How to increase the release of growth hormone. Human growth hormone is considered a "key" hormone
Pharmacological group: Analog growth hormone; Recombinant somatotropic hormone.
Pharmacological action: Recombinant growth hormone, identical in composition and effects pituitary hormone human growth. Stimulates skeletal growth and weight gain; stimulates the transport of amino acids into the cell, accelerating intracellular protein synthesis and thereby manifesting anabolic effect. Causes nitrogen retention in the body, mineral salts(calcium, phosphorus, sodium) and liquid. Increases blood glucose levels.
Effect on receptors: Growth hormone receptor; epidermal growth factor receptor.
Description
As the name suggests, human hormone growth hormone (HGH) is important mediator human growth process. This hormone is endogenously produced by the anterior pituitary gland, and is present at particularly high levels in the child’s body. The growth stimulating effects of HGH are very broad and can be divided into three individual areas: bones, skeletal muscles and internal organs. The hormone also supports protein, carbohydrate, lipid and mineral exchanges, and can also stimulate the growth of connective tissue. Although human growth hormone has vital important V early period human life, it is also produced in the human body throughout adult life. Levels and biological role growth hormone levels decrease with age, but the hormone continues to support metabolism, growth and maintenance muscle tissue and reduce body fat levels throughout life. Somatropin is a pharmaceutical human growth hormone that was synthesized using recombinant DNA technology. Somatropin (recombinant human growth hormone, rhGH) is biologically equivalent to human growth hormone (hGH) of pituitary origin.
Somatropin is a synthetic form of human growth hormone (hGH). In reality, it is a variable endogenous hGH protein containing the same 191 sequence but with the addition of an additional |amino acid]]. For this reason, Somatropin is commonly called methionine human growth hormone. Somatropin is considered the therapeutic equivalent of pituitary-derived growth hormone. As an HGH drug, Somatropin is valued by bodybuilders and athletes for its ability to promote fat loss and the growth of muscle and connective tissue. Although Somatropin is considered the equivalent of human growth hormone, it is not a naturally occurring protein in the human body. During treatment, the likelihood of developing antibodies to growth hormone may increase.
Antibodies bind to the growth hormone molecule, interfering with its ability to bind to receptors and exhibit its activity. In one of clinical trials, two out of three children who received Somatropin for one year had antibodies to growth hormone in their bodies. In a similar study of the use of Somatropin for one year, only 1 out of 7 patients had serum antibodies to growth hormone. It is important to note that in both studies, the antibody responses were not particularly strong and did not appear to significantly reduce the therapeutic efficacy of the drugs. A decrease in activity was observed in a very small number (less than 1%) of patients taking Somatropin.
IN medical purposes growth hormone is used to treat a number of various diseases, first of all, pituitary dwarfism (dwarfism), a disease in which linear growth is inhibited due to insufficient endogenous production of growth hormone. The drug is often given to patients childhood, and although it is not able to completely correct the defect, it can significantly increase linear growth before it stops in adolescence. Somatropin is also widely used in cases of growth hormone deficiency in adulthood, usually associated with pituitary cancer or its treatment. It may also be prescribed healthy people, concerned about the problem of aging. Somatropin maintains the level of growth hormone in the body close to the period of youth, which explains the rejuvenating effect of the drug. Although this use is not supported with medical point vision, the use of somatotropin for this purpose is very popular in North America, South America and Europe. In addition, somatropin is used to combat loss muscle mass associated with HIV infections or other diseases, and may be prescribed to treat a number of other painful conditions, including burns, short bowel syndrome and Prader-Willi syndrome.
Somatropin injections can be administered both subcutaneously and intramuscularly. During clinical studies, the pharmacokinetic properties of somatotropin were determined for both methods of use. At subcutaneous injections somatotropin has a similar, but moderately more high level bioavailability (75% vs. 63%).
The metabolic rates of the drug were also very similar for both methods of administration, and its half-life was about 3.8 hours after subcutaneous administration and 4.9 hours after intramuscular injection. A basic level of hormones are usually achieved between 12 and 18 hours after injection, slower when administered intramuscularly. However, given the delayed rise in IGF-1 levels, which may remain elevated for 24 hours after GH injection, the metabolic activity of human growth hormone will exceed its actual level in the body. Although absorption of the drug is acceptable with both routes of use, daily subcutaneous administration is generally considered to be the preferred method of using growth hormone.
A specific analysis of the activity of somatropin shows us a hormone with a set of diverse effects. In skeletal muscle, it acts as an anabolic, increasing the size and number of cells (these processes are called hypertrophy and hyperplasia, respectively). The hormone also affects the growth of all organs of the body, with the exception of the eyes and brain. Somatropin affects diabetogenic carbohydrate metabolism, that is, it causes an increase in blood sugar levels (a process usually associated with diabetes mellitus). Excessive use of somatropin over a long period of time may cause the development of type 2 diabetes (insulin resistance). The hormone also supports triglyceride hydrolysis in adipose tissue and can reduce fat storage. At the same time, as a rule, the level of cholesterol in the blood serum decreases. The drug also causes a decrease in potassium, phosphorus, and sodium levels, and may cause a decrease in levels of the thyroid hormone triiodothyronine (T3). The latter actually means a decrease in T3-related metabolism and may reduce the effectiveness of growth hormone treatment.
Growth hormone has a direct and indirect impact. The direct effect is that the hGH protein attaches to receptors in muscle, bone and fat tissue, sending messages to support anabolism and lipolysis (fat burning). Growth hormone also directly increases glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) in the liver, and causes resistance to glucose by blocking it
activity in target cells. The indirect effects of growth hormone are largely mediated by IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor), which is produced in the liver and virtually all other tissues in response to growth hormone. IGF-1 also acts as an anabolic in muscle and bone, increasing growth hormone activity. IGF-1, however, can have antagonistic effects on growth hormone. These include increased lipogenesis (fat storage), increased glucose uptake, and decreased gluconeogenesis.
The synergistic and antagonistic effects of these two hormones collectively characterize hGH. In addition, hGH also acts to support lipolysis, increase serum glucose levels, and also reduce sensitivity to.
The use of Somatropin in bodybuilding and athletics to increase the performance of athletes is considered controversial issue. Doubts are raised about the exact potential benefit, which this substance can provide.
Although studies in HIV-positive patients have supported the hormone's potentially potent anabolic and anti-catabolic properties, there have been no studies to date demonstrating similar effects in healthy adults and athletes. In the 1980s, among bodybuilders there appeared a large number of myths about growth hormone that may have been caused by high cost the drug and its name (“growth hormone”). This substance was considered the most powerful anabolic that could be purchased. Today, recombinant human growth hormone is a much more accessible substance. Most experienced users now tend to agree that the main property of somatotropin is fat burning. The drug may support muscle growth, increases strength and causes increased athletic performance, but the results with it are usually less pronounced than with anabolic/androgenic steroids. For advanced athletes or bodybuilders, however, somatropin can help develop body muscles and increase performance beyond what would be possible with steroid use alone.
Story
The first human growth hormone intended for medical use was extracted from extracts of the pituitary gland of human origin. Such preparations are usually called cadaveric (cadaveric) growth hormone preparations. Approximately 1 mg of HGH can be extracted from each cadaver (dosing once daily).
First successful treatment Human cadaver GR is dated 1958. Soon after this medicines were introduced and sold in the United States until 1985.
