Do I need to remove the thyroid gland? Possible consequences of the operation. Radiofrequency ablation of thyroid nodules
Removal thyroid gland(thyroidectomy) is a complex, high-tech operation that requires considerable experience and highly qualified surgeons. Such interventions are carried out quite often, and it is advisable that treatment takes place in a center specializing specifically in diseases of this organ.
Disputes regarding the indications for removal of the thyroid gland continue to this day. It is possible to live without this organ, but the patient is forced to take hormonal medications for the rest of his life, Therefore, before deciding whether surgery is really necessary, the doctor carefully weighs the pros and cons.
Surgeons performing interventions on the thyroid gland have experience working with endocrinological patients, train not only in the field of surgical techniques, but also in endocrinology, and the treatment process itself takes place under close attention from endocrinologists and doctors of other specialties.
Before deciding to undergo surgery, the patient must choose the place where it will be performed, since The outcome and outcome of treatment largely depends on the doctor’s experience. It is believed that to achieve the required level of skill, a surgeon must perform at least 50 operations per year, and it is better if this figure reaches 100. In such cases, the specialist acquires a sufficient amount of knowledge in the field individual characteristics structure and location of the gland, character pathological processes in it.
On modern stage The process of removing the thyroid gland is aimed not only at excision of the organ, but also, which is extremely important, at preserving the recurrent laryngeal nerves, since their intersection is the main adverse consequence that patients experienced during standard operations performed in the very recent past. The use of modern low-traumatic technologies and endovideosurgical manipulations allows us to minimize the incidence of complications and improve the quality of life in the postoperative period.
Removal of the thyroid gland, performed by a competent and an experienced doctor in compliance with modern standards, does not pose a threat to the life and health of the patient, is accompanied by a minimal frequency of complications and does not require long-term hospitalization and rehabilitation. Subsequent hormone therapy is well tolerated by most patients and does not limit their life activity in any way. The mortality rate during thyroidectomy does not exceed a hundredth of a percent, so the procedure can be considered safe.
When is a thyroidectomy necessary?
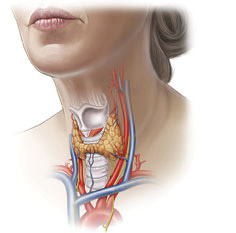 Indications for complete removal of the thyroid gland remain a subject of debate among endocrinologist surgeons; they are often carried out unjustifiably. Today, doctors agree that surgery is indicated in cases where other treatment methods are ineffective or for malignant tumors.
Indications for complete removal of the thyroid gland remain a subject of debate among endocrinologist surgeons; they are often carried out unjustifiably. Today, doctors agree that surgery is indicated in cases where other treatment methods are ineffective or for malignant tumors.
Patients with asymptomatic nodules are not included in the group of those who require intervention; they only need dynamic observation, and the operation will be performed when signs of pathology progression or the possibility of malignant transformation appear.
In Europe and the USA, total removal of the thyroid gland for thyrotoxicosis is considered a last resort, but in post-Soviet space it is still practiced, especially where there are no specialized centers and the treatment is carried out by surgeons in ordinary general hospitals.
In addition, the lower percentage of operated patients in developed countries is associated with greater availability of modern conservative treatment. The realities of domestic healthcare are such that it is easier for the surgeon and the patient to remove an organ and forget about the problem than to look for ways and means for drug therapy.
Among patients with thyroid pathology more women than men, most of them are young or mature people. In females, infertility may occur against the background of thyrotoxicosis, so surgery may be an opportunity to restore reproductive function by eliminating metabolic disorders.
Surgery to remove the thyroid gland is indicated for:
- Malignant tumors;
- Node or diffuse goiter with compression and/or displacement of the neck organs, regardless of hormonal activity;
- Retrosternal goiter, compressing the structures of the mediastinum;
- Fine-needle biopsy data that does not reliably exclude malignant growth;
- Thyrotoxicosis resistant to conservative treatment;
- Increased production of thyroid hormones, when treatment with iodine isotopes is contraindicated (allergy, individual intolerance);
- Deposition of calcium salts in the parenchyma of the gland, which may indirectly indicate a high risk of carcinoma.
The last three indications can be considered relative, therefore in such cases the decision to operate is made individually and only after the doctor is convinced that the operation is the only possible way help the patient. In some cases, surgical treatment is performed for cosmetic reasons, when a protruding formation in the organ causes aesthetic discomfort.
The extent of the planned operation depends on the nature of the pathology affecting thyroid gland. Possible:
- Total thyroidectomy– removal of the entire organ;
- Subtotal thyroidectomy– almost all of the gland is excised, except for small areas and the location area parathyroid glands(impossible for cancer, indicated for diffuse toxic goiter);
- Hemithyroidectomy– removal of half of the organ with the isthmus (with limited nodes of one of the lobes).
