Multinodular goiter and its types. Multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland: symptoms and treatment.
This disease thyroid gland People over 50 years of age who live permanently in areas of iodine deficiency suffer. This pathology affects 5% of the population, but the female population is 3 times more likely. The reason due to which such pathologies occur is the connection hormonal changes with an imbalance of thyroid hormones.
The disease affects people as they age. The majority of patients with this diagnosis are aged 45–60 years.
How the disease manifests itself and what troubles should be expected from this pathology
Multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland - this name refers to all nodular neoplasms of various origins and structures with parameters of 10 mm or more. This is a tumor that differs in structure and composition from the tissues of the organ.
The nature of the nodes is:
- Follicular.
- Cystic.
- Colloid and others.
Most often, nodules do not interfere with the performance of the thyroid gland’s duties.
The presence of nodes in the thyroid gland may not interfere with its activity, but treatment is required. Because ignoring this problem can become a threat to life.
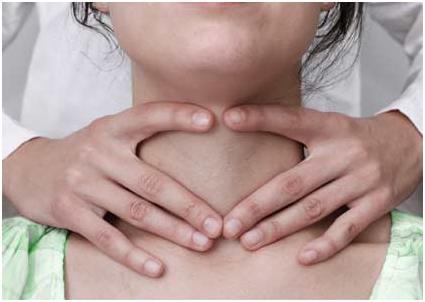 Classification according to the degree of thyroid enlargement:
Classification according to the degree of thyroid enlargement:
- Zero degree - no increase is felt, but symptoms are already appearing.
- First degree - visual changes are imperceptible, but are felt during palpation. An ultrasound examination shows a volume of up to 30 cm³.
- Non-toxic goiter of the 2nd degree is a clearly noticeable increase that is felt upon palpation. Ultrasound records an increase of more than 30 cm.
The size may increase due to diffuse hypertrophy of the thyroid gland or due to colloid nodules.
The main reason for the manifestation and growth of pathology may be due to insufficient consumption of iodine-containing products. It has been noted that more than a third of the population is susceptible to pathology when there is insufficient iodine consumption of 50% per day of the required amount over a long period - 10 years or more.
Iodine deficiency contributes to the gradual destruction of thyroid tissue. In this situation, foci of colloidal formations are actively formed, which have a capsular limitation. They, progressively increasing in parameters, often reach enormous sizes.
 The following reasons can become a catalyst for the development of the problem:
The following reasons can become a catalyst for the development of the problem:
- High body weight.
- For anemia.
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal system.
- Sometimes a second pregnancy, and sometimes breastfeeding.
- Inflammation in the thyroid gland.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Infectious diseases.
- Hormonal disorder.
- Toxic substances can provoke thyroid dysfunction.
Some endocrinologists argue that multinodular goiter begins to appear when the DNA cell is damaged. It has been noticed that this disease more often affects people with low incomes who eat poorly.
A large number of thyroid tumors almost always develop as benign and are not a threat to the patient’s life, but very rarely such formations can become malignant. And this situation clearly poses a danger to humans. In any case, if even a small symptom appears, you should consult a doctor.
 Most often the pathology is many nodular goiter develops as a colloidal form, in which initial stage symptoms do not appear or are absent at all. With this form of development, its manifestation can be noticed only when the size of the thyroid gland begins to increase.
Most often the pathology is many nodular goiter develops as a colloidal form, in which initial stage symptoms do not appear or are absent at all. With this form of development, its manifestation can be noticed only when the size of the thyroid gland begins to increase.
When multiple formations develop, the symptoms of a multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland have a pronounced character:
- Mood changes frequently and dramatically.
- Hand twitching that starts unexpectedly.
- Weight fluctuations in both directions: both decrease and increase.
- Neck deformity.
- Difficulty remembering, frequent forgetfulness.
- Distracted attention, inhibited movements.
- Tachycardia.
- Discomfortable neck condition.
- Hard breath.
- Sweating increases.
- Chills, then thirst.
- Disorders
- Chronic fatigue.
 Colloid goiter of the thyroid gland is benign education. There may be several nodular formations or a single instance. A formation is formed when the outflow of colloidal composition from the follicle is disrupted. The iron-like structure contains thyroglobulin, iodine and amino acid. With this disease, there is a pathological enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Colloid goiter of the thyroid gland is benign education. There may be several nodular formations or a single instance. A formation is formed when the outflow of colloidal composition from the follicle is disrupted. The iron-like structure contains thyroglobulin, iodine and amino acid. With this disease, there is a pathological enlargement of the thyroid gland.
The thyroid gland consists of follicles: vesicles filled with liquid colloid.
Thyroids are produced in this liquid substance.
The colloid form of the disease begins to develop during:
- uncontrolled enlargement of follicles;
- the number of follicles increases rapidly.
Based on structural changes, multinodular goiter is divided into 3 types:
- Nodular – increases unevenly. More often, women who have had uterine fibroids suffer from it.
- Diffuse – the increase occurs evenly. This type is more common in the younger generation.
- Mixed - the name is endemic nodular goiter. Some areas are uniform, others grow unevenly.
Multinodular colloid goiter is not dangerous problem thyroid gland. Modern methods diagnostics allow us to identify the disease and find effective treatment.
 The choice of treatment is made taking into account:
The choice of treatment is made taking into account:
- forms of the disease, stages of development;
- the patient's age is taken into account;
- the presence of other pathologies is determined.
When the disease is benign, it is advisable to use conservative treatment.
Often used to treat nodes ethanol, which is administered using the puncture method.
Sometimes used hormonal drugs containing thyroid.
The diffuse form can be cured with the use of antithyroid drugs and iodine -131.