The FDA banned their sale this year after it was shown that their use may be linked to the development of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), a highly degenerative and ultimately fatal brain disease. The disease can be transmitted from one person to another under exceptional circumstances (usually through blood transfusion or organ implantation), and is most likely initiated by the extraction of hGH from infected cadavers. CJD has a very slow incubation period and the disease was diagnosed after 4-30 years of treatment with cadaver growth hormone. In 2004, it was estimated that at least 26 patients taking cadaveric GH in the United States suffered from this disease. The overall incidence was therefore less than 1%, since it is known that this drug treated approximately 6,000 patients.
In 1985, the FDA approved the first synthetic human growth hormone. It is the first available synthetic growth hormone product in the world, produced through a process called Inclusion Body Technology. This technology involves inserting DNA encoding the hGH protein into bacteria coli(E. coli) that assemble and synthesize pure protein. The synthesis produces pure hormone without biological contaminants, eliminating the possibility of CJD transmission. The approved drug was called somatrem (Protropin), and was based on a manufacturing technology developed by Genentech in 1979. Somatrem was developed at the right time, since cadaveric GH was withdrawn from the market that same year. This hormone is actually a slightly different protein from hGH, but displays biological properties natural hormone. Protropin was initially quite successful synthetic product GR. By 1987, however, Kabi Vitrum (Sweden) had published methods for producing pure synthetic growth hormone with the exact amino acid sequence of endogenous growth hormone. Somatrem's unnatural structure has also been found to cause a much higher percentage of antibody reactions in patients, which may reduce the drug's effectiveness.
Somatropin is seen as a more reliable drug, and the drug retains its leadership in HGH sales worldwide.
How supplied
Somatropin is most often supplied in multi-dose vials containing a white lyophilized powder that must be dissolved in sterile or bacteriostatic water before use. The dosage per vial can vary from 1 mg to 24 mg or more. Somatropin is also available as a premixed solution (Nutropin AQ), which is the biological equivalent of soluble somatropin.
Storage
Do not freeze. Refrigeration (2° to 8°C (35° to 46°F)) is required before and after reconstitution.
Structural characteristics
Somatropin is a human growth hormone protein produced using recombinant DNA technology. It has 191 amino acid residues, and a molecular weight of 22.125 daltons. It is identical in structure to human growth hormone of pituitary origin.
Side effects (general)
The most common adverse reactions to somatropin are: joint pain, headache, flu symptoms, peripheral edema (water retention) and back pain, increased growth of nevus (moles and birthmarks), gynecomastia and pancreatitis. Less common adverse reactions include inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nose (rhinitis), dizziness, infections of the upper respiratory tract, bronchitis, tingling or numbness in the skin, decreased sensitivity to touch, general swelling, nausea, bone pain, carpal carpal tunnel syndrome, chest pain, depression, gynecomastia, hypothyroidism and insomnia.
Abuse of growth hormone can lead to diabetes, acromegaly (the development of visible thickening of bones, especially in the legs, forehead, arms, jaws and elbows) and enlargement internal organs. Due to its effect on cell growth, the drug should not be used in patients with active or recurrent cancer.
Side effects (impaired glucose tolerance)
Somatropin may reduce sensitivity to and cause an increase in blood sugar levels. This may occur in patients with pre-existing diabetes mellitus or impaired glucose tolerance.
Side effects (at injection sites)
Subcutaneous injection of somatropin may cause redness, itching, or swelling at the injection site. Localized loss of fat tissue may also be caused, which may be exacerbated by repeated injections in the same location.
Somatropin: instructions for use
Somatropin is intended for subcutaneous or intramuscular administration. One milligram of somatropin is equivalent to approximately 3 International Units (3 IU). When used to treat growth hormone deficiency in adults, the drug is usually used at a dosage of 0.05 mg/kg per day to 0.01 mg/kg per day. This equates to approximately 1 IU to 3 IU per day for a person weighing approximately 180-220 pounds. Dosage for long-term use is determined after consideration of the patient's IGF-1 levels and clinical response.
When used in sports, growth hormone is typically administered in doses between 1 and 6 IU per day (2-4 IU is the most common dose). The drug is usually taken in the same way as anabolic/androgenic steroids, for 6-24 weeks.
The peak effect of GH and the period of metabolism to IGF-1 is 2-3 hours when administered subcutaneously.
The drug's anabolic effects are less noticeable than its lipolytic (fat burning) effects and usually take longer and at higher doses to occur.
To cause a stronger reaction, other drugs are usually used in combination with somatropin. Thyroid drugs (usually T3) are especially used given the effect of somatropin on thyroid gland, and can significantly increase fat loss during therapy. Insulin is also often used in conjunction with somatropin. In addition to counteracting some of the effects that somatropin has on glucose tolerance, insulin may increase the sensitivity of IGF-1 receptors and decrease levels of IGF-binding protein-1, which promotes greater IGF-1 activity (growth hormone itself also reduces IGF binding protein levels) . Anabolic/androgenic steroids are also commonly taken with somatropin to maximize the potential muscle-building effects. Anabolic steroids may also further increase free IGF-1 levels by decreasing the binding of IGF proteins. It should be noted that somatropin should be used with great caution in combination with thyroid and/or drugs, given that these drugs are particularly strong and have potentially serious or life threatening side effects.
Availability
Somatropin is produced by various pharmaceutical companies and is sold in almost all developed countries of the world. Most famous trademarks are: Serostim (Serono), Saizen (Serono), Humatrope (Eli Lilly), Norditropin (Novo Nodisk), Omnitrope (Sandoz), and Genotropin (Pharmacia).
Somatropin products have a large number of counterfeits. Many counterfeits are very close to the original, and can be found in both illegal and legal distribution channels. Some counterfeit products growth hormone is produced by simply re-sticking the stickers on bottles of hCG ( human chorionic gonadotropin), which has a strong visual resemblance to somatropin. In order to determine the presence of hCG in the hCG package, it is used home test for pregnancy. This test detects hCG level in urine. A few days after starting to use somatropin, the user should use an injection of the drug at a dose of 3-4 IU before bedtime. After waking up, you need to use a pregnancy test, and positive result will show whether counterfeit hCG products were used. The powder in the somatropin vial should be a solid (lyophilized) disk. Do not purchase a product containing a crumbly substance.
Availability of growth hormone
Somatotropin (Somatropin, Human Growth Hormone, HGH, Somatropin) is one of the main hormones that plays a key role in the construction of tissues in the body. It is responsible for many functions and processes in the body, gives energy, speeds up metabolism, burns fat, stimulates muscle and bone growth. Somatropin is available in the US under trade name Protropin from Roche. In Europe and most countries of the world, the vast majority of growth hormone preparations are the corrected 191-amino acid sequence of Somatropin. In most European countries (including Russia), growth hormone (Somatropin) is sold from pharmacies only with a doctor's prescription.
:Tags
Support our project - pay attention to our sponsors.
In the sports field, when talking about anabolic steroids, you can often hear the name “growth hormone”. What is this notorious drug and what is it combined with? Growth hormone or somatotropin is a hormone of the peptide group, and is produced by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, which is part of the human brain. The drug causes a strong anabolic effect on the growth of muscle tissue and a catabolic reaction, which promotes increased fat burning.
Growth hormone contains 191 amino acids. It received its name for the expressive effect, which is characterized by the growth of tubular bones in length in young people.
Somatotropin was first obtained in the seventies of the last century. It was extracted using a special extract from the pituitary gland of corpses, which was a very expensive undertaking.