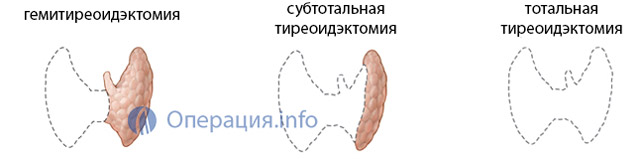
Radical surgery is rarely performed, mainly in oncological practice, and may be accompanied by the removal of muscles, tissue, and lymphatic system of the neck. Most often, surgeons try to preserve at least a small part of the functioning parenchyma, which will provide the patient with hormones after surgery. It is important to leave the laryngeal nerve and parathyroid glands intact.
Methods for removing all or parts of the gland depend on the nature of the pathology, location and volume of the nodes. Intracapsular the method is applicable when single nodes, which can be excised without significant loss of the organ parenchyma itself. Intrafascial The method consists of preserving the fascia of the neck, which eliminates the possibility of damage to the laryngeal nerves and leaves the parathyroid glands intact. Extrafascial The operation option is considered the most traumatic and is used for treatment oncological diseases organ.
Preparing for surgery to remove the thyroid gland
Preparation for surgery to remove a hormone-producing organ is a very important stage of treatment, because the patient’s insufficiently compensated condition with thyrotoxicosis and concomitant severe pathology create a risk serious complications. The doctor’s task at this stage is to provide minimal risk from intervention, maximally stabilizing the patient’s condition.

When planning thyroidectomy, they are indicated as standard diagnostic procedures, including general and biochemical tests blood tests, urine tests, fluorography, coagulograms, tests for HIV infection, hepatitis, syphilis, and special examinations carried out specifically for thyroid pathology.
All patients, without exception, need to determine hormonal status– hormones T3, T4, thyroid-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland (TSH), if necessary, calcitonin, thyroglobulin level, tumor markers are determined.
From instrumental methods Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and organs of the neck, vocal cords is shown. To clarify the nature of the disease, CT, MRI, and scintigraphy can be performed. Fine needle biopsy is a standard procedure indicated for patients with nodal forms organ damage. It allows you to confirm or exclude malignant process, determine the nature of adenomatous nodes.
At all stages of preparation for surgical treatment The patient is consulted by an endocrinologist, therapist, cardiologist. On final stage Based on the general condition, the therapist gives his permission for the operation, and the patient signs the consent, already being aware of possible risks, the amount of treatment and subsequent life without the gland.
A significant obstacle to a planned thyroidectomy may be increased hormone production– thyrotoxicosis, which negatively affects general state, heart activity, metabolic parameters. Under such conditions, total removal of the gland can be fatal due to the risk of developing a thyrotoxic crisis. Mortality in this condition is due to shock, acute insufficiency heart, development of coma and reaches 40%.
To achieve euthyroidism, when hormones return to normal, it may take from several weeks to several months, during which the patient is prescribed thyreostatics (Mercazolil), beta-blockers to normalize the heart rhythm, and glucocorticosteroids. Pregnant women are more likely to take propylthiouracil, which is safer for the developing fetus.
A long preparatory stage is justified, and surgery will be scheduled only when hormones return to normal levels. Accelerating this period or carrying out treatment before achieving euthyroidism is considered gross medical error which could cost the patient his life.
Technique of thyroid surgery
When all preparatory procedures passed, and the patient’s condition does not raise any doubts about the favorable outcome of the operation, a date and time are set. On the eve of the intervention, the patient is placed in the clinic, an anesthesiologist, surgeon, and therapist talk with him.
The operation itself is technically relatively uncomplicated, but quite labor-intensive, requiring careful, consistent and precise actions by the surgeon. Its duration is on average an hour and a half, but possibly longer, and is carried out under general anesthesia. Previously used local anesthesia, which allowed the patient to speak, and the surgeon thus checked the safety of the laryngeal nerve. Modern views operations on the thyroid gland eliminate the possibility of damage to this nerve, therefore general anesthesia is quite justified and advisable.
 The classic approach to the organ is a transverse incision in neck area,
stepping back about one and a half centimeters from the upper edge of the sternum. The surgeon cuts the skin subcutaneous tissue, fascia, sequentially ligating the vessels, of which there are quite a few on the way to the gland.
The classic approach to the organ is a transverse incision in neck area,
stepping back about one and a half centimeters from the upper edge of the sternum. The surgeon cuts the skin subcutaneous tissue, fascia, sequentially ligating the vessels, of which there are quite a few on the way to the gland.
The most important manipulation during thyroidectomy is the isolation of the laryngeal nerve and parathyroid glands. The laryngeal nerve ensures the movement of the vocal folds during voice production; its injury leads to hoarseness or complete absence voices that count severe complication with incorrect intervention technique.
The parathyroid glands are located inside the parenchyma of the organ, in the posterior part of the lobes; their removal significantly affects calcium metabolism, which can lead to seizures and even death without appropriate treatment. Their preservation is very important for the patient, although malignant formations this is no longer possible.
Having reached the thyroid gland, the surgeon excises it completely or removes a part (lobe, isthmus, node), and then sutures it in the reverse order soft fabrics neck. Sometimes a small silicone drainage remains in the wound, which is removed the next day. The surgical incision area is processed special compounds, helping to improve regeneration and prevent excessive scarring. Patients may also be recommended special patches and gels against scars.