Surgical intervention is used in the following cases:
- the tumor rapidly increases, and thyroid tissue is destroyed;
- very large deformation of the neck.
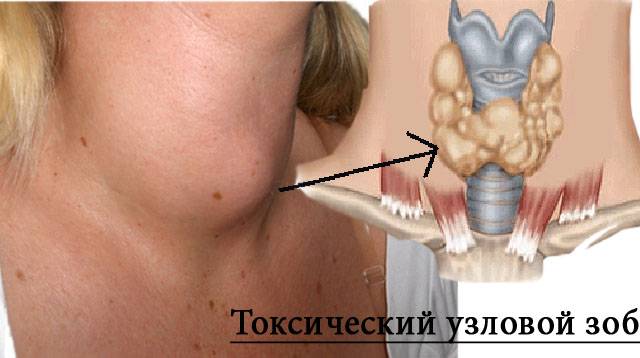 IN in good condition thyroid produces the required amount of hormones, that is, with an increase in TSH, the vigorous production of hormones by the gland contributes to a decrease in TSH. Thyroid-stimulating hormone is produced in the pituitary gland in quantities that maintain the balance of thyroid hormones in the blood.
IN in good condition thyroid produces the required amount of hormones, that is, with an increase in TSH, the vigorous production of hormones by the gland contributes to a decrease in TSH. Thyroid-stimulating hormone is produced in the pituitary gland in quantities that maintain the balance of thyroid hormones in the blood.
On the body of the thyroid gland there are sensitive receptors that respond to TSH. When the TSH content increases, thyroid cells begin to actively produce hormones.
If a patient begins to develop nodular toxic goiter, then its receptors do not perform their functions, but require the thyroid gland to constantly produce hormones, regardless of their content in the blood. This state is called "node autonomy". Such focal neoplasms are very rarely accepted malignant form. If a change occurs, then it is possible at the initial stage, when it is just being formed and its size is still small.
When the nodule is still small, it does not have the ability to influence the amount of hormones. Negative qualities appear when the node size is 25 - 30 mm. Under such conditions, the activity of the thyroid gland, quite possibly, will lead to the appearance of an increased amount of hormones, such a pathology causes a state of thyrotoxicosis.
 At the same time, the pituitary gland reduces TSH, so the thyroid gland stops its activity, but hormones are still produced by focal neoplasms. Multinodular toxic goiter is a problem during which only the affected nodule becomes active, and the organ is dormant.
At the same time, the pituitary gland reduces TSH, so the thyroid gland stops its activity, but hormones are still produced by focal neoplasms. Multinodular toxic goiter is a problem during which only the affected nodule becomes active, and the organ is dormant.
The catalyst for the development of nodules are:
- Insufficient iodine intake from foods.
- Genetic problems.
- High background radiation, poisoning with harmful substances.
- The diet does not satisfy the body's needs for vitamins and minerals.
- Smoking.
- Stressful situations.
- Infectious and viral diseases nasopharynx.
Pathology is manifested by symptoms:
- The patient often gets irritated for any reason.
- Performance decreases.
- Hair falls out, nails break.
- The skin of the body becomes more moist and hot.
- Problems arise in the cardiovascular system.
Toxic multinodular goiter is not accompanied by protrusion of the eyes.
Diagnosis and treatment
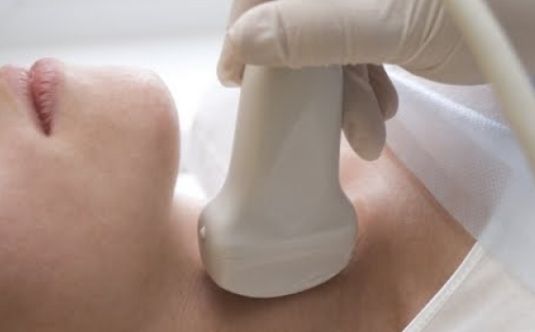 To make the diagnosis of the disease more reliable, after palpation the following is performed:
To make the diagnosis of the disease more reliable, after palpation the following is performed:
- donate blood for TSH, T4, T3 levels;
- biopsy;
- scintigraphy to identify the causes of thyrotoxicosis.
Only after studying all the results does a choice become possible effective treatment. Treatment begins with proper diet. When the level of development of thyrotoxicosis is determined, measures are applied to suppress the activity of tumor foci that synthesize hormones in excess.
Surgery is considered the most reliable treatment method. Sometimes one lobe of the gland or the entire organ must be removed if a multinodular process develops. After surgery, manifestations of thyrotoxicosis disappear.
Treatment using radioactive iodine
The thyroid gland is capable of accumulating iodine that enters the body. But when the organ itself is in an inert state, and the nodular formations are active, then these formations accumulate iodine, but only in the nodular tissues.
When using this method, iodine -131 is injected into the patient's blood, which accumulates in the nodular tissues. This accumulation allows I -131 to have a destructive effect on the composition of the nodular tissue.
Uninfected thyroid tissue is not damaged.
This method is the most effective. There are no traces left after it is carried out and the disease itself disappears. But people are skeptical about this method. It is very difficult to accept that radiation in this case is therapeutic.
Has an increased size. In some cases, this pathology does not pose any danger, but most often endocrinologists diagnose multinodular goiter. It occurs due to poor ecology and lack of iodine in the body. Nodes are most often benign, but sometimes they can degenerate into a malignant tumor, which is removed surgically. In this article we will look at what a multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland is. Treatment and reviews about it will also be considered.
Description of the disease
Due to insufficient iodine content in food and water thyroid-stimulating hormones begin to be produced by the thyroid gland in large quantities, since the organ itself is not able to produce the required amount of its own hormones.