From 1981 to the present day, the drug has been synthesized artificial method. In 1989, the Olympic Committee banned the use of growth hormone. However, he found wide application in bodybuilding. In sports, growth hormone is used to increase strength and increase lean muscle mass. Today it can be purchased in many online stores. Behind last years its sales increased several times.
In medicine, growth hormone is used to treat dwarfism in children, and also to prevent age-related disorders.
Thanks to its unique pharmacological properties, growth hormone in bodybuilding is key. It has the following effects on the human body:
- stimulates the growth of muscle tissue;
- reduces body fat;
- has a rejuvenating effect on human skin and organs;
- promotes fast healing wounds and recovery from injuries;
- accelerates bone growth in young people under the age of twenty-five;
- helps strengthen ligaments, bones and cartilage;
- increases strength indicators;
- reduces the breakdown of muscle fibers;
- strengthens the immune system;
- regulates metabolism;
- increases blood glucose levels;
- has a regenerating effect on internal organs.
It should be noted that somatotropin in combination with other steroid drugs is responsible for the main effect that promotes rapid muscle growth in a bodybuilder.
As practice shows, if before using growth hormone a bodybuilder had good proportions and good muscle mass, then after using it the quality of the athlete’s muscles improves several times. These include: increased venousness and dryness of the body, bulge and a clearly defined muscle contour.
HGH Dosages
A safe dosage of somatotropin is within 30 IU (international units indicating the degree of activity of a substance).
Depending on the effectiveness of the drug, daily dosages may vary within the following limits:
- from 2 to 4 IU for speedy rehabilitation from injuries;
- from 4 to 10 IU to enhance the fight against adipose tissue in the body;
- from 8 to 30 IU to increase muscle mass and increase strength.
When injecting throughout the day, it is necessary to imitate the natural production of the hormone. To do this, you will need to administer about five equal-volume portions of somatotropin every four hours.

The use of combined hormone courses
Using somatotropin in combination with other hormones, you can significantly increase the volume and definition of muscles. The course is usually based on a base drug (growth hormone) in combination with testosterone or sustanon.
How is growth hormone taken? Today, many athletes are puzzled by this question. Using only one growth hormone, it is impossible to achieve a significant increase in muscle mass. This drug exhibits its anabolic effect only in combination with androgenic hormones and steroids. Its properties are most pronounced in the presence of insulin. When gaining muscle mass, it is recommended to use up to 10 IU of this drug. But it is necessary to take into account that at the stage of fat burning it will be necessary to exclude the use of insulin, since it significantly inhibits the process of lipolysis (the breakdown of fats).
Growth hormone for women is used in cases where figure correction and elimination of excess weight are required. For girls who want to look athletic and attractive, it is additionally recommended to start eating right and sign up for classes at the gym.
At the stage of using the combined course, it is necessary to inject drugs that would stimulate the production of your own growth hormone. For these purposes, the following pharmacological agents can be used:
- GHRP-2, GHRP-6 (Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide). This drug is the most powerful and safe booster (stimulator) of somatotropin secretion of all those existing today. When used, the production of growth hormone can increase tenfold or more.
- CJC-1295 DAC (Drug Affinity Complex). This is a peptide hormone that consists of 30 amino acids and has a long half-life - about two weeks. Combines well with GHRP-2 and GHRP-6.
- Ipamorelin. It is a peptide hormone that helps maintain the natural production of growth hormone at certain hours. Included in growth hormone boosters latest generation(GHRP). A synergistic effect occurs when used together with CJC-129.
- Sermorelin. The drug consists of forty-four amino acids. The half-life is thirty minutes. It is an analogue of testosterone propionate, popular among bodybuilders. To achieve a synergistic effect, it must be used together with GHRP-2 and GHRP-6 peptides.
- Mod GRF 1-29. This peptide has a longer half-life (several times) than sermorelin. It is recommended for use by people aged forty years and above to prevent changes associated with age.
It is necessary to take into account that when using growth hormone with supplements containing arginine and glutamine, the effect of the drug increases three times. To avoid serious disorders in the body, the combined course is not recommended for more than seven weeks.
Nutrition for bodybuilders
In order to build a significant amount of muscle mass, one exercise is not enough. strength training and reception anabolic steroids. Helps you get in good shape A complex approach in combination with proper nutrition, and sculpted muscles will not take long to appear.
From the very beginning of the training process, you must avoid the following products:
- smoked meats;
- foods containing high levels of salt;
- confectionery products;
- fatty foods;
- chocolate;
- ice cream;
- carbonated drinks;
- alcohol;
- heat-treated juices;
- semi-finished products.
An athlete's daily diet should consist of 50% proteins, 30% carbohydrates and 20% fats. The basis of a bodybuilder’s nutrition is natural protein products. These include:
- chicken's meat;
- veal;
- fish;
- cottage cheese;
- legumes;
- chicken eggs.
The following are used as carbohydrates:
- rice, buckwheat and oatmeal;
- durum wheat pasta;
- tomatoes;
- cucumbers;
- lettuce leaves;
- apples;
- bran.
Must be consumed as fat vegetable oils: olive, flaxseed and sunflower.
Products containing simple carbohydrates, since they are quickly processed by the body and turned into fat. It is also necessary to exclude salty foods from the diet, as they retain water in the body.
Burning fat during the drying period
At the stage of drying the body, it is necessary to carefully approach not only the diet, but also you need to start using growth hormone for weight loss. To eliminate excess fat deposits, thyroid hormones and somatotropin are used.
Thyroid hormones are represented by the following types:
- thyroxine (T4);
- triiodothyronine (T3);
- calcitonin.
These hormones help increase metabolism in body tissues from 60 to 100%. The use of thyroid hormones is quite dangerous. The consequences of uncontrolled use can be irreversible and lead to serious metabolic disorders.

Using growth hormone to burn fat is a fairly safe procedure. But during the course, it is necessary to set the dose within 4-10 IU per day. Only in this case the effect will be most pronounced.
It is worth noting that to increase the fat burning effect, it is necessary to use the following drugs in combination with growth hormone:
- adrenalin;
- testosterone;
- adaptogens;
- glucagon;
- endorphin;
- amino acids;
- vitamins.
During the period of extreme drying of the body, water is removed, and along with it calcium and other valuable elements are washed out. This process is very Negative consequences for ligaments and joints. Thus, at the stage of enhanced fat burning, during training, the athlete may damage his knee or foot, since these joints are subject to the greatest impact. It should be borne in mind that in everything you need to observe moderation.
When using growth hormone sports nutrition is also necessary. Today, all of these products can be found in numerous sports stores.

The use of melatonin in bodybuilding
One of important elements When doing bodybuilding, you need to take a drug called melatonin. It is a hormone produced pineal gland person, and is designed to provide good night athlete. But wow beneficial effect not limited to only healthy sleep. Melatonin also affects other body functions. These include:
- strengthening immunity;
- normalization of the gastrointestinal tract;
- reducing the risk of cancer;
- normalization blood pressure;
- reducing the risk of developing stress;
- rejuvenation of the body;
- reduction in obesity levels.
Today, analogues of the human hormone are sold on the domestic market. Types of medications containing melatonin:
- "Melaxen";
- "Melaxen balance";
- "Circadin";
- "Epithalamine."