A standard operation may lead to an unsatisfactory cosmetic result, since the scar will be noticeable in one way or another. To reduce trauma, endoscopic techniques are used, when microsurgical equipment and a video camera are applied to the thyroid gland through several small incisions.
It is also possible to remove the organ through the axillary approach, then there will be no traces of thyroidectomy left on the neck. However, this method is so complicated and requires such a delicate operating technique from the surgeon that it is used only in isolated cases.
It happens that during intrauterine development, the thyroid gland is formed not on the front surface of the neck, but behind the sternum, in the chest cavity. With the enlargement of such an abnormally located organ, shortness of breath, heart rhythm disturbances, and possible fatal outcome, so surgery is necessary.
Surgical treatment of an abnormally located goiter is fundamentally different from standard thyroidectomy and requires penetration into the chest cavity, which is both traumatic and technically difficult to perform. Surgeons come to the rescue endoscopic methods, allowing to minimize trauma from surgery with high treatment results.
The most dangerous consequences Surgeries to remove the thyroid gland are considered:
- Transection of the laryngeal nerves, resulting in loss of voice;
- Unjustified excision or damage to the parathyroid glands, fraught with a decrease in calcium levels, convulsions up to tetany, cardiac arrest;
- Bleeding in the postoperative period, which requires re-intervention;
- Suppuration postoperative wound(subject to the observance of technique and asepsis rules, this is extremely rare).
After operation…
If all the rules for surgical interventions on the thyroid gland are followed, the risk of complications is extremely low, postoperative period takes no more than 10-12 days, in the case of endoscopic interventions - 2-3 days. The patient's bandages are changed daily, hormonal levels and general well-being are monitored.
 If after the operation the voice does become impaired (it becomes quieter, hoarseness appears), there is no need to panic, this does not always indicate irreversible damage to the laryngeal nerves. In the postoperative period, swelling of the soft tissues is possible, which irritates these nerves, and after a few days the symptoms of voice impairment will go away on their own.
If after the operation the voice does become impaired (it becomes quieter, hoarseness appears), there is no need to panic, this does not always indicate irreversible damage to the laryngeal nerves. In the postoperative period, swelling of the soft tissues is possible, which irritates these nerves, and after a few days the symptoms of voice impairment will go away on their own.
When the thyroid gland is completely removed, hormones are no longer released after the operation, so the patient needs replacement therapy. The standard is considered to be the drug L-thyroxine, prescribed daily at a dose of 50-100 mg, half an hour before breakfast. The dose is selected strictly individually based on metabolic characteristics, weight, concomitant pathology specific patient. Treatment is prescribed for life.
Life after removal of the thyroid gland in the vast majority of cases does not require any restrictions, patients retain their former activity, women become pregnant and give birth healthy babies. There are often questions regarding the pregnancy period in reception conditions hormonal drugs, because any future mom worries about the development and health of the child. Doctors reassure: with an adequately selected dose of L-thyroxine and careful monitoring of hormonal metabolism throughout pregnancy, there is no risk for either the woman or the fetus, and the pregnancy ends with the birth of a healthy baby.
In women, problems with the thyroid gland may be accompanied by infertility, which cannot be treated by a gynecologist. Timely correction of hormonal levels, even through surgery, is the key to restoring fertility and the ability to bear children. Many women wishing to have children become pregnant soon after surgery, so judgments regarding negative influence thyroidectomy on the ability to give birth to a child is erroneous and has no justification.
Patients who have undergone total removal of the thyroid gland are assigned a third disability group. Unlike many others serious illnesses, seriously limiting life activity, in the case of thyroidectomy, the presence of disability is rather a formality that allows you to have some benefits for the purchase of medicines or, say, travel to public transport. Many patients deliberately do without disability, not wanting to get involved in numerous procedures to establish it.
Thyroid operations can be performed either for a fee or free of charge. They are provided free of charge under the general health insurance system, according to a quota. Free treatment available, including in highly specialized endocrine surgery centers, where the patient can go himself or be referred by a doctor at his place of residence.
If desired, the patient can pay for both the operation and examinations, and to the maximum comfortable conditions hospital stay. The cost will include payment for examinations (approximately 10 thousand rubles), the operation will cost about 15 thousand, and the entire period of treatment will require costs of approximately 50-60 thousand rubles.
Surgery on the thyroid gland is difficult. But they are being done, it should be noted, successfully. Therefore, if the doctor insists, after the tests, it is better to perform an ultrasound to remove the thyroid gland; the consequences in women (reviews confirm this) in most cases are not negative character. After operations, the patient’s body condition is normalized by 90%, complications occur in in rare cases. The postoperative period is not long, there may be consequences, complications, but they are extremely rare.
The thyroid gland is small in size, but is closely interconnected with many organs and affects their functioning. If its work is disrupted, it is infected, then the rest of the human organs will not work normally. Therefore, when images of nodes and tumors are detected on ultrasound, doctors prescribe surgery. The disease does not select a person’s gender, but more women are affected.