Thyroid-stimulating hormones produced by the pituitary gland provoke the proliferation of gland cells, resulting in its rapid increase. As soon as the need for these special substances begins to decrease, the accumulated colloid in the tissues of the organ leads to the formation of large follicles. Outwardly, it resembles a large goiter, which is visible to the naked eye and can often be felt by the patient himself.
After a certain amount of time, the body restarts the production of thyroid hormones, and the thyroid goiter continues to enlarge.
Types of disease
Multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland is of three types:
- nodular - it is diagnosed in case of uneven enlargement of the organ, which occurs due to its excessive activity;
- diffuse - in this case, the gland tissue grows evenly due to a decrease in its secretory function;
- mixed - rare, with the organ having an uneven increase, but some areas retain their homogeneity.
If more than two nodes exceeding 1 cm in diameter are detected, a test is prescribed. Most often, they are benign. Basically, these neoplasms do not have any effect on its function, and such a disease is called “multinodular euthyroid goiter" Only in 5% of cases the nodes can be malignant.
In our country, multinodular toxic goiter occurs in 12% of the population, and women suffer from it more often than men. With age, the likelihood of developing this pathology increases, and it is most often detected at 45-60 years of age.
Although the presence does not in any way affect the functioning of this organ, the disease still needs to be treated. There are situations when inattention to the problem can pose a threat to life.
Causes of the disease
The exact reasons why multinodular goiter occurs are not fully understood, but doctors confidently say that it is the lack of iodine that largely provokes this disease.
Other factors contributing to the formation of this pathology are:
- malfunctions of the central nervous system;
- psychological stress;
- oppression humoral immunity;
- harmful working conditions;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- genetic predisposition to the occurrence of this disease;
- diseases of the liver and digestive system;
- overloads caused by adaptation;
- exposure to radiation;
- frequent inflammation in the thyroid gland;
- poor nutrition.
Symptoms
A person may not know that he has a multinodular goiter, the symptoms of which are early stage may not manifest themselves in any way and may not cause any discomfort to the patient. While the nodes are small, about 2 cm in diameter, it is quite difficult to see them with the naked eye, so they are often detected on ultrasound during a routine examination.
If this problem is left unattended, hyperthyroidism may develop after some time. The patient begins to worry about excessive sweating, irritability, tachycardia occurs, blood pressure rises, and general health worsens. Tingling sensations may appear in the heart area, appetite increases, the person wants to drink all the time, and he begins to lose weight. There is trembling of the fingers, tongue and whole body. At night, patients feel unbearably hot, and they begin to experience fear and anxiety. Such symptoms lead to decreased sexual desire.
![]()
Sometimes a multinodular toxic goiter can grow so large that it begins to put pressure on nearby organs. The patient's voice changes, it becomes difficult for him to swallow, breathe, and a feeling of constriction or suffocation occurs in the neck area, especially in a supine position.
Diagnosis of goiter
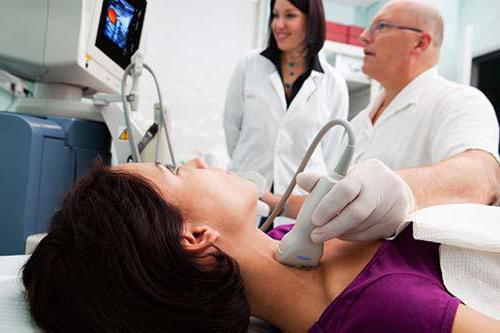
If there is a suspicion that the patient has a multinodular goiter, then the thyroid gland is diagnosed. First, the patient is examined by a doctor, then he is sent for an ultrasound scan of this organ. If the nodes exceed 1 cm in diameter, then puncture and fine-needle biopsy of these tumors is prescribed. Hormone tests and organ x-rays are also carried out. chest when a feeling of squeezing occurs, MRI and scintigraphy.
Methods of treating the thyroid gland
Since at the very beginning of its development a disease such as multinodular goiter is practically asymptomatic, after some time a person begins to feel its destructive effects. The patient loses weight sharply, irregularities occur in the heart, and increased nervousness and severe fatigue.

If a diagnosis of multinodular goiter has been established, the doctor may prescribe the following treatment:
- daily iodine supplement medical supplies, the course of treatment in this case is quite long;
- injection into a diseased organ which helps to reduce nodes.
If such treatment does not help, the multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland is subjected to surgical intervention, especially with its large size.
Treatment with LITT
If conservative methods fail to stop the growth of the goiter, the doctor may prescribe laser-induced interstitial thermotherapy (LITT). In this case, a light guide is inserted into the node. As a result, the protein structures of the goiter tissue begin to be affected by a temperature of 41-46 degrees, due to which the cells stop dividing.
The advantages of this method are that no preliminary preparation is required before the procedure, treatment can be carried out without anesthesia, and all functions of the thyroid gland are preserved.
But this method of treatment also has contraindications:
- somatic diseases;
- severe forms of thyrotoxicosis and hypothyroidism;
- mental illness;
- inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
Traditional methods of treatment
If a person is diagnosed with a multinodular goiter, treatment (reviews eloquently testify to this) folk remedies can significantly improve the patient's condition. As a result, the normal production of hormones in the body is restored, and it is replenished with the necessary amount of iodine.
Should be consumed every day seaweed, drink hawthorn tincture, take warm baths with sea salt etc. Using various medicinal herbs The multinodular goiter returns to normal.

The following medications bring the greatest effect:
- Grass spring adonis mix equally with peppermint, tricolor violet, oregano, medicinal calendula flowers, chamomile and cudweed. This fee is insisted on hot water two hours and taken before meals.