The mechanism of action of drugs containing melatonin is quite simple - after administration, the substance penetrates the blood and then into the neurons of the brain. Melatonin does not accumulate in the body. It can be used for a long time - a month or more.
Side effects from using hormones
Despite the large number positive properties, somatotropin also has side effects. These include:
- Increased blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). If you abuse somatotropin, you may experience hormonal disbalance. Sugar levels are lowered by using insulin or insulin substitutes. If there is not enough insulin produced by the pancreas, diabetes can occur.
- Increased blood pressure. During the course, you will need to reduce your drug intake or use antihypertensive medications.
- Numbness of the limbs. Eliminated by reducing the dose of the drug.
- Swelling of the body. This effect can be prevented by avoiding salty foods and alcohol.
- The risk of hypertrophy of the heart and other vital organs. For elimination side effects The drug should not be abused and the prescribed course must be followed.

Nanodrop - a device for determining the amount of protein
The device was developed for research nucleic acids and proteins. It is necessary in cases where the dose of the substance for analysis is very limited.
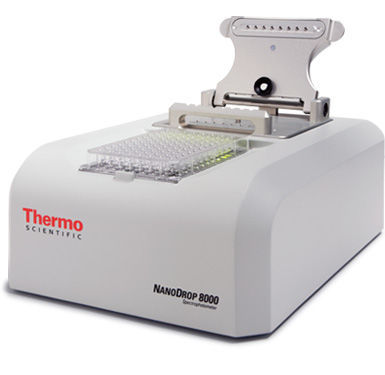
Area of application of the device:
- establishing the concentration of nucleic acids;
- determination of protein amount;
- cell research;
- determination of structural characteristics and quantity of nanoparticles;
- measuring the amount of labeled proteins;
- carrying out general diagnostic measures.
The NanoDrop spectrophotometer is developed using a special technology that does not require cuvettes or capillaries. The sample under study is pipetted onto the surface of the measuring device, and the automated system determines the optical distance from 0.05 mm to 1 mm, which will be optimal for the sample under study.
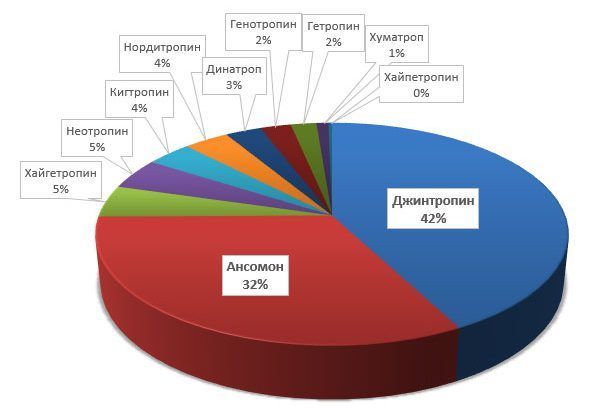
Rating of drugs for the production of growth hormone
A rating was compiled based on reviews of growth hormone. It looks like this:
- Jintropin.
- Ansomon.
- Neotropin.
- Getropin.
- Kigtropin.
- Hypetropin.
- Dynatrope.
- Genotropin.
- Saizen.
- Humatrope.
In order to avoid purchasing counterfeits, muscle growth hormone must be purchased from reputable and trusted online portals.
HGH (Human growth hormone) or human growth hormone is considered a “key” hormone, since it is responsible for so many functions in humans. HGH is responsible for youth, strength, energy, it reduces weight by burning fat. Other names for HGH are Somatropin, Somatotropn, Somatropin.
Human (HGH, Growth Hormone, or GH) consists of 191 amino acids. The genetically engineered recombinant human growth hormone is completely identical to the growth hormone produced by human body. Growth hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland and is rapidly converted in the liver into its metabolite, insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1).
Somatotropin It is the most effective therapy to cause a reverse aging effect. Growth hormone is responsible for growth in childhood, as well as tissue regeneration. By the age of 30, our bodies no longer produce sufficient amounts of growth hormone, which is associated with aging and the deterioration of many body processes. How older man becomes, the less growth hormone is produced. Researchers have shown that growth hormone therapy can reverse the biological effects of aging. HGH is also very popular among athletes, bodybuilders and athletes.
What is growth hormone (GH)?
Somatotropic hormone, somatotropin is a polypeptide secreted by the adenohypophysis. It contains 191 amino acids and has a molecular weight of about 22 kDa. GH is released into the blood under the influence of the hypothalamic somatotropin-releasing factor (GRF) and somatostatin. The timing and frequency of release are regulated by somatostatin, while the amount of GH released is regulated by GRF.
GH is an anabolic hormone, it stimulates protein synthesis, cell mitosis processes and enhances lipolysis, increasing the release of free fatty acids from adipose tissue. It also accelerates glucose transport and promotes glycogen storage. Disorders caused by hyposecretion include arrested development and failure to achieve growth potential. Hypersecretion is associated with gigantism and acromegaly. Acromegaly may also be associated with hypersecretion of GRF.
The development of pituitary dwarfism (dwarfism) in the vast majority of cases is associated with insufficiency of the somatotropic function of the anterior pituitary gland. Violation of GH production by the pituitary gland is usually caused (about 70% of cases) by a primary lesion of the hypothalamus. Congenital aplasia and hypoplasia of the pituitary gland are very rare. Any destructive changes in the hypothalamic-pituitary region can lead to growth arrest. Most often they can be caused by craniopharyngioma, sarcoidosis, toxoplasmosis and cerebral aneurysms.
- Positive effects of taking human growth hormone:
- Reduction excess fat deposits, especially abdominal fat. (A decrease in abdominal fat has been noticed in almost all people)
- Reducing waist to hip. (That is, fat is removed mainly from the waist, where it is associated with a high risk coronary disease)
- Increased muscle mass and physical strength
- Wrinkle reduction on the skin, as well as some other consequences of skin aging.
- Resumption of growth and regeneration of some internal organs that have atrophied with age.
- Increased bone density.
- Strengthening immune system.
- Developing a sense of general well-being.
- Improvement of brain cognitive activity (improves the ability to learn and cognition).
- Stimulation of cell production bone marrow, which produce red blood cells.
- Reducing the likelihood that you will spend the last years of your life in a nursing home.
- Growth hormone slows progression cardiovascular diseases and reduces the risk of death from cardiovascular disease. HGH may also slow the progression of cardiovascular disease by improving your cholesterol profile.
Medical research confirms that after 15 years of age, the body’s production of human growth hormone significantly decreases, which subsequently leads to its deficiency in adults. As the level decreases, immunity decreases, and the aging process of the body begins.
Impact on humans
Under the influence of growth hormone in older people, rejuvenation body for 10-20 years. Moreover, this is data from the most authoritative scientists with references to many experiments, both on humans and animals. For example, its use in old mice significantly increases their survival. In groups of mice treated with growth hormone, most mice remain alive when the control group almost completely dies out.
If in the first half of life, approximately up to 30 years, creative processes predominate in our body, then after 30-40 years, and especially in old age, when the restorative processes are extremely weak and the destructive ones are very strong, the use of somatropin can give positive effect. Here, growth hormone can take on the role of creative genes, which are already almost “silent”.
Experts often emphasize that for life extension Small prophylactic dosages of growth hormone are used, which make it possible to raise its level to the norm characteristic of a young person.
It makes sense to use it for those over 30-40 years old. However, on this moment injections are very expensive. The cost of an annual course can be thousands or even tens of thousands of dollars. But it is worth using it under the supervision of a doctor and it is very important to conduct studies of its level in the blood.