Cancer is the stage when formations begin to form from cells:
- papillary - over 80% of patients suffer from a papillary tumor;
- follicular - about 29% of patients are sent for surgery;
- medullary – only 8% of patients require surgery;
- there is still a lot rare pathology anaplastic, it affects only 1% of identified patients.
An increase in the number of sick people has been observed after the Chernobyl accident.
How many people who live in risk areas have not had an ultrasound scan? But some forms of the disease can only be determined using ultrasound.
During ultrasound, endocrinologists have the opportunity to identify what types of tumor formations there are. For example, if a follicular tumor is detected, surgery will be required.
Otherwise, infected cells will penetrate the vessels, and then, with the help of blood, they will be carried to new places where they can form metastases.
 The greatest risk of cancer is observed in:
The greatest risk of cancer is observed in:
- adolescence 10 – 20 years;
- mature age 45 – 65 years.
According to statistics, there are four times more women who are sick than men. Although men are not always concerned about their health.
There are very few deaths among people with thyroid cancer. According to statistics, this figure is less than half a percent. Usually the operations are successful.
Only complete removal of an organ with an accurate diagnosis of cancer is a cause of disability. Partial removal, for example, the right side, does not provide such an opportunity. It is believed that you can live and work normally with the right lobe; having half a healthy part of the gland is better than not having it at all.
Cancer with diffuse and multinodular toxic goiter
Autoimmune disease is a hereditary disease during which hypersecretion is observed, that is, follicular tissue increases endocrine gland. According to statistics, the number of women affected by this disease is tens of times greater than that of men.
The severity of this disease is determined when a person works at half capacity, and only then the following signs are considered. This means that the body, weakened by the disease, can no longer cope with normal stress. This aspect is a signal to do an ultrasound and go through the entire diagnostic process with an endocrinologist.
The degree of malaise with diffuse toxic goiter is classified into three stages:
- Relatively mild, that is, the first degree. Nervous overexcitation, increased heart rate are observed, a person may lose weight, and performance decreases.
- The second degree is determined by the same signs, but they are brighter.
- The most difficult third degree is when a person cannot work at all. In addition, the liver increases in size, and heart problems appear.
The disease is sometimes accompanied by the formation of several nodes. They produce excess amounts of hormones that negatively affect the body. The presence of nodes and their size can be detected during an ultrasound examination by an endocrinologist. The node has the appearance of a dense ball; it can be located on the right, left lobe or on the isthmus. Only ultrasound shows the presence of small nodes.
The disease can be treated with medications, but this method is not very effective. Greater effect It turns out when endocrinologist surgeons suggest performing an operation. Only after removal of all nodes can the patient fully recover and carry out normal activities, taking a hormonal drug prescribed by the endocrinologist.
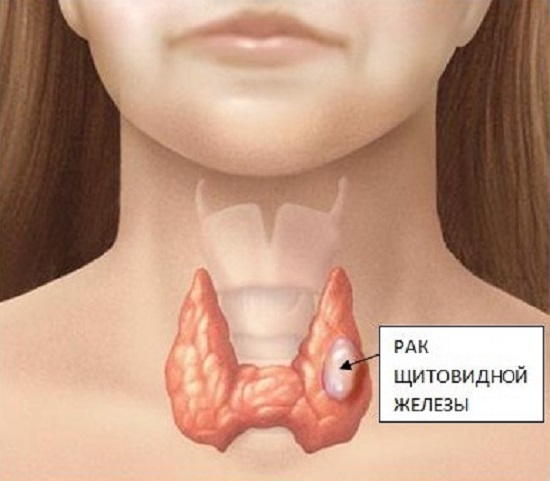
 A tumor can be malignant or benign.
A tumor can be malignant or benign.
Benign tumor- This is a thyroid adenoma. This tumor has the appearance of a well-defined oval. Develops slowly. There is always a risk of an adenoma turning into cancer.
Thyroid adenoma can be treated with medication, but in cases where there is no effect, removal is recommended. It usually develops on one lobe. In exceptional cases, complete or almost complete removal of the thyroid gland is performed. When the lobe is removed, a postoperative period begins, consequences, complications that therapy is intended to relieve.
In any case, there are a number of pathologies in which removal of the thyroid gland is the only right opportunity treatment.
- Complete removal together with lymph nodes, parathyroid glands. This option is possible, for example, if an ultrasound reveals: complete deformation of the organ or both right and left lobes are damaged.
- Removing only the damaged part. In this case, the parathyroid glands remain untouched.
- Cutting off one right lobe.
- Removal of cyst, node. In this case, the sex of the organ will be removed. For example, when removed right part, the left one will perform all functions.
 Removal operationthyroid gland causes the development of postoperative hypothyroidism A. Removal of the diseased part and lobe of the thyroid gland allows you to leavehealthy part. Remaining the healthy part of the lobe will perform all functions. If thyroid gland removedeverything, in this case hypothyroidism will definitely appear. Therapy will help patients overcome it.