- Mixed medicinal valerian, lemon balm, dried rowan fruits, plantain leaves, high clover, leftwort, wormwood, wild strawberry leaves, yarrow, leaves medicinal sage, pour boiling water and leave. It is necessary to take the infusion every day, 15 minutes before meals.
- Mix in equal proportions medicinal calendula, cudweed, heart-shaped linden, prickly hawthorn, chamomile flowers, rose hips, garden thyme and pour boiling water over it. The collection is heated in a water bath, left for about 2 hours, filtered and consumed several times a day.
- Connect together such medicinal plants, like prickly rose hips, lemon balm, chamomile, oregano, narrow-leaved willowherb, comfrey, azure blue, big plantain and garden thyme. Not a large number of the collection is crushed into powder and poured with boiling water. You should drink several times a day.
Herbal medicine usually lasts 1.5-2 months, after which they take a break of several weeks.

To consolidate the result when improving the condition of the thyroid gland, the following medications are recommended:
- Take equal amounts of calendula, pharmaceutical chamomile, valerian, peppermint And wild strawberries, mix and pour boiling water. Infuse for 2 hours in a warm place, then filter and take three times a day 15 minutes after meals.
- Mix St. John's wort, leaves narrow-leaved fireweed, rose hips, oregano, dried flowers of the heart-shaped linden, pour boiling water and infuse in a warm room. Strain and consume 4 times a day after meals.
Conclusion
So, we have looked at what a multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland is. Treatment (reviews from many people confirm this) is quite successful if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. Can't run this dangerous disease, because it is fraught with many life-threatening complications.
An increase in the shape of the thyroid gland and its structure is fraught with serious consequences for the entire body. Complications can range from discomfort in the throat when swallowing to choking or cancer. Signs of the disease may appear in areas unrelated to the source of the problem.
An increase or decrease in the hormones of this gland can occur in both adults and children, which can result in a new formation. Treatment of the disease may involve adjusting the behavior of hormones, bringing the amount of iodine to normal, using folk remedies and observing special diet. The degree of pathology affects the treatment method.
Nodular goiter of the thyroid gland - what is it?
In many people it can be found signs of development of nodular compaction in the thyroid gland. Compaction may occur under thyroid cartilage front of the neck. The thyroid gland consists of two parts, located on either side of the tracheal tube, connected by a jumper.
The organ is part of endocrine system, which forms hormonal background person. In terms of composition, iron is a series of spherical cells of the same structure.
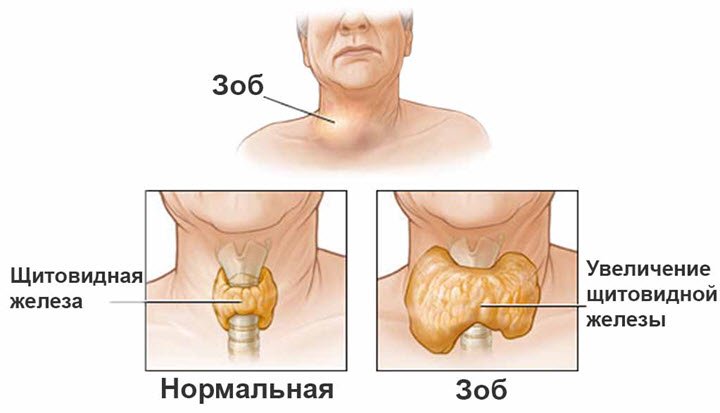
Changes in the cells that form the gland cause the formation of a nodular compaction. Induration in the initial stage is not oncology. An increase in nodular formation can lead to various diseases.
The disease is often found in women. During examination, in addition to nodal disease, women may find uterine fibroids, oncology in the thyroid gland, and microadenoma. The disease is found less often in men than in women. As the number of years increases, the likelihood of lump formation increases.
Causes of appearance and classification
Reasons for the formation of the disease, affecting the thyroid gland, expressed by the appearance of nodular compaction:
- lack of iodine in the body;
- constant nervous environment, stress;
- impact environment, radiation;
- age;
- diseases leading to increased load on the gland;
- inflammation in the endocrine system;
- use medications long time;
- heredity.
Considering the hormonal background formed by the endocrine system, the disease can be classified according to the level of functioning of the thyroid gland. Increased level hormones in the endocrine system leads to a toxic appearance.
As the level decreases, the goiter becomes non-toxic. Nontoxic goiter is determined by nodular or diffuse enlargement. If the hormonal levels are normal, the nodular goiter is euthyroid. If hormone secretion is low, the goiter is considered hypothyroid.
Based on the number of compactions in the thyroid gland, nodular goiter is divided into types:
- solitary (one node);
- multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland;
- conglomerate (connected nodular formations).
A seal becomes multi-node if there are more than two seals.
An uneven structural enlargement of the thyroid gland determines nodular goiter. If the increase is uniform, secretory function decreases, the goiter is diffuse.
There is a structural type of disease called endemic or mixed nodular goiter. The disease is determined by uneven enlargement of the thyroid gland with preservation of homogeneous areas. If, along with the formation, fluid accumulates in the follicles of the gland, it is a colloid type.
There are five degrees of development of thyroid nodules.
- If in men or women the disease has degree 1, it is characterized by the absence visible symptoms disease, nodular goiter can be identified by palpation.
- A grade 2 thyroid goiter is visible when a person swallows.
- The third degree changes the shape of the neck.
- In the fourth stage of the disease, changes in the neck lead to a visible bulge.
Pathology of the 5th degree leads to pressure of the thyroid gland on the organs of the neck.
Symptoms of thyroid goiter
The formation and increase in size of a nodular formation in men and women is accompanied by visible consequences, which are found in the area of the thyroid gland.