But due to the high cost of such injections, attempts continue to find cheaper ways to increase growth hormone in the body. On given time There are several such tools. These are, first of all, the amino acids arginine, ornithine, glutamine, etc. Also zinc and some drugs (sodium hydroxybutyrate, etc.). It has been proven that the use of these supplements in high dosages can help increase growth hormone levels by 30% or more.
Over the course of each decade, the level of growth hormone in the body drops by approximately 15%. That is, a person at 40 years old who takes supplements that increase growth hormone levels can expect to return his levels to his 20s. Of course, this does not mean that a person will look 20 years younger, because growth hormone is far from the only factor responsible for rejuvenation.
Research on the effects of growth hormone
IN medical journal New England Issues Issues clinical study human growth hormone, clinical trial results have been published anti-aging effects man Daniel Rudman. And these results were stunning.
Dr. Radman saw patients ranging in age from 61 to 81 years at the Medical College of Wisconsin-Milwaukee. After 6 months of study, Dr. Radman stated that the aging process of patients who received injections of human growth hormone was reversed by 10-20 years. In patients in the control group (patients who did not receive injections), the aging process continued.
Other clinical studies conducted over the past 30 years have shown that patients using intramuscular growth hormone experienced decreased body fat, increased muscle mass, improved libido, smoothed wrinkles, eliminated cellulite, and improved immune function. This is the main hormone that is produced by the pituitary gland and, both directly and indirectly, responsible for the balance of all the most important hormones human body.
- Spinal flexibility
- Loss of fat mass
- Duration of penile erection
- Emotional stability
- Load tolerance
- Frequency of nighttime urination
- Tides
- Healing abilities
- Wound healing
- Sexual function, sexual potency
- Strength, training and body fat mass, muscle strength
- Muscle size
- Normalization menstrual cycle
- Skin and hair care, skin structure
- Skin thickness
- Skin elasticity
- Disappearance of wrinkles
- New hair growth
- Energy, emotions and memory, tone
- Memory
- Resistance to common diseases
Dr. Chain, of the Life Extension Institute in Palm Springs, saw 202 patients. And here are the results of his observations:
Patients noted improvement in the following parameters:Dr. Chain notes a loss of 10 to 12 percent of body fat mass every six months in the presence of obesity and an increase of 8 to 10 percent of lean body mass every six months. These changes occur every six months until the body regains the shape it had when the person was 20 years old (treated with human growth hormone in combination with certain other hormones). Dr. Chain says, “If your hormone levels are not the same as they were when you were twenty, I will give you back all the money you paid.”
In recent years, there has been growing evidence that maintaining healthy level growth hormone has a beneficial effect on cardiovascular system . Statistically, people with low levels of growth hormone in their body are more likely to die from cardiovascular disease. Low level is often the underlying cause of increased risk of stroke compared with individuals receiving therapy. To achieve the best therapeutic effect Several weeks to several months of therapy are required.
A group of scientists from the Spanish Complutense University, led by Jesus Tresguerres, conducted a series of studies that studied the effect of growth hormone on the lymphocytes of old rats. In fact, the influence age-related changes on the functioning of the neuroendocrine and immune systems have hardly been studied.
Aging mammals is largely associated with a deterioration in the immune response; this most strongly affects the functions of lymphocytes.
Aging also occurs in endocrine system, which significantly reduces the secretion of various hormones, including growth hormone. The scientists were faced with the task of studying the effect of replacement therapy on the functioning of lymphocytes in old rats. Their ability to chemotaxis, proliferative activity in response to a special stimulator (mitogen) concanavalin A, secretion of interleukin 2 (IL-2), as well as the activity of natural killer (NK) cells were studied. As a result, a decrease and, in some cases, a reverse development of age-related changes in the immune system was discovered, until the indicators approached those in young rats (6 months).
Substances that release growth hormone stimulate its production in the body. The human hormone is stored in the pituitary gland and the body releases it in response to sleep, exercise and limited food intake.
- What:
- Helps burn fat and convert it into energy and muscle.
- Improves resistance to diseases.
- Accelerates wound healing.
- Helps in tissue restoration.
- Strengthens connective tissues to keep tendons and ligaments healthy. Enhances protein synthesis for muscle growth.
- Reduces urea levels in blood and urine.
Weight normalization and growth hormone.
 As a teenager, you can eat fatty, fried, fast food foods and not worry about overweight. However, with age, such food leads to excess weight. The reason is the loss of your own growth hormone with age. Growth hormone produced by the pituitary gland in the human body decreases by 60% when we reach the age of 40 years.
As a teenager, you can eat fatty, fried, fast food foods and not worry about overweight. However, with age, such food leads to excess weight. The reason is the loss of your own growth hormone with age. Growth hormone produced by the pituitary gland in the human body decreases by 60% when we reach the age of 40 years.
Decreased levels of human growth hormone are visible through various signs aging such as loss muscle tone, decreased sleep quality, increased body fat, loss of energy and stamina, decreased sexual energy and increased body fat.
One of the most important roles of growth hormone in our body is is weight control. It works by increasing the amount of IGF-1, a hormone that is secreted by the human liver. IGF-1 in turn prevents the transfer of glucose into fat cells, thereby forcing the body to burn fat for energy. Basically, the human body uses all glucose for energy, but as we age, it does not convert fat into energy. Human growth hormone empowers your body to use energy from fat stores first, resulting in significant weight loss and also helps our body to produce new muscle cells and increases the number of muscle cells in human body. In addition, it helps to lose weight and increase muscle density, and also leads to increased energy and improved metabolism. Increased metabolism means increased weight loss.
In fact, human growth hormone helps you lose weight without exercise, promotes healthy weight, and increases strength.
The most important substances releasing growth hormone, are the amino acids ornithine, arginine, tryptophan, glycine and tyrosine, which work synergistically (more effectively together than alone) with vitamin B6, niacinamide, zinc, calcium, magnesium, potassium and vitamin C to trigger the nighttime release of growth hormone. Growth hormone secretion peaks approximately 90 minutes after we fall asleep.
Natural levels of the hormone decrease as you get older. Somewhere in age Around age 50, growth hormone production almost completely stops..
But by adding amino acids and vitamins to the diet that stimulate the release of growth hormone, you can restore its production to the level young man. Ornithine And arginine, two of several amino acids involved in human growth hormone secretion, are among the most popular amino acid supplements today, mainly because they can help you lose weight and improve your body shape while you sleep (that is, while the hormone is being released growth). While some hormones encourage the body to store fat, growth hormone acts as a fat mobilizer, helping you not only look physically fit, but also have more energy.
Ornithine stimulates the release of insulin and helps insulin act as an anabolic (muscle-building) hormone, the use of which has increased among bodybuilders. Taking extra ornithine will help increase arginine levels in the body (in fact, arginine is formed from ornithine, and ornithine is released from arginine during constant cycling). Because ornithine and arginine are so closely related, all characteristics and warnings regarding one can be applied to the other (see section "Arginine"). As a supplement, ornithine works best if taken at the same time and in the same way (on an empty stomach with water or juice - no protein).
Growth hormone and aging
Production growth hormone declines with age in all animal species tested to date. In humans, the amount of growth hormone drops by about 14 percent between the ages of 21 and 31, and by the age of sixty, the average daily production of the hormone is reduced by half. In absolute numbers, we produce approximately 500 micrograms of the hormone every day at the age of 20, 200 micrograms at the age of 40, and 25 micrograms at the age of 80.