Removal operationthyroid gland causes the development of postoperative hypothyroidism A. Removal of the diseased part and lobe of the thyroid gland allows you to leavehealthy part. Remaining the healthy part of the lobe will perform all functions. If thyroid gland removedeverything, in this case hypothyroidism will definitely appear. Therapy will help patients overcome it.
Why does hypothyroidism occur? This is a disease caused by hormonal deficiency. Hypothyroidism affects not only the function of of cardio-vascular system, but also the brain, as well as the genitals, etc. Hypothyroidism develops in everyone after removal of the thyroid gland, so hormonal pills You need to drink everything the doctor prescribed during the postoperative period.
During the period of time after surgery, patients feel:
- a sore throat;
- discomfort in the neck and more;
- the incision site may swell;
- Voice disturbances and hoarseness may follow.
There may be others discomfort. Postoperative illness goes away within a few weeks if there is no fever.
 If the thyroid gland has been removed, how to live? Therapy will help the patient normalize later life. Yes, you will have to take pills throughout your life, but you can get used to it. It will be necessary to increase the level of hormones artificially, otherwise complications are possible. Hormonal problem will be solved with the help of tablets. When there is a decrease in calcium in the body, you should replenish it by taking calcium supplements. How much you need to take - the doctor will determine the norm.
If the thyroid gland has been removed, how to live? Therapy will help the patient normalize later life. Yes, you will have to take pills throughout your life, but you can get used to it. It will be necessary to increase the level of hormones artificially, otherwise complications are possible. Hormonal problem will be solved with the help of tablets. When there is a decrease in calcium in the body, you should replenish it by taking calcium supplements. How much you need to take - the doctor will determine the norm.
Life after removing the shield ovary gland will improve completely, you just need to get used to small changes, not only in the body.
Women and men live after surgery normal life , following certain rules. Even the reproductive system is restored. You just need to be more attentive to yourself.
Every operated woman and man is systematically examined by an endocrinologist after a certain period.
When the doctor performs an examination, checks for an ultrasound, takes into account the general condition and the presence of complications:
- Does cough bother women?
- Do you have headaches?
- whether the lymph nodes are enlarged;
- Do your bones hurt?
- Are there any new formations in the throat?
If we talk about nutrition, after surgery you can eat almost everything. There are no special restrictions. If an operation is performed to completely remove an organ, then the use of iodine-containing products is no longer so relevant. But if the removal is carried out partially, that is, part of the organ remains and performs its functions, for example, the right one is removed, but the left one remains, in this case it is necessary to consume products containing iodine.
When creating your own menu, you should take into account that you need to eat so as not to gain too much excess weight, especially female representatives, they are the ones who are more worried about their own weight, and in the postoperative period the metabolism is slowed down.
It would be better to follow some tips:
- Reduce consumption of baked goods.
- Exclude from the menu foods that should not be consumed: fried, fatty foods. It is better to boil foods, bake them or steam them.
- Increase the amount of fruits, vegetables, steamed and boiled fish in your diet.
- The consumption of which foods will need to be reduced: peas, corn, beans. These products do not promote the absorption of hormonal drugs.
- It is forbidden to go on any weight-reducing diets if you want to lose weight. Why? Diets are stress, and it is undesirable.
- Be sure to drink water.
- Do not drink alcoholic, carbonated drinks, strong coffee, tea.
- Don't smoke - this mainly applies to men.
You can eat everything, but in moderate portions.
 Reasonable caution won't hurt:
Reasonable caution won't hurt:
- Sports are acceptable. You can exercise, but you should avoid big ones physical activity, which happen during intensive training. There is no point in participating in sports competitions. But you can use sports to improve your health. You need to choose a sport that your body, weakened after illness, can withstand. Sport should help create an upbeat mood and increase joyful energy.
- It's not worth spending all day in the sun. You should not choose hot places to relax without consulting your doctor.
- It is worth giving up steam rooms in the bathhouse and taking hot baths.
- You will have to dress warmly even in cool weather. Your wardrobe should have warm mittens, socks, scarves, hats, and sweaters.
- Sleep at least 8 hours as prescribed. You can take it in the morning cold shower to relieve drowsiness.
- Don't be nervous, avoid stressful situations. Life should become measured, calm, filled with positive emotions.
- A joyful smile must appear on the patient’s face! Watch comedy films, read humorous works.
- It's worth doing brain training. You can start solving crosswords, math problems, and learning languages.
Why not be attentive to your health.
Suspicious cough, fever has risen, unpleasant sensations have appeared, increases in right side- to get rid of anxious thoughts, it is better to go to see a doctor. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Optimism is something that the operated patient must become friends with. Removing the thyroid gland is not a death sentence.
It would not be amiss to remind you what the thyroid gland is or colloquial speech– thyroid gland. This important organ endocrine system located in the middle third of the front of the neck. Sometimes this organ gives hormonal disbalance and in this case it is necessary, the consequences for women are greater than for men.