As women increase in size, men develop discomfort When swallowing, signs of obstruction and pain are felt in the throat.
The disease may have signs of coughing and voice changes. Signs of the disease may include dizziness and breathing problems.
Signs of pathology can be indirect, caused by a failure of the endocrine system:
- feeling of nausea;
- arrhythmia, hypotension;
- swelling;
- low temperature;
- dyspnea;
- drowsiness during the day, insomnia at night, depression;
- weight loss.
Consequences of education may occur in the form of persistent respiratory diseases.
In men, the disease leads to a decrease in potency; signs of thyroid goiter in women can manifest themselves in disruptions of the menstrual cycle, which is caused by hormones.
Problems with the endocrine system can lead to miscarriages and infertility in women. In children, signs include developmental delays. There have been cases of deterioration in memory and attentiveness in children. It is believed that bulging eyes may be a sign of the formation of a nodular goiter in the thyroid gland.
Multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland
Along with the formation of one nodular goiter, new compactions may appear in the thyroid gland. The pathology develops, the formation of more than 2 nodular seals leads to a multinodular form of the disease. The size of the seals is considered to be more than 10 mm.
Multinodular goiter can occur due to a cyst; there are colloidal and follicular multinodular formations. Different types multinodular formations can be combined.
Signs of a multinodular seal similar to symptoms with single seal. Men and women may not experience unpleasant sensations indicating the formation of a multinodular goiter for years.
When the size reaches 1 cm, the knot can be felt. Ultrasound and hormonal tests will help confirm the presence of a multinodular formation. Your doctor may order a cell test for the node.
Multinodular goiter is classified according to its degree:
- Grade 1 – multinodular disease is not noticeable;
- 2nd degree – multinodular goiter is palpable;
- Grade 3 – multi-nodular compaction becomes visible.
Multinodular disease may have serious consequences, on its basis oncology can arise. In most cases, formations are benign; the percentage of malignant multinodular diseases is minimal.
Without starting treatment on time, multinodular disease can have consequences such as increased activity thyroid gland.
Colloid and diffuse goiter
Colloid goiter associated with the accumulation of colloidal fluid with a gel consistency in the follicles of the thyroid gland. The cause of the colloid type is due to the problem of the outflow of colloid from the follicle.
Signs of colloid type similar to the symptoms of a normal nodular non-toxic compaction. The consequence of the formation of the colloidal form may be an increase or decrease in the production of hormones due to the occupancy of the inside of the follicle by the colloid. The colloid type is characterized by edema.
Patients with colloid type gain weight along with a decrease in the amount of hormones. If the colloidal form has increased hormone production, the person will gain weight. The sensation of dry skin may be due to the colloidal appearance.
Patients with colloid disease note decreased sweating leniya. Colloidal fluid may accumulate in the cyst. The cyst is located in a membrane; colloidal fluid can accumulate inside it, which leads to an enlargement of the organ. It is necessary to observe the cyst when it forms.
Colloid goiter can be:
- diffuse,
- nodal,
- non-toxic,
- mixed.
Diffuse disease can occur with a uniform increase in the size of the gland. Diffuse goiter is a consequence of a decrease in its secretory function.
Diffuse disease characterized by a mixed form, combining the properties of nodular and diffuse formation. Mixed type is determined by an increase in the volume of the thyroid gland and uneven diffuse nodules. The diffuse form is considered a common endocrine disease.
Diffuse type disease may be observed in children when moving to adolescence when hormones act. Among women the diffuse type can occur during menopause and is a consequence of the work of endocrine system hormones.
When women become pregnant, there is an enlargement of the organ, signs of a diffuse form due to a lack of hormones. In men, those employed in hazardous work can be diagnosed with the diffuse type.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out in several stages.
- If signs of pathology occur, a person should consult a doctor who will examine the thyroid gland by palpation.
- The doctor, having confirmed the signs, will send you for an ultrasound to determine the size of the formation and the degree of the disease.
- When the size of the formation reaches 1 cm, a biopsy is prescribed, and the pathology is checked for malignancy. As part of the diagnosis, the patient must undergo a hormone test.
- Determination of the functional autonomy of the thyroid gland is carried out by radioisotope scanning.
- X-rays of the esophagus and chest will help detect the consequences of pathology.
- The size of the thyroid gland, structure, outline, and degree of pathology can be seen through tomography.
Treatment methods for thyroid goiter
Treatment of pathology may involve the use of one method or a complex. The disease can be treated with hormone tablets. Treatment of the disease can be carried out with radioactive iodine.
- As the size increases, surgery will be prescribed as part of the treatment. Slowing down the activity of the gland as part of the treatment of the disease can be achieved with antithyroid drugs.
- Nodular nontoxic thyroid disease can be treated with radiation. The doctor does not cancel treatment with folk remedies unless they cause the consequences of an increase in the size and severity of the disease.
- Having detected a diffusely nodular goiter of the thyroid gland, treatment will be carried out with drugs that normalize the functioning of hormones. Additionally, the doctor will prescribe iodine supplements to normalize the functioning of the organ.
- Multinodular goiter is treated with L-Thyroxine to reduce the level of thyroid hormones. If the level of hormones of the endocrine system is exceeded, the doctor will prescribe thyreostatics. To treat multinodular formation, you can use radioactive iodine 131.
Treatment of thyroid goiter in women is necessary during periods of changes in hormone concentrations, disruptions in the endocrine system during adolescence, pregnancy, and menopause. With the aim of
Treatment with folk remedies - how to treat goiter in women

Having determined the thickening of the thyroid gland, symptoms and treatment with folk remedies, you need to undergo an examination by a doctor to determine the course of treatment and choose folk remedies that will not lead to negative consequences.