As mentioned above, the easiest way to measure the amount of growth hormone in the body is to measure the level of IGF-1 in the blood plasma. A value below 350 IU is evidence of hormone deficiency. Less than 5 percent of people aged 20 to 40 have an IGF level of less than 350 IU per liter of blood. healthy men. But after reaching the age of 60, such a low amount of the hormone is found in 30 percent of apparently healthy men. And after 65 years, approximately half of the population experiences complete or partial deficiency of growth hormone.
The decline in the level of growth hormone is directly related to the swelling, wrinkling, flabbiness - decrepitude of the creatures that we sooner or later begin to see in the mirror. Those of us who naturally have low levels of hormones age much faster and more visibly than those who, through genes or active exercise, maintain higher levels of secretion for a longer time. The loss of the hormone with age resembles the situation observed during menopause. And they even gave it a similar name - somatopause.
Adapted from: Journal of NIH Research, April 1995.
Interestingly, studies of patients with pituitary disease show that the decline in hormone production by this gland occurs in a certain sequence. First comes growth hormone, followed by gonadotropins, luteinizing (LH) and follicle-stimulating (FSH) hormones, and finally thyroid-stimulating hormone and adrenocorticotropin (ACTH), so that the loss of growth hormone from the pituitary gland begins a cascade-like reduction in the production of pituitary hormones.
Why does the amount of growth hormone decrease with age?
The answer to this riddle remains to be found. Studies have shown that the aging growth hormone cell of the pituitary gland is still capable of producing the same amount of growth hormone as it produced in youth when adequately stimulated.
This means that the failure occurs somewhere among the factors that regulate its release. Something is happening in the ring feedback between IGF-1 production in the liver and the hypothalamus. Typically, a drop in IGF-1 levels tells the hypothalamus to stimulate the pituitary gland to produce more growth hormone. But with age, this wonderful scheme stops working somewhere.
Some researchers believe the problem lies with somatostatin, a natural inhibitor growth hormone. It has been found to increase in amount with age and may potently block growth hormone secretion. When the researchers suppressed the effects of somatostatin in old rats, their GH surges became as intense as those in young rats. Other scientists believe that the precursor hormone, growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRR), which stimulates the release of growth hormone, becomes less responsive to feedback signals. It is possible that both the first and the second occur.
This is very similar to what happens with another hormone, insulin. As we age, we become less responsive to insulin. As a result, we do not absorb glucose as efficiently and therefore its level in the blood increases. In about a third of the elderly population, this insulin resistance, which is directly related to the "hollow" obesity observed in old age, reaches a sufficiently serious stage and becomes a disease - type 2 diabetes. Unlike the more common type 1 diabetes, the problem is not that the body is unable to produce insulin, but that the body's tissues behave as if there is no insulin. Recently, scientists are inclined to believe that something similar is happening with growth hormone. The problem is not only a decrease in the amount of hormone available to the tissues, but also that the tissues cannot even respond to the hormone that is available. From this perspective, aging can be viewed as a disease of growth hormone resistance, just as type 2 diabetes is a disease of insulin resistance.
Growth hormone decline is not inevitable
The most latest research show that, whatever the reasons for the decline growth hormone levels, this decline is neither irreversible nor permanent. Physiology professor William Sonntag and his colleagues at the Bauman-Gray School of Medicine in Winston-Salems, North Carolina, recently completed an experiment that clearly demonstrates that the decline in growth hormone secretion with age is reversible. Old rats, like old people, experience a decrease in the rate of growth hormone release. But when Sonntag and his colleagues restricted caloric intake in aged rats at 26 months of age, growth hormone production returned to previous levels within two months.
According to Sonntag: "We completely restored the amplitude of growth hormone secretion, and this shows that what happened is not a problem of anatomy or permanent changes in the hypothalamus." A few years ago, he showed that L-dopa, which scientists know stimulates growth hormone, also restored growth hormone surges to levels seen in young age. The main idea that can be gleaned from this is that the decline in growth hormone production with age can be reversed. Even if the activity of growth hormone releasing hormone decreases, the activity of somatostatin increases, or the receptors become less responsive to the effects of growth hormone, all this can be overcome by external replacement of growth hormone or its stimulants. Newly developed artificial substances do the job even better than natural HGH releasing hormone.
Global action of growth hormone
Growth hormone has its effect on every system of the body, both directly and indirectly through insulin-like growth factors. As we will see in subsequent sections, almost nothing escapes his magical touch. Just as it increases the size of bones in children, it increases the size of all organs and tissues. Even the brain is subject to it. The most recent animal experiments show that it can regenerate damaged brain tissue.
An excerpt from a recent report by a group of researchers led by Jens Sandahl Christiansen from the municipal hospital in Aarhus, Denmark, sums up the issue of the ubiquity of the hormone's effects.
"It has been found that when adult patients with GH deficiency are left untreated, they experience increased mortality from cardiovascular disease, worsening physical form, muscle strength decreases, kidney function, sweating and thermoregulation deteriorate, energy expenditure and metabolic rate decrease, and the absorption of thyroid hormone deteriorates. the heart muscle weakens, Clinical signs premature atherosclerosis. In the structure of the body, the mass of fats abnormally increases, the mass of non-adipose tissues, the ratio of muscle mass to fat mass, the volume of extracellular fluid, the mineral content in bones decrease, and obesity appears. In addition, two independent groups showed a deterioration in their psychological state."
The effects of growth hormone are not as dramatic as those of some other hormones in the body. A sudden drop in insulin levels, for example, can cause you to go into insulin shock, which can be fatal. But falling levels of growth hormone after age thirty can cause the slow decline of the entire body that we call aging. Why do we age, and can the hormone increase life expectancy and improve its quality?
DNA and aging
Prominent specialist in plastic surgery and the fight against aging, Vincent Giampapa, director of clinical research at the International Institute on Aging in Montclair, New Jersey, argues that “aging is programmed into DNA under the guise of the telomere, the “clock” at the end of each chromosome that shortens with each division cells. To truly reverse aging at the cellular level, we will need a substance that can restore telomere length and thus turn old cells into young ones. Such a substance is not yet available, but Giampapa believes that this will be a matter of the next decade. Until then, growth hormone and its assistant, IGF-1, does the next most important thing - it helps keep the cell as healthy as possible.
The functional abilities of a cell depend on the genetic material, DNA, located in the nucleus of the cell and encoding all the proteins, hormones and enzymes that make the cell work. DNA resembles an army under constant attack free radicals oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, heat coming from the body and other destructive factors. Although DNA has the ability to repair itself, as we age it does not do this job as well, falling victim to the same aging process that affects the entire cell. At one time, the damage caused accumulates in the energy center of the cell, the mitochondria, which has its own DNA. Until now, one of the few ways available to us to limit DNA damage was to take antioxidant supplements, such as vitamins C and E, to strengthen our defenses.
But according to Thierry Hertog and Giampapa, new research from Europe suggests that growth hormone and IGF-1 may go further and do what antioxidants cannot.