The role of the thyroid gland in the female body before surgery (removal)
In fact, every second inhabitant of the Earth has abnormalities in the activity of the thyroid gland. Also gland pathologies varying degrees found in 20 percent of the female half, while in men the statistics are 18 times lower. Sometimes surgery is required.
The thyroid gland's job is to control metabolic processes through hormones. Thanks to this, the body does not lack iodine. This element is contained in produced hormones. Due to the fact that the gland does not have excretory ducts, the secretion enters the blood through absorption.
The thyroid gland is a source of two types of hormones called triiodothyronine and thyroxine, which not only monitor correct exchange substances, but also ensure the full functioning of the reproductive and cardiovascular systems in men and women. In addition, thanks to hormones, the psyche and digestive organs are brought back to normal. If there is too little concentration of these hormones in the blood, the brain reacts by intensely increasing the generation of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH for short). In addition, substances are produced that activate the gland. After donating blood for tests, you can establish the fact that hormones are contained in the required quantity or prescribe necessary treatment: surgery, hormone use.
The sooner a person suspects a problem and contacts medical institution, the higher the likelihood of successful recovery
The thyroid gland monitors the state of natural hormonal levels, so it is of exceptional importance for the fairer sex. Representatives of men do not suffer from the so-called hormonal changes, which are specific female body. Processes such as: menstrual cycle, the ability to get pregnant, the onset of menopause (menopause), which are unique to the weaker sex. The unsatisfactory state of the thyroid gland affects the functioning of the woman’s body and the body of men, her ability to continue the human race, as well as many other purely female problems. Determining why the functionality of the gland is impaired is solely within the competence of the endocrinologist, who decides on the method of eliminating the problem. Thyroid surgery is necessary in two cases:
- the presence of any tumor, subsequently goiter;
- hormone secretion is insufficient or, conversely, excessive.
It is precisely that the signs of the disorder are accompanied by ailments that ultimately affect reproductive function, there is a serious danger for women, including men. Consequently, a woman, having discovered any undesirable phenomenon in the area of the uterus or other organs, should check the condition of the thyroid gland, just in case.
Symptoms of problems for surgery
If the size of the thyroid gland has slightly increased, possibly from a goiter, then this cannot serve as a prerequisite for its removal. Most likely, taking medications, it will be possible to normalize the functioning of the organ. Experience shows that in regions with significant iodine deficiency, disease statistics tend to increase. For the purpose of prevention, it is advisable to consume foods in which the concentration of this microelement can compensate for its deficiency. These mainly include seafood, for example, seaweed.
 Abnormalities of the thyroid gland can be caused by infections, head injuries, pregnancy and hereditary factor
Abnormalities of the thyroid gland can be caused by infections, head injuries, pregnancy and hereditary factor Official medicine does not encourage self-diagnosis at home and treatment at home. The choice of drug treatment option should correspond to the type of pathology; you should know at what stage the disease is. The same applies to taking medications for plant based, even if herbs have miraculous properties. Sometimes the operation is performed by “amateur doctors”, which can have a negative impact. Who else but an endocrinologist, who has vast experience behind him, will be able to choose the optimal set of drugs offered by official and traditional medicine?
Due to the characteristics of modern busy life, many people push health problems into the background, ignore the symptoms that appear, exposing themselves to a certain risk. As a rule, people are examined when the tumor progresses, the disease becomes running form. On the Internet you can find many photographs that clearly demonstrate the consequences of unprofessional treatment. Viewing them should make a person think about the seriousness of this problem.
What symptoms should make a woman ask herself the question: “Should I consult a doctor and get examined?” First of all, there is a feeling as if something is pressing in cervical spine, makes it difficult to breathe and, when eating, to swallow. It is quite possible that the cause should be sought in overgrown tissues and the appearance of a small tumor. The biopsy material is examined, on the basis of which a conclusion is made about whether the tumor is malignant. If terrible diagnosis If this is not confirmed, then you can breathe a sigh - you can wait a little longer with surgical intervention. Precautionary measures include healthy image life. Proposed compliance proper nutrition. Of course, generally protect yourself from harmful factors It will not be possible completely, but we must try to reduce their influence to a minimum.
Consequences of surgery
The consequences of removal of the thyroid gland in women are directly dependent on the disease itself and the nature of the surgical intervention. We cannot ignore the fact that this method treatment does not pass without a trace, it is very difficult to fully predict all the consequences for the vital systems of the female body. It will take a period during which the body will be able to readjust, “get used to” the complete or partial loss of one of its organs.
The patient who lies down on the operating table is probably worried about what sensations he will experience immediately after such a not very pleasant procedure. The throat will hurt for some time (it is a wound after all), swelling will appear, and the location of the suture will swell. Moreover, the pain can be traced not only in the area of the incision, i.e. in front of the neck, but also radiates to the back of it. Sometimes the voice changes - it becomes hoarse and hoarse. All the discomfort described will have to be endured; by the end of the second or third week it will gradually disappear.