- You can cure pathology with folk remedies through milk and iodine.
To prepare a folk remedy, you need to add a drop of iodine to the milk and treat with the remedy 2 times a week. - Among the folk remedies there are garlic treatment. Garlic cloves should be strung on a thread and left on the neck overnight to cure the disease.
- A similar folk remedy as part of treatment traditional medicine presented amber beads.
- Iodine is an effective folk remedy for the treatment of pathology. At night, apply iodine to your heels or elbows, this will help cure the disease.
Nutrition for nodular goiter of the thyroid gland

The diet of children, women and men who have been diagnosed with pathology should contain foods rich in iodine. The doctor will prescribe a diet to support the body. It is impossible to cure a disease with diet alone; the diet consists of a complex treatment of endocrine disease.
Diet for men, is the same for women and children. Products contained in the diet should contain large amounts of carbohydrates, salts, and vitamins.
- Fish (herring, cod) is required as part of the diet.
- Vegetables in the diet are dominated by beets and garlic.
- Citrus fruits and bananas should be included in the diet.
- Fermented milk products are not excluded from the diet.
- Meat in the diet is represented by beef.
- Diet restrictions include chocolate, tea, and coffee.
Drugs for the treatment of thyroid goiter

The main method of treating the disease is to prescribe iodine preparations or medications that help normalize hormone production. In children they are prescribed iodine-containing drugs. If children have not started transitional age, tests did not show an excess or decrease in hormone production, radioactive iodine is prescribed.
Treatment in children will be carried out with folk remedies, a diet with a minimal prescription of the drug. The drug is prescribed for children Diiodotyrosine. If the severity of the disease increases, the doctor will prescribe different treatment.
Women may have a combination of drugs depending on the causes of the disease. A doctor can treat the disease in women with drugs that replace hormones of the endocrine system. Treatment in both women and men can suppress the organ's production of hormones.
If you treat the disease in women with hormones, it may improve menstrual cycle. Improved sexual function may occur in men when taking hormones.
The drug that can be used to treat the disease is Mercazolil. To cure the disease, the doctor may prescribe Propylthiouracil. Treatment can be carried out Carbimazole.
Goiter prevention
Prevention of thyroid goiter is considered the best remedy to prevent the need to treat pathology. The presence of signs of predisposition to the disease should indicate the need to bring the daily amount of iodine to normal.
Taking vitamins in men, women and children will help improve the functioning of the endocrine system.
Children, women and men should have fish in their diet. It is beneficial to consume iodized salt daily. You need to salt food after cooking.
A visit to the doctor if signs of an enlarged gland are detected is an important point of prevention.
Italian Renaissance artists often depicted women with an enlarged thyroid gland in their paintings, apparently at that time - this phenomenon was so common that it was the norm.
Also, over the past decades, there has been a steady increase in the incidence of thyroid pathologies in the population.
Among endocrine diseases, their incidence is close to diabetes mellitus. The reason for such high rates is poor ecology, low-quality food and lack of iodine in water and food.
What is a multinodular goiter?
Multinodular goiter is a disease that unites all formations in the thyroid gland in the form of nodes that have different origins, structure and size more than 10 mm.
Nodes can be of different natures:
Follicular;
Cystic;
Colloidal and others.
In some cases, a combination of several types of nodes is simultaneously observed in one patient.
Depending on the structural changes In the structure of the gland, multinodular goiter is divided into 3 types:
Nodular: diagnosed with uneven enlargement of the thyroid gland, which is caused by its excessive activity.
Diffuse: occurs when the gland tissue grows uniformly, which indicates a decrease in its secretory function.
Mixed: quite rare and is called “endemic nodular goiter”. In this case, the thyroid gland is unevenly enlarged, but some of its areas remain homogeneous.
If more than two nodes are detected, the size of which exceeds 1 cm in diameter, a puncture of the thyroid gland is recommended. The vast majority of identified thyroid nodules are benign. As a rule, such neoplasms do not affect its function, and with such a development of the disease they speak of multinodular euthyroid goiter. Only 5% of detected nodes turn out to be malignant.
The mechanism of development of cancerous malignant and benign neoplasms is different. Tumor nodes are formed by abnormal rapid division of one of the gland cells due to damage to its genetic code. Malignant nodes cannot be replaced healthy cells glands, but penetrate between them. In a benign pathological process, the node grows and compresses the surrounding tissue.
Despite the fact that the presence of nodes in the thyroid gland may not affect its normal work, the disease requires mandatory treatment. In some cases, ignoring such a problem poses a threat to life.
Symptoms of multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland

Multinodular goiter may not affect the function of the thyroid gland for many years, and the patient does not experience discomfort or complaints. Until the node reaches a size of 1–2 cm in diameter, it is quite problematic to see it externally. With this course of the disease, nodes are often detected during routine examinations using an ultrasound machine. If you do not pay attention to this problem in time, hyperthyroidism, or hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, may develop over time.
The clinical picture of multinodular goiter resembles toxic diffuse goiter, but there is no ophthalmopathy and myxidema. The patient may be bothered increased sweating, irritability, deterioration general well-being when the outside temperature rises, rapid heartbeat And arterial hypertension. Sometimes the patient may complain of tingling in the heart and in the area of the shoulder blades, as well as increased appetite, constant thirst, diarrhea and weight loss. In addition, there is trembling of the fingers, tongue and whole body. At night, such people are haunted by a feeling of heat, they are characterized by fear and anxiety. Against the background of such symptoms, potency and libido are significantly reduced.
