon are poorly known and controversial. On the one hand, insufficient hormone levels can contribute to miscarriage if the uterus has not been properly prepared and the lining transformed to support the pregnancy. This may be due to too low production of progesterone by the ovaries in the second phase of the ovulation cycle. On the other hand, many doctors argue that the problem is more complex. In this model, low progesterone is only the first symptom of an abortion, which is dismissed for other reasons, such as genetic disorders in the developing embryo.
If the regulation of the menstrual cycle by the hypothalamic-pituitary system is disturbed, the level of steroid hormone in the blood may increase. To confirm the diagnosis, excess progesterone must be recorded in all phases of the ovulatory cycle, additional examinations and analyses.
Symptoms of hyperprogesteronemia
In some cases, women do not notice a deterioration in their health. If high level If the steroid hormone is fixed during pregnancy, expectant mothers complain of weakness, nausea, drowsiness, dizziness, and pain in the lower abdomen.
Therefore, adding progesterone is pointless. It is definitely not determined which of these two versions is correct, and these questions remain a hot topic. Suspecting a connection between a miscarriage and the secretion of progesterone, this hormone concentration is checked in the second phase of the menstrual cycle. The diagnostic tool is also microscopic examination mucous membrane of the uterus for the occurrence of disturbances in endometrial receptivity.
Researchers' interest is also focused on other sex hormones - androgens. A connection is suspected between abnormal androgen levels and the risk of recurrent miscarriage. It has been reported that elevated androgen levels in early follicular phase or follicular maturation may predict miscarriage.
Other symptoms increased progesterone among women:
- frequent mood swings, nervousness, depression;
- acne;
- increased body hair growth;
- low blood pressure;
- migraine;
- blurred vision;
- allergic reactions: itchy skin, rashes, erythema;
- fast fatiguability;

Hypothyroidism and abortion
If you are looking hormonal reasons miscarriage, you also need to get closer to thyroid gland- an organ located in the neck, apparently, has little to do with fertility. However, this gland plays a very important role in metabolic and hormonal balance the entire system. When this gets worse, the effects can affect every element of the body and therefore fertility.
This may be associated with certain types of pregnancy loss, but the exact nature of this relationship is still being studied. Both of these conditions can lead to pregnancy and baby loss. In the case, it is less clear about the effect of hypothyroidism on miscarriage. It is suspected that autoimmune processes associated with thyroid gland, but opinions about their effect on the miscarriage process are divided.
- menstrual irregularities;
- swelling, pain in the mammary glands;
- increased sweating;
- weight gain;
- increased libido;
- fragility, hair loss;
- flatulence, constipation;
- vaginal dryness;
- swelling of the face;
- infertility, miscarriages early stages pregnancy.

An increase in progesterone levels leads to a decrease in immunity, a woman is more susceptible to sexually transmitted infections, viral diseases. Inflammatory diseases often develop into chronic form, the vaginal microflora changes, they die beneficial lactobacilli, the mucous membranes are colonized by fungi.
A disturbance in the proliferation of the endometrium of the uterus, caused by an increase in the production of progesterone, a change in the number of hormonal receptors, can lead to the formation of benign nodes in the uterus (fibroids), cysts, malignant tumors, endometriosis.
Increasing progestin levels promotes muscle relaxation digestive tract. As a result, the woman eats more food and rapidly gains weight. Obesity is also caused by impaired lipid metabolism, slowing down the breakdown of fats and the release of energy.
If elevated levels of progesterone are diagnosed in pregnant women, aging and placental abruption develop. In some cases, this is a symptom of multiple births.

How to lower progesterone levels
To determine the concentration of steroid hormone, women take venous blood for analysis. First of all, pregnancy, which increases progesterone, is excluded. To identify the cause of the violation hormonal levels do ultrasound, CT abdominal cavity, studies for tumor markers, ELISA and PCR diagnostics. Patients must be examined by a gynecologist or endocrinologist.
With a slight increase in progesterone levels, women are advised to follow a diet that limits the consumption of protein foods. It is necessary to avoid stress, overwork, healthy image life, give up bad habits. You should follow a sleep-wake schedule; night rest should be complete and last at least 6–8 hours.
Treatment of hyperprogesteronemia begins with eliminating the main cause of the pathology. Drug therapy or surgery helps normalize hormone levels and get rid of symptoms of illness.
To correct hormonal levels, combined oral contraceptives are most often prescribed:
- Anteovin;
- Yarina;
- Diana is 35.