 If the operation took place without any incidents, the patient stays in the clinic for no more than three days
If the operation took place without any incidents, the patient stays in the clinic for no more than three days It is important to take measures to ensure that the tumor does not form again and surgery is not necessary. This phenomenon can be triggered by the secretion of the pituitary gland. Therefore, in the early stages of the postoperative period, you will have to take a hormone called levothyroxine. Taking other hormonal medications will slightly mitigate the consequences of surgery.
The most common complications observed in the postoperative period are:
- The recurrent nerve, damaged during surgery, is completely restored during subsequent treatment.
- With the help of medications, parathyroid dysfunction is eliminated. Sometimes prescribed medications are taken for the rest of life.
- In only two cases out of a thousand, bleeding occurs after surgery.
How successfully the rehabilitation process is going can be determined through numerous analyses. This will help avoid complications.
When prescribing surgical treatment, doctors make an informed decision; do everything possible to avoid completely removing the organ, but at least, leave at least the parathyroid glands and the poles of the thyroid gland. Thus, in the future you may not need to take hormonal medications, but only be under the supervision of a specialist. In practice, the operation, resection, in no way makes any special adjustments to the patient’s plans. There will be no restrictions placed on her life. A woman may well devote herself to her family and enjoy, for example, traveling. Traces of stitches and scars, if they are noticeable, the patient can, if desired, make them invisible with the help of plastic surgery.
Rehabilitation period after thyroid surgery
The patient returns to her normal rhythm of life two months after the operation was performed. Regardless of whether the thyroid gland was removed completely or only part of it, life can be considered conditionally complete. A woman is forced to constantly take restorative medications, regularly visit an endocrinologist and conduct ultrasound examinations of the body and complex treatment. All this will allow you to control hormonal background and keep it normal.
 The gland is removed exclusively in extreme cases
The gland is removed exclusively in extreme cases The situation is somewhat different during surgery. malignant tumor thyroid gland. This is considered a more complex type of surgical treatment. The peculiarity is that traditionally a course of radiation and chemotherapy is prescribed, the patient becomes unable to work.
Some women have unfounded prejudices regarding hormonal drugs. I would like to reassure such patients. If the recommendations of the endocrinologist are followed exactly, the drug is taken exclusively in the prescribed doses, then no side effects should not be observed. After all, the calculation is made in such a way that the body will receive active substance in quantities necessary for recovery natural balance. Also, you should not worry about reproductive function, i.e. ability to procreate.
They appear only in one of two cases: with an incorrectly selected dosage or refusal to take the hormonal drug. Treatment in this case becomes more complicated.
IN short time and most importantly, “Monastery tea” will help effectively cure the thyroid gland. This product contains only natural ingredients, which have a comprehensive effect on the source of the disease, perfectly relieve inflammation and normalize the production of vital hormones. As a result, everything metabolic processes will work correctly in the body. Thanks to unique composition“Monastery tea” is completely safe for health and very pleasant to the taste.
The issue of nutrition for those who have undergone thyroid surgery must also be taken seriously. Whenever possible, preference should be given entirely to nutritious and quality food rich in elements such as iodine and iron. Fortified foods, especially those containing vitamin C, are beneficial for the body during this period.
From all of the above, we can conclude that treatment with removal of the thyroid gland and the consequences in women will have absolutely no impact on the quality of life.
0 1,572
The thyroid gland is the synthesizer of most hormones in the human body. Hormones are responsible for vital energy, normal work organs. Disruption of the thyroid gland leads to a failure of the entire mechanism. Every fifth woman is susceptible to changes in the thyroid gland; men suffer almost twenty times less. In case of irreversible changes, the specialist prescribes removal of the gland ─ complete or partial. The operation will make adjustments to the patient’s future life.
Conditions for extirpation and contraindications for surgery
Changes in thyroid tissue early stages do not entail the need to scalp the organ. An increase to three centimeters has no reason to. A thorough clinical examination is carried out to determine whether the increase is a consequence of cancer.
Using a biopsy, thyroid tissue is examined; the analysis makes it possible to determine the extent of the disease. In the first stages of the disease drug treatment, give excellent results. Radical surgical intervention carried out in cases:
- fourth-fifth degree pathological changes thyroid glands;
- oncological diseases;
- types of carcinoma that react negatively to traditional treatment radioactive iodine;
- to sizes that interfere with breathing;
- formation of malignant adenoma;
- goiter large sizes with toxic signs;
- lack of positive dynamics due to drug treatment.
Contraindications to removing the thyroid gland include:
- infectious disease in the acute stage, relapse of a chronic disease;
- biopsy results confirm benign education, treatment of which is carried out with traditional medications;
- special attention to surgical intervention in elderly patients with complex cardiology.
Preliminary preparation

Removal of the thyroid gland is carried out after a complete comprehensive examination. Ultrasonography Before removal, analyzes the structural composition, size, and density of tissues. The procedure allows you to determine the blood circulation pattern in the thyroid gland. Diagnostics determines tumors, nodes, and the size of enlarged thyroid glands.