Sometimes the thyroid gland grows and takes on irregular shapes, which are noticeable not only to the doctor, but also to his patient. Usually by this point the gland is so large that it compresses nearby organs. In this case, there is a change in voice, difficulty swallowing, breathing, a feeling of compression or suffocation in the neck, this feeling is especially clear in a lying position.
You can try to detect a nodule on the thyroid gland yourself. A healthy gland is homogeneous and elastic; if dense areas are detected upon palpation, these may be nodes. They are usually not connected to the skin and are mobile when swallowed.
A multinodular goiter, which does not manifest itself externally, is detected during examination with an ultrasound machine. After this, a hormonal examination and, if necessary, examination of the node cells are prescribed. The prescription of further treatment depends on the results of these tests.
Degrees of multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland
At pronounced signs Goiter of the thyroid gland, the disease is divided into 3 degrees:
1st degree multinodular goiter. Upon external examination and palpation of the thyroid gland, there is no manifestation of multinodular goiter. To diagnose the disease and confirm the diagnosis, studies are carried out using other methods.
2nd degree multinodular goiter. There is a slight increase in the volume of the gland, which is determined only by palpation; during an external examination, changes in its size are not determined.
3rd degree multinodular goiter. Significant proliferation of thyroid tissue, which becomes obvious not only upon palpation, but also upon external examination of the patient.
A goiter may not lead to a visible enlargement of the thyroid gland or provoke its significant growth, in which it occupies the entire neck and even descends behind the sternum.
The exact causes of the development of the disease are not fully understood, but insufficient iodine intake from food has a significant impact on the development pathological process.
In addition, the following may be provoking factors:
Disruption of the central nervous system;
Diseases of the liver and digestive system;
Psychological stress;
Overloads associated with adaptation;
Suppression of humoral immunity;
Radiation exposure;
Harmful working conditions;
Frequent inflammatory processes in the thyroid gland;
Long-term use of certain medications;
Poor nutrition;
Genetic predisposition to the disease.
Purpose proper treatment depends on understanding the processes occurring in the thyroid gland. With iodine deficiency, the secretory activity of the organ decreases and iron begins to reduce the production of thyroid hormones, which stimulate its activity. A signal about hormone deficiency enters the brain, and the pituitary gland begins active production hormone TSH stimulating the thyroid gland. Under the influence of pituitary hormones, thyroid cells actively divide, causing the gland to increase in size. This can be called a compensatory response to iodine deficiency. Thus, the body strives to independently increase the volume of the thyroid gland in order to more effectively remove the required amount of iodine and other substances from the blood.
When the body's need for thyroid hormones decreases, colloid accumulates in the gland. Clinically, this manifests itself in the form of the formation of a voluminous goiter. Inside it is filled with follicles that contain colloidal substance. When the body again needs an increased concentration of hormones, the thyroid tissue grows again. Such wave-like processes can be observed over several years, this leads to the appearance of a multinodular goiter.
The female body is more susceptible hormonal pathologies from the thyroid gland due to hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause and monthly during menstruation. Negative influence increased secretion of specific hormones triiodothyronine and tetraiodothyronine in women can have an effect.
One more important factor, influencing the occurrence of goiter are internal autoimmune processes. Against the background of a decrease in humoral immunity, specific protein substances appear in the blood, which activate the body’s resistance to its own thyroid hormones. Similar condition against the backdrop of unfavorable external environment often leads to a significant decrease in the activity of the thyroid gland (hypothyroidism), which can ultimately cause cancer.
Treatment methods for multinodular goiter are determined depending on the reasons that caused its appearance. According to endocrinologists, not all types of this disease require mandatory treatment. In some cases, doctors recommend regularly monitoring the condition of the gland and, in case of active growth of nodes, using therapy methods. With a competent doctor’s approach, and the patient follows all the necessary preventive rules, he can live with this disease for several decades and not need treatment. surgical intervention. Treatment of multinodular goiter can be either conservative or surgical.
L-thyroxine. Conservative therapy prescribed to patients with elevated or reduced level thyroid hormones in the blood. For hypothyroidism, treatment with L-thyroxine is prescribed; its dose is determined based on the results of the analysis, depending on the TSH level. The dosage of the drug and the duration of its use are selected only in individually. Typically, a decrease in goiter is observed after 6–8 months of regular use of the drug. Sometimes longer therapy is required, which can last up to two years. After completing the course of treatment, medications containing iodine are prescribed for a year to prevent the disease.
Thyrostatics. Increased output thyroid hormone treatment involves taking thyreostatics that suppress its activity, and drugs that accelerate the metabolism of these hormones in the body. In addition, they are appointed combination drugs, which contain iodine. This is necessary to iodine tyrosine in the thyroid gland and slow down the synthesis of TSH, which leads to stopping the growth of goiter. Such therapy is used in the first stages of the disease and in preparation for surgery.
For multinodular eutheroid colloid goiter medications are not prescribed due to the fact that active ingredients These funds are not able to affect these formations. Therefore, if the origin of the pathological process is not determined in time, then treatment conservative methods will be meaningless and will not bring results.
Radioactive iodine-131. Injection of radioactive iodine-131 into the thyroid gland has been successfully used to treat the disease. This isotope causes the death of node cells. Similar procedure allows you to target the neoplasm, while surrounding healthy tissue remain undamaged. Subsequently, the gland acquires a normal volume, the size of the nodes decreases or their complete disappearance is observed.
Are common preventive actions in case of thyroid diseases, provide healthy image life, dietary diversity and rationed physical exercise. Increased consumption of iodine-containing foods and complex vitamins only necessary after consulting a doctor.