Growth hormone and IGF-1 act as couriers, delivering the raw materials necessary for cell renewal and repair. IGF-1 ensures the delivery of nucleic acids. DNA and RNA directly into the cell nucleus, where the DNA is located. Nucleic acids are used to repair DNA damage and stimulate cell division. Growth hormone initiates the transport of amino acids, building material for proteins and nucleic acids into the cell cytoplasm - the area surrounding the nucleus. This region includes cell membranes and intracellular organs such as mitochondria. Thus, growth hormone and IGF-1 not only minimize DNA damage and cellular structures, but also help heal the cell and DNA. These two hormones actually treat the root cause of aging.
Growth hormone and longevity
Does growth hormone extend lifespan?
 When gerontologists talk about life expectancy, they are actually discussing two completely different questions. One of them is the average life expectancy, that is, the age reached by half of the population. It has tripled since Roman times and is currently around 77 years in the US. Another issue is maximum life expectancy—the age reached by the oldest members of the population. At present it appears to be approximately 121 years. Most gerontologists would like to “flatten the curve,” i.e., move the line average duration life closer to maximum, so that at least half of the population reaches the age of one hundred.
When gerontologists talk about life expectancy, they are actually discussing two completely different questions. One of them is the average life expectancy, that is, the age reached by half of the population. It has tripled since Roman times and is currently around 77 years in the US. Another issue is maximum life expectancy—the age reached by the oldest members of the population. At present it appears to be approximately 121 years. Most gerontologists would like to “flatten the curve,” i.e., move the line average duration life closer to maximum, so that at least half of the population reaches the age of one hundred.
Blackman, who conducts the tests growth hormone at Johns Hopkins University, believes that this will definitely happen with the use of growth hormone.
“We are adding years to life, moving closer to people’s destined longevity. We do not think that any intervention could change the destined maximum life expectancy of people, but through healthy intervention we can move them towards this very maximum life expectancy, which is somewhere in the range between 110 and 120 years."
As we will hear from people who have taken HGH, in some ways increase in life expectancy already takes place. If you judge by the fact that you feel cheerful when you wake up in the morning and like a child eager to start a new day without gloomy preoccupation with how to survive the next twenty-four hours, then growth hormone seems to give you an extra twenty years of life, in the sense what else can you do? Just think how many times have you said to yourself: “If only I had my thirty years back, I would start a new business, I would build a house, write a book, sail around the globe, learn to ride a saddle or learn to scuba dive.” By using GH replacement therapy, you no longer have any reason to consider yourself too old for any new endeavor. You can get your old years back.
There is ample evidence that growth hormone therapy reduces the likelihood of your premature death from illnesses, that is, in other words, increases your chances of celebrating your 120th birthday. It has been shown to regrow in animals most important organ immunity - thymus (see Chapter 7). If growth hormone can restore the thymus in humans - and there is no reason to believe that this is not the case - then we will enjoy the same freedom from disease in old age as we did at the age of 10 - in highest point immune function! As detailed in Chapter 8, growth hormone fights disease in two ways: by reducing risk factors and by reversing the progression of disease if you do get sick.
Why are we so sure that growth hormone treatment will increase average life expectancy? Because we know what hormonal replacement can do. The results of the largest lifespan experiment in history are now arriving. Estrogen replacement therapy in postmenopausal women has halved the incidence of heart attacks and strokes and increased life expectancy. Growth hormone will work even better, since its effect on the body is much more profound.
Thierry Ertog, MD, a Belgian physician and endocrinologist, has no doubt that growth hormone has a profound effect on human aging and longevity. “In Bengtsson’s study of 333 patients with pituitary insufficiency,” he says, “they died twice as often normal people(see chapter 2). An adult aged 50 years produces the same amount of growth hormone as a young person with GH deficiency. Therefore, a 50-year-old person is twice as likely to die compared to a person treated with growth hormone. I find it sad that people age and have a poor quality of life when they could be on hormone therapy. This is the medicine of the future."
Increased maximum lifespan
But the question remains whether growth hormone can expand the outer limits of human longevity. Many gerontologists, myself included, are of the opinion that maximum life expectancy is not fixed. By developing genetic engineering technologies, we will move the border human life up to 150 years and beyond. Therapies like growth hormone replacement will allow us to live long enough to wait for new treatments to emerge that will provide a new jump in life expectancy. But although the available evidence is very preliminary, there are strong indications that growth hormone increases not only the quality of life, but also the quantity.
Currently the only one practical way to test the effect of therapy on lifespan is to use short-lived animal species, preferably mammals, whose situation bears some resemblance to the human situation. In 1990, two researchers from the University of North Dakota, David Hansari, Ph.D., and Thomas Gustad, Ph.D., attempted to answer this question. They injected growth hormone into a group of 26 mice at 17 months of age—three-quarters of their average lifespan of 21 months. The animals were already showing signs of aging, and members of the original colony of sixty mice began to die. A control group of 26 mice of the same age received placebo injections saline solution. After thirteen weeks, sixteen animals (61 percent) in the control group had died, while all but two, or 97 percent, of the growth hormone-treated group were alive! In other words, the vast majority of animals treated had already exceeded the expected lifespan for that species.
At this point in the experiment, the scientists killed four animals from each group to study their immune function. The remaining mice were allowed to live without treatment for another four weeks. During this time, the control group completely died out, and from the group treated with the hormone, only one animal died. Hansari and Gustad resumed GH therapy, extending it for another six weeks until their supply of the hormone ran out and they were forced to end the experiment by killing all the animals. During this study period, only one mouse died. This means that out of 26 mice in the original group, they died natural reasons only four. 18 mice (4 were killed) remained alive for 22 weeks after the start of the experiment, while the control group (again minus the four mice killed) died out after 16 weeks. The researchers say the results "indicate that long-term GH therapy significantly increases life expectancy in hormone-treated mice."
The treated animals not only looked younger, they also had younger immune systems, which were assessed based on several standard tests (see Chapter 7). The researchers began their experiment when the animals were already showing signs of aging and weakened immune systems, including cancer and infections. “Thus,” the scientists write, “the observed increase in life expectancy in the hormone-treated group appears to be due to the delay or prevention of aging-related diseases.”
One can only wonder what would have happened if the researchers had been able to continue their experiment until the last animal died. Would they be able to increase the maximum lifespan for this species? Very few therapies have ever achieved this. And the most best method who gave sustainable results All representatives of the animal kingdom - from single-celled protozoa to fruit flies and rodents - are subject to dietary restrictions.
In properly performed experiments, animals that were restricted in caloric intake had more than twice the average lifespan of their species. On a human scale, this meant living over 150 years!
Could growth hormone be a significant factor in this animal's ability to defeat death? Dr. William Sonntag of the Bauman-Gray School of Medicine at Wake Forest University in Winston-Salem, North Carolina, observed what happens to the secretion of growth hormone and IGF-1 in food-restricted animals. Typically, as we age, the amount of growth hormone and IGF-1 decreases along with a decrease in protein synthesis—the production of new proteins that do all the work of cells and tissues. But Sonntag and his collaborators found that the opposite happened in animals on a restricted diet. In young rats on a moderate diet, growth hormone secretion decreased, and by the time they reached 26 months of age—an old age by rat standards—growth hormone secretions were equal to those seen in the young control rat.
"We tried to link this to the fact that calorie-restricted animals of this age have a greater ability to synthesize proteins in their tissues," says Sonntag. While the levels of protein synthesis in the old control rats fell, the old calorie-restricted rats increased the synthesis of new proteins in the heart by 70 percent and in the diaphragm by 30 percent compared to controls. Interestingly, IGF-1 levels did not increase, but the number cell receptors for IGF-1 increased by 60-100 percent.