The next step is to determine your hormonal levels using a blood test. Concentration fluctuation thyroid-stimulating hormones indicates interruptions in work, an increased amount of hormones destroys the thyroid gland. The presence of antibodies aggressive towards thyretropes indicates pathological disorders thyroid functions requiring surgical intervention.
It is possible to examine it with a radioisotope scanner, which determines the location and size of the gland. The thyroid gland is removed after patient preparation, which includes:
- analyzes that determine allergic reactions on the drugs used;
- cardiac examination.
Based on the indications, the thyroid gland is partially removed; irreversible changes require resection of the entire organ. The consequences of removing the thyroid gland are unpredictable; before the operation, the patient is referred to a consultation with a psychologist.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. An incision is made six to eight centimeters in size, the thyroid gland is isolated from the surrounding tissues, partial or complete resection of the organ occurs, and sutures are applied.
Consequences
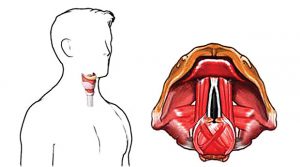
Removing the thyroid gland is an unpredictable process. Modern medical technologies allow the operation to be performed without serious complications, but some risks exist.
The thyroid gland is located in close proximity to vocal cords. A change in voice timbre is not dangerous, but an unpleasant irreversible surprise that the patient may discover.
The most common complication is damage to the irreversible nerve. Breathing is impaired, it is difficult to swallow, especially difficult cases food can be thrown into the trachea.
Non-surgical removal
Suture size is important for all patients. There is a video-assisted method, during which a video probe is inserted into an incision two to three centimeters long, the process is displayed on the screen, surgeons perform the operation, guided by video observations, using thin surgical instruments. The equipment for performing the operation is expensive; video assistance is currently only carried out by specialized clinics.
The need to remove the thyroid gland in patients who have contraindications to classical surgical method, suggests a method of destruction. Special substances injected directly into pathologically altered tissues destroy their structure. Laser thermotherapy and radiofrequency thermotherapy have the same consequences.
Operation is not a death sentence
The thyroid gland is responsible for human hormonal levels. When an organ is removed, production stops necessary substances gland. The subsequent life of people with removed thyroid glands requires the use of certain hormonal medications, supervised by the attending physician. At correct observance appointments, the absence of an organ does not in any way affect a person’s life expectancy, his social adaptation, family relationships.
Women who have had radical surgery successfully give birth to healthy babies. Sports after certain period rehabilitation strengthens the body and improves health.
There are a number of indications for mandatory surgical intervention for thyroid pathologies.
First of all, these include established diagnosis thyroid cancer. It should be noted that timely surgical intervention for this disease in the vast majority of cases leads to a complete cure.
Moreover, even the presence of nodular formations of the thyroid gland, in relation to which, according to research data, there is a suspicion of possible malignancy, is an indication for surgery. This especially applies to patients in whom fast growth nodular formations, or the formations themselves reach a size of more than three centimeters.
Patients with nodular formations in chronic autoimmune thyroiditis are also susceptible increased risk tumor development.
If a nodular formation of the thyroid gland provokes an increased release of hormones into the body, this is an indication for surgery.
In addition, surgery is prescribed for thyrotoxicosis, when therapeutic methods no treatment given desired results, or the growth of the thyroid gland, even in the absence of nodes, leads to difficulty swallowing and breathing.
Although surgery may not be prescribed, however, if there is weak absorption radioactive iodine, surgical treatment is also indicated.
If the patient was previously exposed to radiation for treatment of the skin in the neck and head area, the resulting nodularity of the thyroid gland leads in 60% of cases to thyroid cancer and can lead to the need for surgical intervention.
An examination of the thyroid gland shows its structure and function, and a puncture of the gland tissue is also performed. The obtained research results determine the indications for surgical treatment, in addition, the expected volume of the operation is also clarified.
IN modern medicine It is believed that the smallest volume permissible during surgery on the thyroid gland is the removal of one lobe entirely. The maximum, of course, is the removal of the entire gland. The fact is that previously considered “sparing” operations, in which nodular formations were removed separately, and parts of the thyroid gland that were considered “healthy” were left, proved to be flawed, since most of the patients returned for repeated interventions, since nodular formations continued to reappear in the remaining parts of the gland.
Surgery is performed through a short incision in the middle of the lower part of the neck. By spreading the central muscles of the neck, the lobes of the thyroid gland are removed, having previously prepared the recurrent and superior laryngeal nerves going to the vocal cords and the parathyroid glands, which regulate the level of calcium in the body.
Patients are being treated replacement drugs thyroid gland, and this is done even when a small part of the thyroid gland is removed to prevent hypofunction of the gland.
After removal of the thyroid gland, patients should be observed by a doctor at least twice a year to monitor the condition of the gland.
Interventions on the thyroid gland are tolerated by patients and strength is restored quickly. However, such operations are very complex and delicate procedures in surgical practice, and therefore it is necessary to very carefully choose the right hospital and surgeon. It is imperative to find out whether this hospital has the necessary funds to carry out such interventions.