Author of the article: Valentina Ivanovna Zubolenko, endocrinologist, especially for the site ayzdorov.ru

- Symptoms of pathology
- Traditional medicine in the fight against multinodular goiter
Multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland is a fairly common pathology. Thyroid diseases are mostly associated with one problem - lack of iodine in the body. For example, in the region where a sick person lives, the drinking water does not contain iodine.
With diseases of the thyroid gland, a goiter appears. Goiter pathologies are divided into several groups. There is a nodular goiter, which forms a kind of knot on one side of the neck. The situation is more complicated if a person has a multinodular toxic goiter of the thyroid gland. The disease occurs quite often. Toxic multinodular goiter is characterized by the formation of several nodular cones inside the thyroid gland of a malignant nature. If the node is less than 1 cm in diameter, then it is not considered a node. They are called “incidentalomas,” which translates as “chance finds.” They do not pose any danger to the body.
Multinodular goiter is diagnosed in the same way as nodular goiter. If thyrotoxicosis is observed, then scintigraphy is performed to find out why the thyroid gland produces an excess of hormone.
Many people treat multinodular goiter by applying iodine grid. But this method of treatment cannot help if the treatment is not approached comprehensively. Moreover, multinodular goiter is not considered as a separate disease; it is usually a concomitant manifestation of the underlying disease.
Provoking factors and symptoms of multinodular goiter
Return to contents
Causes of multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland
The appearance of multiple nodes on the thyroid gland can provoke any disease, such “provocateurs” include: 
- Euthyroid colloid goiter, quite often manifests itself in the form of a multinodular goiter.
- Autoimmune thyroiditis.
- Toxic multinodular goiter.
- Cancers in the thyroid gland.
The appearance of a multinodular goiter may be preceded by certain circumstances:
- Food lacking iodine-containing products.
- Polluted environment.
- Bad habits in humans: drinking alcohol and drugs, smoking.
- The presence of the disease in close relatives.
- Diseases that have become chronic.
Return to contents
Symptoms of pathology
Symptoms of multinodular goiter depend on the severity of the disease. If this is associated with eutheroid colloid goiter, then there are almost no complaints, the only thing is that the patient may complain about the unaesthetic appearance of his neck.
With hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, the symptoms manifest themselves as follows: a person loses weight sharply, the skin dries out, sleeps poorly at night, and increased nervousness.
To find out exactly how many nodes were formed, ultrasonography. Ultrasound finds even the smallest nodes. In order to exclude oncology, a biopsy and cytological examination are prescribed.
Return to contents
Thyroid goiter: treatment
 Multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland is eliminated through surgery. But there may also be contraindications to surgical method treatment. For example, elderly age patient, intolerance to anesthesia, exhaustion of the body, various chronic diseases. In this case, radioiodine therapy is prescribed.
Multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland is eliminated through surgery. But there may also be contraindications to surgical method treatment. For example, elderly age patient, intolerance to anesthesia, exhaustion of the body, various chronic diseases. In this case, radioiodine therapy is prescribed.
If a multinodular goiter arises as a result of oncology, in addition to the endocrinologist, an oncologist deals with this problem. And he already prescribes diagnostics and subsequent treatment.
If the disease does not cause any other disorders and is detected by chance and has several small nodules, then treatment in this case is not advisable, much less surgical intervention. You should periodically see an endocrinologist and do an ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
In some cases, when a goiter deforms the neck, especially in women, patients themselves ask to remove the nodes through surgery. But if nodular goiter is diagnosed incorrectly, then surgery will not help.
At oncological diseases the operation is provided. Benign tumors are removed, and subsequently hormonal drugs are prescribed. Malignant tumors provide combination treatment. Surgery removes the focus of pathology, then chemotherapy is carried out in order to destroy cancer cells in order to prevent their spread throughout the body.
If surgery is not indicated, your doctor may prescribe medications to suppress the synthesis of thyroid hormones. In addition to this, medications are prescribed that accelerate the metabolism of thyroid hormones in the body.
This disease does not cause dire consequences. A person can live with this diagnosis for many years. But you will have to follow all the doctor’s instructions for treatment and preventive measures.
Multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland is rarely a manifestation of oncology. But it still doesn’t hurt to get checked further.
Return to contents
Thyrotoxicosis as a manifestation of multinodular toxic goiter
 Thyrotoxicosis occurs when a person has an excess of thyroid hormones in the blood. One of the reasons for thyrotoxicosis, due to which the thyroid gland begins to secrete this hormone into the blood, can be a multinodular goiter.
Thyrotoxicosis occurs when a person has an excess of thyroid hormones in the blood. One of the reasons for thyrotoxicosis, due to which the thyroid gland begins to secrete this hormone into the blood, can be a multinodular goiter.
With an excess of T3 and T4 in the blood, all metabolic processes in organism. Characteristic symptoms thyrotoxicosis can be:
- increased sweating;
- dyspnea;
- hypertension;
- fatigue;
- diarrhea;
- irritability, sudden weight loss;
- decreased sexual activity.
With multi-node toxic goiter Hormones are produced not by the entire thyroid gland, but by its nodal connections, which appear as a result of nodular goiter. This production of thyroid hormones can be erratic. Often this picture is observed in people living in areas where there is a significant lack of iodine.
Thyrotoxicosis is diagnosed in multinodular goiter radioisotope research thyroid gland.
Often in the treatment of thyrotoxicosis with threostatic drugs desired effect does not occur, since multinodular goiter cannot be treated with these drugs. Thereostatic drugs can only suppress excess thyroid hormones and improve the patient's condition. The multinodular goiter of the thyroid gland itself cannot be cured. Multinodular goiter is mostly treated surgically or using traditional medicine.