Some people who want to extend their lives have already begun their dietary restriction programs, reducing their calorie intake by 20 to 30 percent of their normal levels. But this experiment shows that one of the important factors there may be an increase in life expectancy increased secretion of growth hormone. You can achieve the same goal without resorting to a spartan diet, which can be nearly impossible to maintain.
Raising the bar on life expectancy
Currently the best way anti-aging is to limit DNA damage by antioxidants, vitamins and minerals and DNA treatment with a growth hormone stimulation program involving diet.
In the next five to fifteen years, we will have agents that will repair cell damage, stimulate telomere regrowth, and manipulate DNA.
Then we will have a true means of reversing aging. Old cells will turn into new, energetic, active cells that have no less division potential than young cells. Some scientists believe that further study of telomeres will make it possible to move the hands of this cellular “clock” back. This progress will allow us to change the very basis of aging and build a stronger and more durable building on the ruins of cells. This will be the end of aging and the beginning new era unlimited health and longevity.
But the train is leaving, and anyone who has already survived their thirty-fifth birthday will then bite their elbows. Listen to what Giampapa has to say:
"If you don't start limit cell damage and treat DNA now, over the next five to ten years, during which telomere stimulators and other DNA modifiers become available, your chromosomes and DNA will be so damaged that you will not be able to help them. The best prescription for people over 40 is to use what is known in anti-aging now to minimize DNA damage and allow it to benefit from anti-aging therapies that are on the horizon. This formula is the bridge that will take you to the future."
And this future is truly golden. We predict that the use antioxidants, the first of medical anti-aging technologies, will add ten years to the average life expectancy, estimated at seventy-seven years. Replacement therapy using growth hormone and other hormones make up the second third of anti-aging technology that could add another thirty years to life.
Somatotropin is a hormone that is actively involved in protein metabolism and is synthesized by the anterior lobes of the pituitary gland. Somatotropin is necessary for growth, normal functioning internal organs, secretion of various substances, as well as to improve metabolic metabolism.
How is somatotropin produced?
The production of somatotropin does not occur constantly. Several peaks of its synthesis appear during the day. It is at these moments (approximately every 4-5 hours) that it is generated. One of the highest and most active peaks occurs at night - sleep stimulates its production.
If we try to explain the mechanism of growth hormone synthesis as clearly as possible, then the whole process will look like this: the pituitary gland produces somatotropin, receiving a command from the hypothalamus, then it enters the blood and is delivered through it to the liver. It is here that it is processed into somatomedin - this is a working substance that is absorbed directly by the muscles, bone tissue and fat cells.
In women during pregnancy, somatotropin, as a result of the expression of a variant gene, can be produced in the placenta, however this type substances are slightly different in molecular composition (15 links of the polypeptide chain are missing). With age, the frequency of secretion peaks decreases.
The structure of growth hormone is a polypeptide chain, which includes 190-191 amino acids. In general, its structure is similar to prolactin. There are several types of somatotropin; they differ in the sequence of amino acids, but the homology remains unchanged. The degree of ordering of each molecule is very high.
Role in somatotropin in the body
Growth hormone (HGH) plays important role in the body, as it affects various areas. The most important impact for a person can be included in a list of three components:
- Stimulating effect on the synthesis of growth factors
- Participation in the production of a number of substances and acids
- Impact on tissues containing somatotropin
This list is general, but research that has been actively carried out on this hormone has significantly supplemented it. So, in the body it is also responsible for the following important factors:
- Changes oxidative metabolism, resulting in greater consumption of fatty acid and protein and glycogen are saved.
- Somatotropin helps increase growth. Along with the acceleration of metabolism, the growth of soft tissues and skeleton occurs.
- Improving protein biosynthesis by increasing insulin production and increasing sensitivity levels.
- Accelerates the healing process for fractures and other injuries. It is also effective against catabolic changes caused by debilitating diseases and age-related changes.
- Increases sexual activity.
- Affects collagen synthesis.
- Helps lower “bad” cholesterol.
- Stimulates the development and growth of cartilage, therefore effective against osteoporosis.
Interaction with other hormones
The main property of the HGH hormone is its metabolic effect, which is why it is widely used in sports. But as a side effect after its use, you can notice a decrease in the secretion of thyroid hormones, which may require additional treatment in the form of replacement therapy.
For this hormone to work as an anabolic steroid, the presence of insulin is required.. Moreover, these substances in combination synthesize protein synergistically, whereas in the case of carbohydrate metabolism act as antagonists. It is the lack of insulin that explains the lag in growth and development in children with type 1 diabetes.
Hormones produced thyroid gland, are also important for obtaining an anabolic as well as fat burning effect. Cortisol and other glucocorticoids can reduce the effectiveness of somatotropin, since they act as antagonists towards it. Estrogens and somatostatin also have a similar effect.
The average concentration of the hormone in the body is 1-5 ng/ml, but during peak periods of development its level increases significantly, sometimes reaching 45 ng/ml. The concentration remains high in humans up to 25 years of age, that is, until the growth zones close.
The use of somatotropin requires caution, since both excess and deficiency of the hormone can provoke negative consequences for humans. Excess normal level, including due to long-term administration large doses substances that can lead to changes in facial features (coarsening), thickening of bones, macroglossia.
Additionally, other complications develop: muscle strength decreases, tissues become more resistant to insulin, compression occurs nerve endings. There is also a risk of the appearance of an adenoma, and in childhood, the associated pituitary gigantism.
 Lack of somatotropin is usually provoked by genetic characteristics Therefore, already from childhood, the appearance of various diseases and pathologies that develop against this background is possible.
Lack of somatotropin is usually provoked by genetic characteristics Therefore, already from childhood, the appearance of various diseases and pathologies that develop against this background is possible.
Growth retardation occurs, sometimes supplemented by delays in puberty and even mental development. Last modified observed with a lack of several types of hormones. Low levels of somatotropin in an adult provoke increased deposition of fat on the body.
If a mutation in the receptor gene for this hormone occurs, the risk of Laron syndrome increases. Its signs are a decrease in the size of the face, slow growth and other related changes.
Use of somatotropin
The drug somatotropin is used in medicine in several areas. The most important of them is the treatment of developmental and growth disorders in childhood. The peculiarity of such treatment is that it should be carried out as early as possible, and only after reaching adolescence the core course must be completed. Growth hormone is currently one of the best ways to treat pituitary dwarfism.
Previously, aging diseases were prevented using growth hormone, but at the moment widespread this practice has not been achieved. This is explained by the fact that the substance cannot be used as a nootropic, which is why it causes quite a lot of side effects. Somatotropin is often used to treat nervous disorders, so it can be used under medical supervision in the treatment of depression.
The use of growth hormone is much wider in sports, although this drug was banned by the Olympic Committee back in 1989 as doping. At the moment, it is most often used in bodybuilding, since it has a good anabolic effect and helps reduce the percentage of body fat.
HGH Frag (176-191) is a fragment of growth hormone located in the amino acid segment from link 176 to link 191. It is used mainly in sports, as it accelerates lipolysis and thus promotes active fat burning. At the same time, it also has the following effect:
- Slows down the aging process
- Does not provoke organ hyperplasia
- Does not affect insulin secretion and glucose levels
- Strengthens bone tissue
- Promotes energy production
The use of somatotropin should be approached wisely, because its long-term overdose can provoke undesirable consequences for the body. If you notice any side effects, you should stop injections immediately.