These drugs contain gestagens and estrogens, which suppress the production of progesterone at the level of hypothalamic-pituitary regulation.
Progesterone inhibitors Postinor, Epostan, Mirolyut are also used for treatment. Medicines are selected individually for each woman. You should not take pills on your own, this can lead to the development side effects. Therapy is also contraindicated during pregnancy.
If cysts of the corpus luteum, malignant tumors of the reproductive system, kidneys are detected, surgical removal neoplasms, chemotherapy. If adrenal pathology is diagnosed, treatment with glucocorticoids and antibiotics is prescribed.

Complications of hyperprogesteronemia
If the pathology is not treated long time, the following complications develop:
- corpus luteum cyst;
- tumors of the adrenal glands, ovaries;
- renal failure;
- infertility;
- endometriosis;
- uterine fibroids;
- false pregnancy;
- increased levels of progesterone cause menstrual irregularities, amenorrhea;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- obesity.
To prevent the development of complications, it is necessary to consult a doctor in a timely manner. Normalizing progesterone levels will help avoid the formation of tumors and cysts, eliminate symptoms of illness, and restore reproductive function.
Treatment with folk remedies
In addition to drug therapy can be used folk recipes. Rowan berry decoction helps normalize hormonal levels and reduce progesterone production. One tablespoon of berries is poured into 0.250 ml of boiling water and left for 2 hours. Then the composition is filtered and drunk 1/3 glass 2 times a day after meals. The duration of treatment is discussed with the doctor.
Helps normalize hormonal levels, reduce higher level progesterone decoction of hogweed, red brush, carnation flowers, wild carrots and large plantain seeds. Herbs are brewed separately or made into mixtures, adding components in equal quantities.
The treatment regimen should be prescribed by a doctor, since some folk remedies taken in the first half of the menstrual cycle, while others drink before the onset of menstruation. The duration of therapy is individual for each woman.
During treatment, you need to regularly take a blood test to check your progesterone level. Laboratory monitoring allows you to evaluate the effectiveness medicines, adjust the dosage of medications taken, if necessary.
There are no similar entries.
In order to lower progesterone, you first need to understand what it is. Perhaps this name doesn’t mean anything to you, but any gynecologist will popularly explain that, in fact, progesterone is the most important hormone for women, because it is responsible for fertilization and the successful bearing of a baby. The term itself goes back to Latin and is translated as “to wear, to bear.”
In short, progesterone is needed to prepare the uterine mucosa for possible pregnancy. After the fertilized egg has successfully settled in the uterus, the body understands that it is necessary to produce this hormone quickly and in large quantities.
How to lower progesterone?
U physically healthy woman the level of the hormone must be normal, since both deficiency and excess lead to quite unpleasant consequences. For example, if progesterone levels are low, this can lead to early miscarriage. Excess progesterone also does not have the best effect on a woman: she feels persistent fatigue, gets tired quickly, and complains of dizziness and pain. General state in this case it can be designated as depressive. If you have had your blood tested and found out that your hormone levels are elevated, you should focus your efforts on lowering progesterone. How to do this? 
Instructions for use
1. First of all, you need to remember that treatment can be carried out in many ways. Perhaps the most popular and reliable method is medications. However, do not forget that using them without specialist supervision is strictly prohibited! You can take pills only as prescribed by your doctor. If for some reason you cannot go to the hospital, but want to start treatment as quickly as possible, turn to traditional medicine. In order to lower progesterone, you can use a tincture of red rowan flowers. It is very simple to prepare: pour one tablespoon of the plant with one glass of boiling water and brew as regular tea. After an hour, strain the broth through cheesecloth. Drink 1/3 glass per day (it is best to do this after meals). If you cannot get rowan flowers, you can take berries. The difference is that they must first be boiled over low heat.
 2. In case there is a deficiency the right hormone affects your skin (for example, you suffer from pustules), then you can use cloves (flowers, buds or leaves) for treatment. Brew a couple of teaspoons of the dried plant and drink a tablespoon four to five times a day. The ideal option is a tincture, but if you don’t have it, a garden tincture will do.
2. In case there is a deficiency the right hormone affects your skin (for example, you suffer from pustules), then you can use cloves (flowers, buds or leaves) for treatment. Brew a couple of teaspoons of the dried plant and drink a tablespoon four to five times a day. The ideal option is a tincture, but if you don’t have it, a garden tincture will do.
3. If you have donated blood for progesterone and realized that your hormone levels are elevated, wild carrot seeds will help you - they prevent the production of progesterone in the body. In what form should the drug be taken? Thoroughly grind three to four tablespoons of seeds and pour big amount hot water. Infuse all this for twelve hours, after which drink one glass three times a day.
Don't forget, however, that ethnoscience cannot become adequate replacement full treatment. Be sure to visit an endocrinologist and gynecologist, then you can continue to drink herbs, combining them with the prescribed tablets.

